Resources
About Us
Neo and Challenger Bank Market Size, Share, Forecast & Trends by Business Model (Digital-only, Hybrid) Licensing Model (Fully Licensed, Partnership) Services (Payments, Savings, Loans, Investments) End-User - Global Forecast to 2035
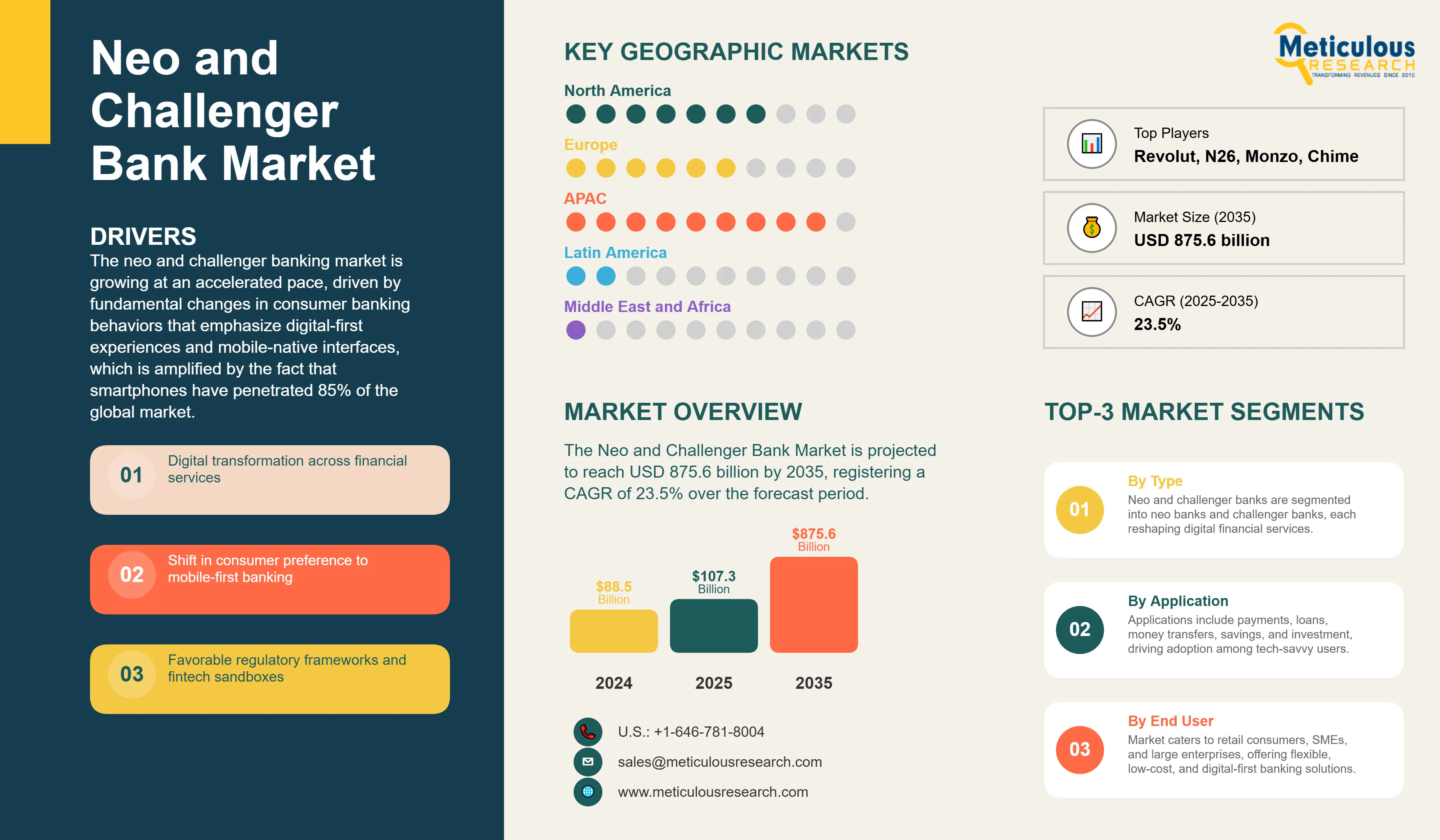
Report ID: MRICT - 1041565 Pages: 230 Aug-2025 Formats*: PDF Category: Information and Communications Technology Delivery: 24 to 72 Hours Download Free Sample ReportThe Neo and Challenger Bank Market was worth USD 88.5 billion in 2024. The market is estimated to be valued at USD 107.3 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 875.6 billion by 2035, registering a CAGR of 23.5% over the forecast period.
