Resources
About Us
Ebb and Flow System Market by System Type (Flood Table Systems, Bucket Systems, Modular Systems), Application (Commercial Greenhouses, Vertical Farms, Nurseries & Propagation, Research Facilities, Home/Hobby Growing), Crop Type, Growing Medium — Global Forecast to 2036
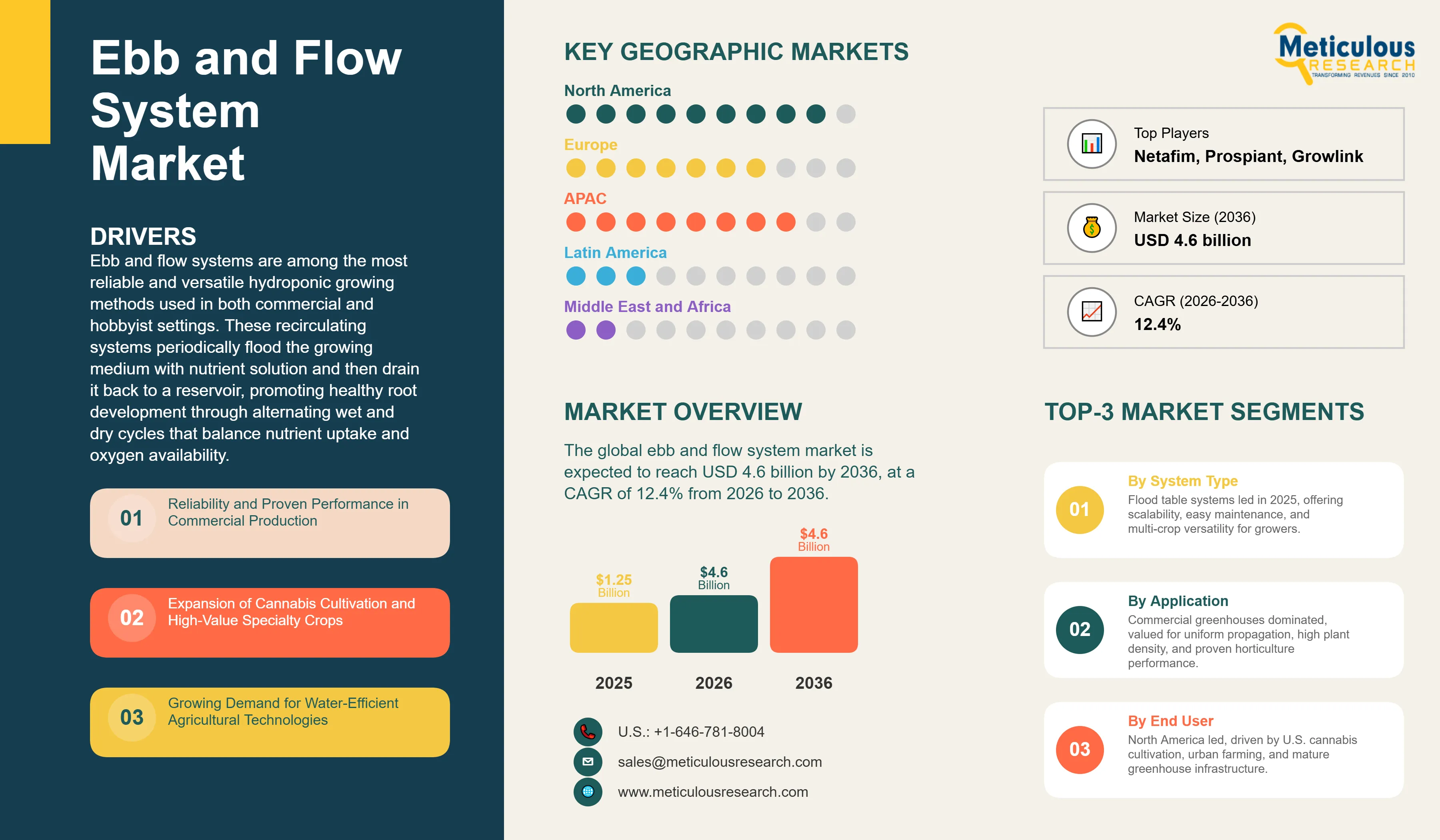
Report ID: MRAGR - 1041646 Pages: 240 Jan-2026 Formats*: PDF Category: Agriculture Delivery: 24 to 72 Hours Download Free Sample ReportThe global ebb and flow system market is expected to reach USD 4.6 billion by 2036 from USD 1.4 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 12.4% from 2026 to 2036.