Neo and Challenger Bank Market - Key Highlights
|
Metric |
Value |
|
Market Value (2025) |
USD 107.3 billion |
|
Market Value (2035) |
USD 875.6 billion |
|
CAGR (2025-2035) |
23.5% |
|
Largest Business Model |
Digital-only Banks (65-70% share) |
|
Fastest Growing Service |
Embedded Finance & BaaS (25.3% CAGR) |
|
Leading Service Category |
Payments & Money Transfers (30-40% share) |
|
Dominant End-User |
Retail Consumers (70-75% share) |
|
Fastest Growth Region |
Asia-Pacific (26.4% CAGR) |
|
Top Country by Users |
China |
|
Market Concentration |
Top 10 players hold 30-40% share |
Neo and Challenger Bank Market Overview
Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
Why the Neo and Challenger Bank Market is Growing?
The neo and challenger banking market is growing at an accelerated pace, driven by fundamental changes in consumer banking behaviors that emphasize digital-first experiences and mobile-native interfaces, which is amplified by the fact that smartphones have penetrated 85% of the global market. 78% of millennials and 67% of Gen Z prefer mobile banking to an actual storefront bank visit, creating a multi-trillion-dollar addressable market for digital-only banking services.
The growth of the neo and challenger banks is also propelled by regulatory support, such as open-banking mandates like PSD2 in Europe and similar controls in Asia-Pacific, which have established API-driven ecosystems and tripled fintech-bank partnerships since 2021. Neo banks operate at 60-70% lower costs than traditional banks, allowing them to offer fee-free accounts, a higher savings rate, and instant account offerings and services that appeal to price-sensitive and digitally literate customers.
The COVID-19 pandemic created lasting changes in banking behavior, with digital account openings increasing 200% during the years of 2020-2024, while 40% of traditional bank branches closed globally. Technology innovations, such as AI-based personalization, real-time payments, and embedded finance capabilities, allow neo banks to better serve their clients and provide a superior customer experience, allowing clients 24/7 access and account opening processes of less than a minute. Neo banks' progress towards providing a comprehensive financial products and services ecosystem will advance growth in the market by expansion into underserved markets, small, medium and enterprise (SME) banking services and Banking-as-a-Service platforms. Neo banks are evolving away from simple payment applications to a comprehensive financial ecosystem.
Neo and Challenger Bank Market Size and Forecast
|
Metric |
Value |
|
Neo and Challenger Bank Market Value (2025) |
USD 107.3 billion |
|
Neo and Challenger Bank Market Forecast Value (2035 F) |
USD 875.6 billion |
|
Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
23.5% |
Market Segmentation
The neo and challenger bank market is segmented by business model, licensing model, services offered, end-user, and geography. The market is divided by business model into Digital-only Banks and Hybrid Banks. By licensing model, the market includes Fully Licensed Banks and Partnership Models. Services offered encompass Payments and Money Transfers, Savings Accounts, Loans, Investments and Wealth Management, Insurance Products, Currency Exchange, and Others. By region, the global neo and challenger bank market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
Digital-only Banks Lead Market with 65-70% Share Driven by Lower Costs and Superior UX
Digital-only banks make up 65-70% of the overall neo and challenger market based on business model, and they have the ability to provide complete banking services, without physical branches, through the use of mobile and web applications. Digital banks have operational costs at least 60-70% lower than traditional banks with a cost-to-income ratio of between 35-40%, while traditional banks are roughly 55-65%. Low costs enable digital banks to provide competitively priced and often free products and services to cost-sensitive consumers.