Ebb and flow systems are among the most reliable and versatile hydroponic growing methods used in both commercial and hobbyist settings. These recirculating systems periodically flood the growing medium with nutrient solution and then drain it back to a reservoir, promoting healthy root development through alternating wet and dry cycles that balance nutrient uptake and oxygen availability. During flooding, stale air is displaced from the medium, while drainage draws fresh oxygen back into the root zone. Modern systems incorporate automation, overflow protection, and precise timing controls to ensure consistent operation. Ebb and flow technology supports a wide range of growing media, including expanded clay, rockwool, coco coir, and perlite, and is suitable for propagating seedlings, leafy greens, herbs, and larger fruiting crops such as tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, and cannabis.
Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
Ebb and flow systems have become a foundational technology in modern hydroponic agriculture, valued for their reliability, operational simplicity, and adaptability across a wide range of crops. Compared with more complex hydroponic methods such as aeroponics or nutrient film technique, ebb and flow systems offer a balanced combination of performance and ease of use. Their core mechanism, periodic flooding followed by complete drainage, effectively addresses the dual requirement of delivering nutrients and oxygen to plant roots. During flooding, roots absorb nutrient solution while accumulated carbon dioxide and stale air are displaced from the growing medium; subsequent drainage draws oxygen‑rich air back into the root zone, supporting vigorous root development, improved nutrient uptake, and greater plant resilience.
The market spans a broad range of system scales, from small hobbyist setups with single flood tables supporting a limited number of plants to large commercial installations featuring interconnected tables covering extensive growing areas. Modern commercial systems typically incorporate advanced automation, including programmable irrigation controls, overflow protection, pH and electrical conductivity monitoring, and integration with temperature and humidity management systems. The long‑standing use of ebb and flow technology in commercial greenhouse propagation, where uniformity and repeatability are critical, has established proven design standards and best practices that support adoption across both industrial and home‑growing applications.
Integration with controlled environment agriculture (CEA) and vertical farming systems is a key growth driver for ebb and flow technology. Multi‑tier vertical farms increasingly favor flood and drain irrigation due to its consistent performance across stacked growing levels, avoiding the pressure variability of drip systems and the leveling sensitivity of nutrient film technique. Equipment suppliers are developing customized ebb and flow configurations for vertical farming, including shallow, low‑volume flood trays and lightweight materials suitable for high‑density, multi‑story installations. The system’s compatibility with sensor‑driven automation, where irrigation is triggered by real‑time environmental and crop conditions rather than fixed schedules, supports maximum production density in urban agriculture facilities.
Modular and scalable system designs are gaining traction, particularly among small and mid‑scale commercial growers seeking incremental expansion. Manufacturers now offer bucket‑based ebb and flow systems that allow growers to begin with a limited number of plant sites and scale using the same control infrastructure. This modularity reduces upfront capital requirements relative to traditional fixed flood tables and enables crop segregation within a single facility, allowing different nutrient regimes for leafy greens and fruiting crops while maintaining centralized automation.
Sustainability and water‑use efficiency are becoming critical differentiators as growers face rising pressure to reduce input consumption and nutrient runoff. Ebb and flow systems inherently conserve water through full recirculation, and recent design innovations further enhance efficiency. Improved drainage profiles reduce residual ponding, antimicrobial materials limit biofilm formation, and intelligent controllers dynamically adjust flood timing based on plant size and ambient conditions. These features support both cost reduction and environmental performance, aligning ebb and flow systems with retailer and consumer expectations for sustainable production.
Driver: Reliability and Proven Performance in Commercial Production
Ebb and flow systems have a long track record of reliable performance in commercial greenhouse operations, particularly in large‑scale seedling propagation where uniform germination and early plant development are critical. Bottom‑flood irrigation delivers consistent moisture across all plant sites, avoiding the dry spots common with overhead irrigation and the variability sometimes associated with drip systems. This uniformity minimizes uneven growth, reduces labor requirements for sorting, and improves overall marketable yield.
The mechanical simplicity, typically involving a submersible pump, timer, and overflow safeguard, supports high system uptime and straightforward maintenance. Unlike more complex hydroponic methods that rely on precise pressure or flow control, ebb and flow systems are tolerant of minor equipment variations without jeopardizing crop performance. This proven reliability makes them a low‑risk and cost‑effective choice for commercial growers investing in long‑term production infrastructure.
Driver: Expansion of Cannabis Cultivation and High‑Value Specialty Crops
The rapid expansion of legal cannabis cultivation is a significant driver of ebb and flow system adoption. Commercial cannabis producers favor flood and drain methods for their ability to precisely regulate root‑zone moisture and oxygen availability, key factors in achieving consistent yields and premium flower quality. Bucket‑based ebb and flow systems are particularly popular, allowing uniform irrigation across individual plant modules while enabling flexible plant spacing, training, and harvest scheduling.
Periodic drying between flood cycles encourages robust root development and supports optimal nutrient uptake, contributing to improved resin production and cannabinoid profiles. As cannabis legalization expands globally and licensed cultivation capacity increases, many producers are standardizing on proven hydroponic technologies, with ebb and flow systems widely adopted across both vegetative and flowering stages.
Opportunity: Integration with Smart Agriculture and IoT Platforms
The relatively simple automation requirements of ebb and flow systems make them well suited for integration with smart agriculture and IoT‑based cultivation platforms. Modern controllers can monitor critical parameters such as nutrient solution temperature, pH, electrical conductivity, and water levels while capturing data on flood cycle performance and system health. Cloud connectivity enables remote monitoring and centralized control, which is particularly valuable for commercial operators managing multiple facilities.
Integration with environmental sensors allows irrigation cycles to dynamically adjust based on temperature, humidity, and light intensity, increasing flood frequency under dry or high‑heat conditions and reducing irrigation during periods of elevated humidity. This data‑driven optimization lowers water and nutrient consumption while maintaining optimal root‑zone conditions. As ag‑tech providers expand comprehensive farm management platforms, the compatibility of ebb and flow systems with standard automation protocols positions them for broad adoption in digitally enabled production environments.
Opportunity: Urban Agriculture and Local Food Production
Urban agriculture initiatives, including rooftop greenhouses, indoor farms, and community growing spaces, are increasingly adopting ebb and flow systems due to their water efficiency, reliability, and adaptability to constrained environments. Public programs supporting local food production often favor controlled‑environment systems that balance performance with operational simplicity, making ebb and flow technology particularly attractive.
The system’s suitability for producing high‑quality leafy greens, herbs, and microgreens supports viable business models serving restaurants, retailers, and farmers markets. Educational institutions also favor ebb and flow systems for teaching hydroponics fundamentals, as the visible flood‑and‑drain cycle simplifies learning and troubleshooting. As cities continue to invest in food security and localized production strategies, demand for hydroponic infrastructure, including ebb and flow systems, is expected to benefit from both public support and growing consumer awareness of controlled‑environment agriculture.
By System Type:
In 2025, flood table systems commanded the largest share of the ebb and flow market. These systems typically utilize rectangular trays ranging from 2×4 feet for small operations to 4×8 feet or larger in commercial settings, offering flexibility across container types and growing media. Commercial propagation nurseries rely heavily on flood tables because they accommodate standard seedling trays, individual pots, and rockwool blocks within the same production cycle. Their large surface area supports high plant densities, often 200–400+ sites per table depending on crop size, maximizing space utilization. Flood tables also integrate efficiently with rolling bench systems common in greenhouses, reducing aisle space and improving workflow efficiency. Leading manufacturers such as Botanicare and Active Aqua (Hydrofarm) offer durable flood tables designed with integrated drainage channels, UV‑stabilized materials, and scalable reservoir options.