Digital banks have improved customer experience (CX). The account opening is less than 5 minutes, they offer cards instantly, both virtual and physical, and provide real time notifications to keep consumers informed and alerts for fraud and budgetary constraints for example. They offer financial insights using AI that typically would take fully qualified human advisors to deliver. Unless traditional incumbents work fast, they will continue to lose market share to digital-only banks.
Market leaders like Revolut serve over 60 million customers globally as of 2025, while Chime has serviced around 12 million accounts in the US by offering features such as early paycheck access, zero-fee overdrafts, and automated savings, which resonate strongly with financially stressed consumers.
As regulatory frameworks mature and consumers become more accustomed to trusting digital-only banking (one study found that 65% rated their neo bank experience better than a traditional bank), this segment will continue to lead the market growth in terms of new products & geo expansion.
Payments and Money Transfers Dominate Neo and Challenger Bank Services Market with 35-40% Revenue Share
Based on services, payments and money transfers hold the largest share of the overall neo and challenger bank market with a 35%-40% revenue share in 2025, being the most commonly used services and the primary engagement channel for acquisition and retention. Neo banks process over 10 billion transactions annually, and average transaction volumes increased by 45% YOY. Everyday spend has shifted for millions of users to digital platforms, including the introduction of real-time payments, split bills, and instant peer-to-peer transfers.
What are the Drivers, Restraints, and Key Trends of the Neo and Challenger Bank Market?
The neo and challenger bank market is on the rise, with an expanding landscape due to digital transformation in financial services, a shift towards mobile-first banking preferences, supportive regulatory frameworks, and technological advancements that improve customer experiences. Moreover, the advantages of lower costs, financial inclusion efforts, and ecosystem partnerships enhance competitive advantage.
Impact of Key Growth Drivers and Restraints on Neo and Challenger Bank Market
Base CAGR: 23.5%
|
Driver |
CAGR Impact |
Key Factors |
|
Digital-First Consumer Demand |
+5.8% |
|
|
Cost Efficiency & Pricing |
+4.5% |
|
|
Regulatory Support |
+3.9% |
|
|
Technology Innovation |
+2.7% |
|
Market Restraints
|
Restraint |
CAGR Impact |
Mitigation Trends |
|
Profitability Challenges |
-2.1% |
|
|
Trust & Security Concerns |
-1.5% |
|
|
Regulatory Complexity |
-1.2% |
|
Digital Transformation and Mobile-First Banking Drive Market Revolution
Neo and challenger banks market is experiencing significant growth as digital transformation is transforming the way financial services are delivered and consumed. Digital banking has emerged as part of the massive digital transformation taking place in many sectors. With 85% of the world utilizing smartphones and 5 billion mobile internet users, neo banks are taking advantage of the shift to a mobile-first banking experience, particularly among millennials and Gen Z who approximately execute 89% of their banking activity through mobile apps. Digital natives require speed and seamless service, which traditional banks aren't able to provide due to legacy systems and branches.
Neo banks operate with modern technology stacks, mainly built on microservices, that allow them to bring new features to life in days versus months, with continuous deployment practice that allows for 50+ updates a week compared to quarterly changes at traditional financial institutions. The experiences these digital banks provide, through easy-to-use designs, personalized insights, and gamification, yield 4.8 stars as an average app store rating compared to 3.2 stars on traditional bank apps. These banks have decreased customer acquisition costs by 40% via viral referral programs and social marketing. For instance, Revolut is acquiring 2 million customers a month at USD 20 per user compared to traditional banks acquiring customers at USD 200/300 per user.
The pandemic accelerated digital adoption by 5-7 years, with branch visits declining 60% permanently while digital engagement increased 200%, creating an inflection point where digital-only banking became mainstream rather than niche. As 5G networks enable richer mobile experiences and younger demographics inherit USD 68 trillion in wealth transfers, neo banks are positioned to capture this generational shift toward fully digital financial lives.
Open Banking and Regulatory Innovation Accelerate Market Expansion
Globally, regulatory frameworks are actively promoting competition and innovation in banking through open banking mandates, digital banking licenses, and fintech sandboxes that lower barriers to entry. The European Union's PSD2 directive, requiring banks to share customer data via APIs with consent, has enabled 500+ fintechs to launch innovative services, while similar frameworks in Australia, Singapore, and Brazil create global momentum for banking transformation. These regulations level the playing field, allowing neo banks to access customer data from incumbent banks and offer account aggregation, financial management, and switching services.
A digital banking license - which is currently offered in more than 40 countries - allows neo banks to offer banking functionalities (deposit-taking and lending) without the requirements of a bank branch, reducing the capital requirements for a new bank by 70%. A regulatory sandbox, such those offered in the UK, Singapore, and UAE, permits neo banks to trial novel products with real customers, and under loosened regulatory obligations, thereby shortening the time to market by 12-18 months. while standardizing APIs through open banking generates network effects so that for each additional participant in the ecosystem, the value for all ecosystem actors increases.
Government support for financial inclusion and competition have led to processes faster to license digital banks, sometimes referencing 2-3 years historically, but in recent years licensing has taken as little as 6-9 months. Given regulators believe neo banks can improve access and reduce systemic risk from diversified digital banks, regulators continue to enact policies that create access, including proportional regulation (risk profile, and/or activities, rather than institutions's type) that that will drive competition in the market.
Competitive Landscape
The neo and challenger banks market features intense competition between pure-play digital banks, licensed challengers, and digital subsidiaries of incumbents, where differentiation is made based on user experience, product innovation and expansion into new geographies. Leading players like Revolut (more than 60 million users), Nubank (around 70 million users) and Chime (12-15 million users) have achieved scale with some aggressive growth plans and have raised billions in venture funding at unicorn valuations of around USD 10 billion and up.
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity continues to accelerate due to revenue pressures from profitability and funding challenges. At least 25+ acquisitions will take place in 2024. Current acquired Till Financial and Monzo merged with ClearScore. Geographic expansion is still a significant growth strategy. European neo banks are entering the U.S. market, while Asian super-apps are expanding their financial services offerings, and incumbent banks are acquiring/pursuing neo banks to accelerate their transformational journey to digitalization rather than building those capabilities in-house.
Neo and Challenger Bank Market Growth, By Key Regions/Countries
|
Country |
CAGR |
|
China |
28.3% |
|
India |
27.8% |
|
Brazil |
23.5% |
|
Indonesia |
21.7% |
|
United States |
19.2% |
|
United Kingdom |
16.4% |
|
Germany |
15.8% |
The neo and challenger bank market is estimated to grow globally at a CAGR of 23.5% during 2025-2035, with the Asia-Pacific region anticipated to see the fastest growth from a massive unbanked population and a mobile-first consumer base. The neo and challenger bank market across Asia-Pacific will be led by China at a CAGR of 28.3% driven by super app platforms that are integrating banking services such as WeChat by Tencent and Alipay by Ant Group which is enabling integrated online banking services for 1 billion users in China. India is next at a CAGR of 27.8% with 190 million adults are now banked for the first time with digital banking services over the last few years.
Country-Specific Growth Analysis
China's Super-App Ecosystem Drives 28.3% CAGR Leadership (2025-2035)
The neo banking sector in China experienced a growth from 20.8% CAGR in 2020-2024. This market is further expected to grow at a CAGR of 28.3% from 2025-2035 as technology firms such as Tencent and Alibaba integrate financial services into their ecosystems with billions of users. WeBank has used social and behavioral data to score customers for AI-enforced micro-loans, making about USD 1,500 on average and serving 320 million users; this resulted in default rates of <1.5%. MYbank leverages automated decisioning and processes 5 million loans a day for SMEs, providing an approval decision in 3 seconds, 0% human. Banking's place within super-app ecosystems creates an engagement like never before; WeChat users use their banking services 15 times daily, getting paid on the app, shopping, and performing banking services like paying at restaurants. Government support with the digital yuan product and policies that focus on financial inclusion has perpetuated the penetration of digital banking; the government is looking for 95% penetration by 2030!