Bucket systems are expected to grow at the fastest CAGR through 2036, driven by adoption among cannabis cultivators and specialty crop producers requiring individual plant management. These modular configurations connect multiple 2–5 gallon buckets to a central controller that regulates shared flood and drain cycles. Bucket systems enable flexible plant spacing, simplified harvesting, and isolation of individual plants when needed, advantages not easily achieved with fixed flood tables.
By Application:
Based on application, the commercial greenhouses segment held the largest share of the overall ebb and flow systems market in 2025, with flood and drain technology widely established as the industry standard for seedling propagation. Large‑scale nurseries rely on these systems to produce millions of uniform seedlings for transplant into both soil‑based and hydroponic production. Bottom‑flood irrigation ensures consistent moisture distribution, reduces disease transmission compared with overhead watering, and supports uniform germination. Automated ebb and flow systems also deliver significant labor efficiencies and integrate seamlessly with standard greenhouse infrastructure, including rolling benches, lighting, and climate control, making them well suited to professional production environments.
The vertical farming application segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR from 2026 to 2036, as urban indoor agriculture expands globally. Ebb and flow systems are particularly well suited to stacked growing environments, as periodic flooding performs consistently across multiple tiers without the leveling sensitivity of continuous‑flow systems. Vertical farm operators deploy customized flood and drain configurations optimized for rack‑mounted installations, emphasizing shallow trays that reduce solution volume, system weight, and pumping energy requirements. The closed‑loop, recirculating design aligns with vertical farming’s focus on water efficiency and sustainability. As vertical farming moves from early adoption toward broader commercial deployment, demand for specialized ebb and flow systems continues to accelerate.
By Crop Type:
Leafy greens, including lettuce, spinach, kale, and chard held the largest share of the ebb and flow systems market in 2025. Their short production cycles and shallow root structures are well suited to flood and drain cultivation, where periodic flooding promotes rapid leaf growth and oxygenation between cycles supports healthy root systems. In many commercial operations, ebb and flow systems are used for germination and early growth before transplanting to other hydroponic systems, while some producers utilize flood and drain through harvest.
Fruiting vegetables and high‑value crops, including tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, strawberries, and cannabis, are expected to grow at the highest CAGR from 2026 to 2036. These crops require longer production cycles and larger root volumes, making bucket‑based ebb and flow systems particularly suitable. In cannabis cultivation, individual plant management is critical for training, spacing, and harvest optimization, driving strong adoption of modular flood and drain systems. Many vegetable producers use ebb and flow during vegetative stages before transitioning to drip irrigation, although some maintain flood and drain throughout the entire crop cycle.
Regional Insights:
In 2025, North America held the largest share of the global ebb and flow system market, led by the U.S. This is mainly attributed to its mature commercial greenhouse sector, rapid expansion of licensed cannabis cultivation, and growing urban agriculture adoption. The U.S. greenhouse operators producing vegetables, ornamentals, and transplants have largely standardized on flood table systems for propagation, while cannabis producers favor bucket‑based configurations for flowering and individual plant management. The well-established distribution networks and extensive technical support from major suppliers make ebb and flow systems widely accessible across North America, from home growers to large‑scale commercial operations.
The Asia‑Pacific ebb and flow system market is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR from 2026 to 2036, driven by government support for modernized agriculture, land constraints in dense urban centers, and rising consumer demand for pesticide‑free produce. Japan and Singapore lead vertical farming deployment, where ebb and flow systems are commonly used due to their reliability in stacked growing environments. China’s greenhouse sector is rapidly modernizing with increasing adoption of automated irrigation, while South Korea and Taiwan show growing interest in hydroponic production for high‑value crops. The growing food safety concerns across the region are further supporting investment in controlled‑environment agriculture despite higher initial capital costs relative to conventional farming.
The European ebb and flow system market also shows strong adoption of ebb and flow systems in greenhouse propagation and nursery operations, particularly in the Netherlands, Spain, Germany, and the U.K. The European growers focus on sustainability and resource efficiency, driving preference for recirculating hydroponic systems that reduce water use and nutrient runoff. Regulatory constraints on fertilizer discharge in sensitive watersheds are further encouraging closed‑loop systems such as flood and drain. This market is also further driven by a well‑developed supplier base serving both professional horticulture and advanced hobbyist markets.
Key Players:
The major players in the ebb and flow system market include Growing Innovations, Inc., Netafim Ltd., Hydro Systems Co., Rivulis Irrigation Ltd., Priva Holding B.V., Autogrow Systems Ltd., Argus Control Systems Ltd., Certhon Group, GGS Greenhouse + Grower Supplies, Prospiant Inc., Vanden Bussche Irrigation, Growlink Inc., and T-Systems Hydroponics, along with several other regional and niche players collectively categorized under others.
The ebb and flow system market is expected to grow from USD 1.4 billion in 2026 to USD 4.6 billion by 2036.
The ebb and flow system market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.4% from 2026 to 2036.
The major players in the ebb and flow system market include Growing Innovations, Inc., Netafim Ltd., Hydro Systems Co., Rivulis Irrigation Ltd., Priva Holding B.V., Autogrow Systems Ltd., Argus Control Systems Ltd., Certhon Group, GGS Greenhouse + Grower Supplies, Prospiant Inc., Vanden Bussche Irrigation, Growlink Inc., and T-Systems Hydroponics, along with several other regional and niche players collectively categorized under others.
The main factors driving the ebb and flow system market include proven reliability and performance in commercial greenhouse propagation and production, expansion of legal cannabis cultivation requiring precise root zone control, growing demand for water-efficient recirculating hydroponic technologies, increasing urban agriculture and vertical farming deployment, modular system designs enabling scalable operations from hobbyist to commercial scale, and integration capabilities with smart agriculture IoT platforms for automated precision irrigation management.
North America will continue to lead the global ebb and flow system market during the forecast period 2026 to 2036, driven by extensive commercial greenhouse infrastructure, rapid cannabis industry expansion, established hydroponic equipment supply chains, and increasing adoption in controlled environment agriculture and vertical farming operations.
1. Introduction
1.1. Market Definition
1.2. Market Ecosystem
1.3. Currency and Limitations
1.3.1. Currency
1.3.2. Limitations
1.4. Key Stakeholders
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Collection & Validation
2.2.1. Secondary Research
2.2.2. Primary Research
2.3. Market Assessment
2.3.1. Market Size Estimation
2.3.2. Bottom-Up Approach
2.3.3. Top-Down Approach
2.3.4. Growth Forecast
2.4. Assumptions for the Study
3. Executive Summary
3.1. Overview
3.2. Market Analysis, by System Type
3.3. Market Analysis, by Application
3.4. Market Analysis, by Crop Type
3.5. Market Analysis, by Growing Medium
3.6. Market Analysis, by Geography
3.7. Competitive Analysis
4. Market Insights
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Global Ebb and Flow System Market: Impact Analysis of Market Drivers (2025–2035)
4.2.1. Reliability and Proven Performance in Commercial Production
4.2.2. Expansion of Cannabis Cultivation and High-Value Specialty Crops
4.2.3. Growing Demand for Water-Efficient Agricultural Technologies
4.3. Global Ebb and Flow System Market: Impact Analysis of Market Restraints (2025–2035)
4.3.1. Higher Initial Capital Investment Compared to Soil-Based Systems
4.3.2. Technical Knowledge Requirements for Optimal System Management
4.4. Global Ebb and Flow System Market: Impact Analysis of Market Opportunities (2025–2035)
4.4.1. Integration with Smart Agriculture and IoT Platforms
4.4.2. Urban Agriculture and Local Food Production Initiatives
4.5. Global Ebb and Flow System Market: Impact Analysis of Market Challenges (2025–2035)
4.5.1. Competition from Alternative Hydroponic Methods