India's Digital India Initiative Propels Neo and Challenger Bank Market at a CAGR of 27.8% from 2025 to 2035
India's neo banking market is expected to flourish from 2025 to 2035, with a CAGR of 27.8%, largely attributed to government-led digitization initiatives and a growing user base of 650 million smartphone users looking for easy access to financial services. The JAM trinity (Jan Dhan accounts, Aadhaar identification, and Mobile connected) has established digital foundations that enabled fast KYC and onboarding of over 400 million erstwhile unbanked citizens. Neo banks such as Paytm Payments Bank brought 60 million users onto their platform while Jupiter and Fi are targeting richer millennials looking for custom wealth management services. RBI's digital banking licenses and ubiquity of the UPI payment rails that process over 10 billion transactions every month, provide a ready basis for growth for neo banks. The roadmap for a USD 5 trillion economy by the year 2030 may require financial inclusion and neo banks are positioned to provide easy access to credit through new and alternative underwriting aspects.
U.S. Neo Banks Capture 18.2% Growth Through Innovation and Venture Funding
The U.S. neo banking market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 19.2% from 2025 to 2035. This is powered by USD 5 billion annually in venture investments and consumer dissatisfaction, with 50 million Americans currently dissatisfied with the current bank services and fees. In addition to 12 million customers, Chime saves customers up to USD 500 a year in no-fee accounts and early direct deposit, while Varo Bank has a national charter that offers full-stack banking featuring USD 1 billion in loan origination. While the CFPB continues to work on an open banking framework, state-level charters for fintech help to lower regulatory barriers to market, which helps neo banks scale. Community banks and neo banks can leverage partner models to attract and retain customers while pushing the envelope on innovation, achieving compliance, and providing FDIC insurance. Neo banks meet the needs created by the student debt crisis and growing wealth inequality in the U.S. by offering more accessible financial services through lower costs and less discriminatory underwriting.
Key Players in Neo and Challenger Bank Market Expand Through Innovation and Scale
Major neo and challenger banks pursue ambitious growth strategies incorporating geographical expansion, new products, and partnerships to achieve profitability or market leadership. Revolut leads globally with over 60 million customers, offering 30+ financial products across 38 countries, and generated nearly $4 billion in annual revenue in 2024, aiming for profitability by 2025. Nubank is the largest player in Latin America with over 114 million customers and quarterly revenue of approximately $1 billion, leveraging proprietary credit models and vertical integration with existing account holders to maintain sustained profitability.
Chime and Current have successfully captured the U.S market via partnerships with regional banks and an emphasis on financially underserved Americans by providing fee-less overdraft protection, fee-less overdraft protection, and access to their paycheck early. The European challengers N26, Monzo, and Starling Bank seek organic, sustainable growth, and compliance to regulations. Starling Bank has achieved profitability through compeititon for SME lending and Banking-as-a-Service.
The larger Asian players WeBank, KakaoBank, and Paytm Payments Bank have leveraged their parent companies ecosystems and super-app integration in order to find huge scale by tapping into hundreds of millions of users. The strategic initiatives at play are partnerships and embedded finance, white-label platform strategies, international consolidation via acquisitions, and being a financial services ecosystem with wealth management, insurance, and crypto service from banks.
Recent Developments in the Global Neo and Challenger Bank Market
In 2024, Nubank expanded its Latin American footprint by launching operations in Mexico and Colombia through acquisitions and organic growth, now serving approximately five countries in the region, including Brazil, Mexico, Colombia, Argentina, and Peru.
In late 2024, Chime filed confidentially for an IPO targeting a valuation in the range of USD 34-40 billion, which would make it one of the largest fintech public offerings since 2021.
|
Item |
Value |
|
Market Size (2025) |
USD 107.3 Billion |
|
Business Model |
Digital-only Banks, Hybrid Banks |
|
Licensing Model |
Fully Licensed Banks, Partnership Models |
|
Services Offered |
Payments, Savings, Loans, Investments, Insurance, Currency Exchange |
|
End-User |
Retail Consumers, SMEs, Large Enterprises |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Revolut, N26, Monzo, Chime, Nubank, Starling Bank, WeBank, KakaoBank, Varo Bank, Current |
|
Additional Attributes |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis, technology impact analysis, open banking adoption, regulatory landscape, profitability metrics, customer acquisition costs, viral growth coefficients |
The global neo and challenger bank market is estimated to be valued at USD 107.3 billion in 2025.