4.5.2. Power Dependency and Vulnerability to Equipment Failures
4.6. Global Ebb and Flow System Market: Impact Analysis of Market Trends (2025–2035)
4.6.1. Modular and Scalable System Designs for Flexible Expansion
4.6.2. Enhanced Automation and Remote Monitoring Capabilities
4.7. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
4.7.1. Threat of New Entrants
4.7.2. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.7.3. Bargaining Power of Buyers
4.7.4. Threat of Substitute Products
4.7.5. Competitive Rivalry
5. Ebb and Flow Systems in Vertical Farming and Controlled Environment Agriculture
5.1. Introduction to Vertical Farming Applications
5.2. System Design Adaptations for Multi-Tier Growing
5.3. Water and Energy Efficiency Optimization
5.4. Automation and Smart Control Integration
5.5. Crop Selection and Production Optimization
5.6. Economic Viability and ROI Considerations
5.7. Technology Innovations and Future Developments
5.8. Impact on Market Growth and Adoption Trends
6. Competitive Landscape
6.1. Introduction
6.2. Key Growth Strategies
6.2.1. Market Differentiators
6.2.2. Synergy Analysis: Major Deals & Strategic Alliances
6.3. Competitive Dashboard
6.3.1. Industry Leaders
6.3.2. Market Differentiators
6.3.3. Vanguards
6.3.4. Emerging Companies
6.4. Vendor Market Positioning
6.5. Market Share/Ranking by Key Players
7. Ebb and Flow System Market, by System Type
7.1. Introduction
7.2. Flood Table Systems
7.2.1. Standard Flood Tables
7.2.2. Rolling Bench Systems
7.2.3. Modular Interlocking Tables
7.3. Bucket Systems
7.3.1. 2-Gallon Bucket Systems
7.3.2. 5-Gallon Bucket Systems
7.3.3. Custom Bucket Configurations
7.4. Modular Tray Systems
7.5. Propagation Stations
8. Ebb and Flow System Market, by Application
8.1. Introduction
8.2. Commercial Greenhouses
8.2.1. Vegetable Production
8.2.2. Ornamental Plants
8.2.3. Cannabis Cultivation
8.3. Vertical Farms and Indoor Agriculture
8.4. Nurseries and Propagation Facilities
8.5. Research and Educational Institutions
8.6. Home and Hobby Growing
9. Ebb and Flow System Market, by Crop Type
9.1. Introduction
9.2. Leafy Greens
9.3. Herbs
9.4. Fruiting Vegetables
9.5. Flowers and Ornamentals
9.6. Cannabis and Hemp
9.7. Microgreens and Sprouts
10. Ebb and Flow System Market, by Growing Medium
10.1. Introduction
10.2. Expanded Clay Pebbles (Hydroton)
10.3. Rockwool/Stonewool
10.4. Coco Coir
10.5. Perlite and Vermiculite
10.6. Mixed Media Blends
10.7. Other Growing Media
11. Ebb and Flow System Market, by Geography
11.1. Introduction
11.2. North America
11.2.1. U.S.
11.2.2. Canada
11.3. Europe
11.3.1. Netherlands
11.3.2. Spain
11.3.3. Germany
11.3.4. U.K.
11.3.5. Rest of Europe
11.4. Asia-Pacific
11.4.1. Japan
11.4.2. China
11.4.3. Singapore
11.4.4. Australia
11.4.5. South Korea
11.4.6. Rest of Asia-Pacific
11.5. Latin America
11.5.1. Mexico
11.5.2. Brazil
11.5.3. Rest of Latin America
11.6. Middle East & Africa
11.6.1. UAE
11.6.2. Israel
11.6.3. South Africa
11.6.4. Rest of Middle East & Africa
12. Company Profiles
(Business Overview, Financial Overview, Product Portfolio, Strategic Developments, SWOT Analysis)
12.1. Growing Innovations, Inc.
12.2. Netafim Ltd.
12.3. Hydro Systems Co.
12.4. Rivulis Irrigation Ltd.
12.5. Priva Holding B.V.
12.6. Autogrow Systems Ltd.
12.7. Argus Control Systems Ltd.
12.8. Certhon Group
12.9. GGS Greenhouse + Grower Supplies
12.10. Prospiant Inc.
12.11. Vanden Bussche Irrigation
12.12. Growlink Inc.
12.13. T-Systems Hydroponics
12.14. Others
13. Appendix
13.1. Questionnaire
13.2. Available Customization
























Published Date: Feb-2025
Please enter your corporate email id here to view sample report.
Subscribe to get the latest industry updates