The market size for neo and challenger banks is projected to reach USD 875.6 billion by 2035.
The neo and challenger bank market is expected to grow at a 23.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
Digital-only banks command 65-70% market share due to lower costs and superior customer experience.
Payments and money transfers represent 35-40% of revenue, serving as the core engagement driver for customer acquisition and retention.
1. Market Definition & Scope
1.1. Market Definition
1.2. Market Ecosystem
1.3. Currency
1.4. Key Stakeholders
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Process of Data Collection and Validation
2.2.1. Secondary Research
2.2.2. Primary Research/Interviews with Key Opinion Leaders from the Industry
2.3. Market Sizing and Forecast
2.3.1. Market Size Estimation Approach
2.3.1.1. Bottom-up Approach
2.3.1.2. Top-down Approach
2.3.2. Growth Forecast Approach
2.3.3. Assumptions for the Study
3. Executive Summary
3.1. Overview
3.2. Segmental Analysis
3.2.1. Neo and Challenger Bank Market, by Business Model
3.2.2. Neo and Challenger Bank Market, by Licensing Model
3.2.3. Neo and Challenger Bank Market, by Service Type
3.2.4. Neo and Challenger Bank Market, by End-User
3.2.5. Neo and Challenger Bank Market, by Region
3.3. Competitive Landscape
3.4. Strategic Recommendations
4. Market Insights
4.1. Overview
4.2. Factors Affecting Market Growth
4.2.1. Drivers
4.2.1.1. Digital transformation across financial services
4.2.1.2. Shift in consumer preference to mobile-first banking
4.2.1.3. Favorable regulatory frameworks and fintech sandboxes
4.2.1.4. Cost advantages and operational efficiency
4.2.1.5. Financial inclusion and underserved market opportunities
4.2.2. Restraints
4.2.2.1. Profitability challenges and path to sustainability
4.2.2.2. Customer trust and security concerns
4.2.2.3. Regulatory compliance complexity across jurisdictions
4.2.3. Opportunities
4.2.3.1. Expansion in emerging economies and underbanked populations
4.2.3.2. Open banking and API-driven ecosystems
4.2.3.3. Embedded finance and Banking-as-a-Service platforms
4.2.3.4. SME banking and business financial services
4.2.4. Trends
4.2.4.1. AI-powered personalization and predictive banking
4.2.4.2. Super-app integration and ecosystem partnerships
4.2.4.3. Cryptocurrency and digital asset services
4.2.4.4. Sustainable and ESG-focused banking products
4.2.5. Challenges
4.2.5.1. Customer acquisition costs and retention strategies
4.2.5.2. Cybersecurity threats and data privacy requirements
4.2.5.3. Competition from incumbent digital transformations
4.3. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
4.3.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.3.2. Bargaining Power of Buyers
4.3.3. Threat of Substitutes
4.3.4. Threat of New Entrants
4.3.5. Degree of Competition
4.4. Technology Impact on Neo and Challenger Bank Market
4.4.1. Cloud-Native Banking Platforms
4.4.1.1. Scalability and rapid product launches
4.4.1.2. Low operational costs and high agility
4.4.1.3. Microservices architecture and DevOps
4.4.2. AI & Machine Learning
4.4.2.1. Personalized financial insights and recommendations
4.4.2.2. Real-time fraud detection and prevention
4.4.2.3. Alternative credit scoring and risk assessment
4.4.3. API-Enabled Open Banking
4.4.3.1. Third-party integrations and marketplace models
4.4.3.2. Embedded finance and white-label solutions
4.4.3.3. Data aggregation and financial management
5. Impact of Sustainability on Neo and Challenger Bank Market
5.1. Carbon footprint reduction through digital-only operations
5.2. Financial inclusion for underserved communities
5.3. ESG investment products and green finance initiatives
5.4. Paperless banking and environmental sustainability
5.5. Ethical banking practices and transparent fee structures
5.6. Support for social causes and community development
5.7. Sustainable technology infrastructure and renewable energy usage
6. Competitive Landscape
6.1. Overview
6.2. Key Growth Strategies
6.3. Competitive Benchmarking
6.4. Competitive Dashboard
6.4.1. Industry Leaders
6.4.2. Market Differentiators
6.4.3. Vanguards
6.4.4. Contemporary Stalwarts
6.5. Market Share/Ranking Analysis, by Key Players, 2024
7. Neo and Challenger Bank Market Assessment—By Business Model
7.1. Overview
7.2. Digital-only Banks
7.3. Hybrid Banks
8. Neo and Challenger Bank Market Assessment—By Licensing Model
8.1. Overview
8.2. Fully Licensed Banks
8.3. Partnership/Banking-as-a-Service Model
9. Neo and Challenger Bank Market Assessment—By Service Type
9.1. Overview
9.2. Payments and Money Transfers
9.3. Savings and Deposit Accounts
9.4. Lending Services
9.4.1. Personal Loans
9.4.2. Business Loans
9.4.3. Overdrafts and Credit Lines
9.5. Investment and Wealth Management
9.6. Insurance Products
9.7. Currency Exchange and International Services
9.8. Cryptocurrency and Digital Assets
9.9. Others
10. Neo and Challenger Bank Market Assessment—By End-User
10.1. Overview
10.2. Retail Consumers
10.2.1. Mass Market
10.2.2. Affluent Segment
10.2.3. Young Adults and Students
10.3. Small and Medium Businesses (SMEs)
10.4. Large Enterprises
10.5. Freelancers and Gig Workers
11. Neo and Challenger Bank Market Assessment—By Geography
11.1. Overview
11.2. North America
11.2.1. U.S.
11.2.2. Canada
11.3. Europe
11.3.1. United Kingdom
11.3.2. Germany
11.3.3. France
11.3.4. Netherlands
11.3.5. Spain
11.3.6. Italy
11.3.7. Rest of Europe
11.4. Asia-Pacific
11.4.1. China
11.4.2. India
11.4.3. Japan
11.4.4. South Korea
11.4.5. Singapore
11.4.6. Indonesia
11.4.7. Australia
11.4.8. Rest of Asia-Pacific
11.5. Latin America
11.5.1. Brazil
11.5.2. Mexico
11.5.3. Argentina
11.5.4. Colombia
11.5.5. Rest of Latin America
11.6. Middle East & Africa
11.6.1. UAE
11.6.2. Saudi Arabia
11.6.3. Israel
11.6.4. South Africa
11.6.5. Nigeria
11.6.6. Rest of Middle East & Africa
12. Company Profiles (Business Overview, Financial Overview, Product Portfolio, Strategic Developments, and SWOT Analysis)
12.1. Revolut Ltd.
12.2. N26 GmbH
12.3. Monzo Bank Ltd.
12.4. Chime Financial, Inc.
12.5. Nubank (Nu Holdings Ltd.)
12.6. Starling Bank Limited
12.7. WeBank (Tencent)
12.8. KakaoBank Corp.
12.9. Varo Bank, N.A.
12.10. Current (Finco Services, Inc.)
12.11. SoFi Technologies, Inc.
12.12. Ally Financial Inc. (Ally Bank)
12.13. Atom Bank plc
12.14. Tandem Bank Limited
12.15. Paytm Payments Bank Limited
12.16. Tinkoff Bank
12.17. MyBank (Alibaba Group)
12.18. Judo Bank Pty Ltd.
12.19. TymeBank
12.20. Other Key Players
13. Appendix
13.1. Available Customization
13.2. Related Reports
























Published Date: Jul-2023
Published Date: Mar-2023
Published Date: Jan-2025
Published Date: Jan-2025
Published Date: Jan-2025
Please enter your corporate email id here to view sample report.
Subscribe to get the latest industry updates