Resources
About Us
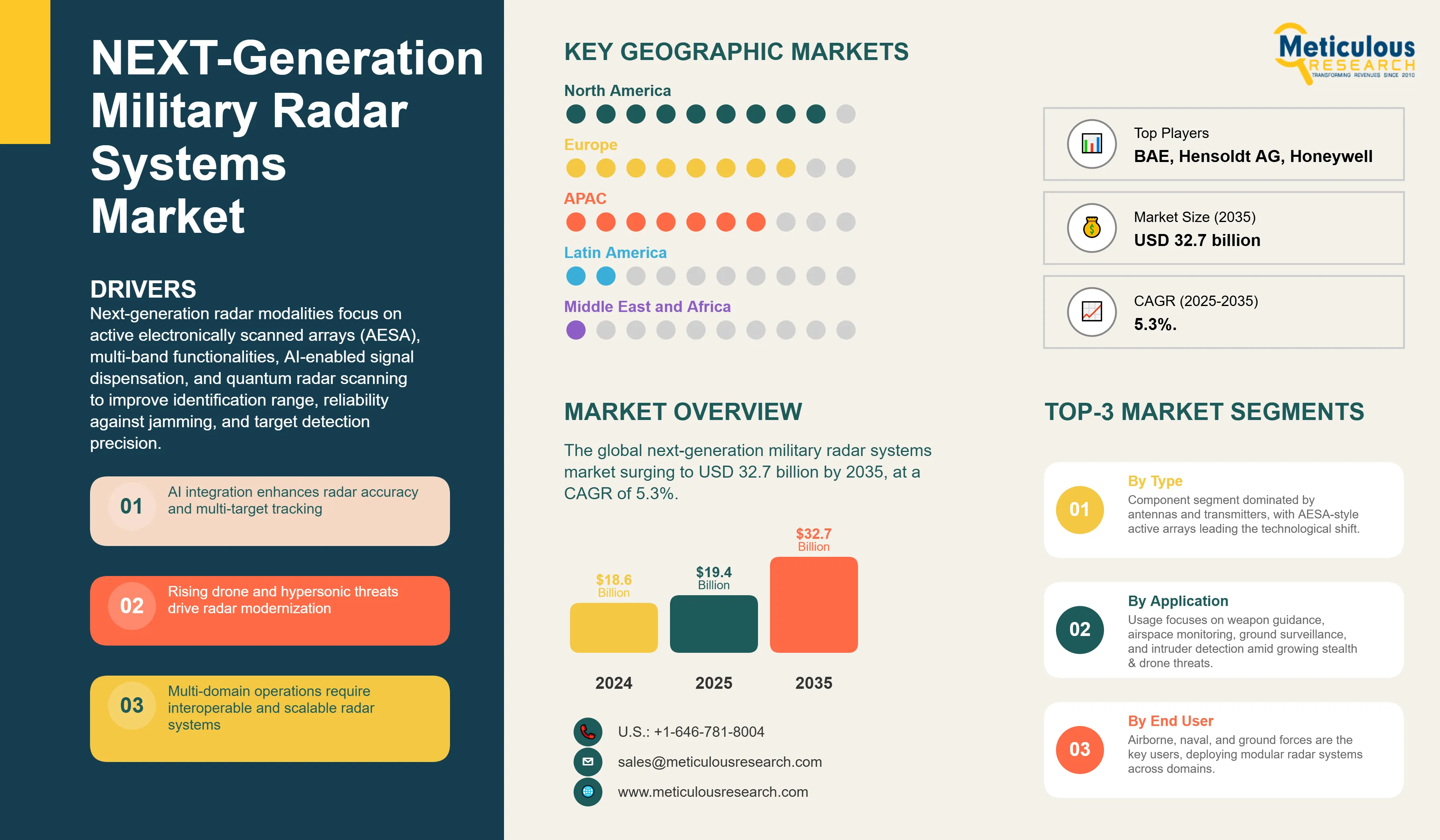
NEXT-Generation Military Radar Systems Market Size, Share & Forecast by Platform (Airborne, Naval, Ground), Frequency Band (X-Band, S-Band, C-Band), Component, Application, and Geography - Global Forecast to 2035
Report ID: MRAD - 1041588 Pages: 204 Sep-2025 Formats*: PDF Category: Aerospace and Defense Delivery: 24 to 72 Hours Download Free Sample ReportThe global next-generation military radar systems market was valued at USD 18.6 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 19.4 billion in 2025, surging to USD 32.7 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of 5.3%. This robust expansion is propelled by the evolving intricacies of new threats, comprising stealth fighters, hypersonic missiles, drones, and unconventional electronic warfare mechanisms.
Next-generation radar modalities focus on active electronically scanned arrays (AESA), multi-band functionalities, AI-enabled signal dispensation, and quantum radar scanning to improve identification range, reliability against jamming, and target detection precision. Need is surging for a radar platform that facilitates multi-province manoeuvres, with applications covering missile detection, border surveillance, and naval situational awareness. The market is shifting from conventional phased-array platforms to software-enabled, modular infrastructures capable of real-time threat detection.
Competitive Scenario of Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market and Insights
Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
The next-generation military radar systems market is highly competitive, with leading defense contractors, electronics specialists, and niche sensor technology firms all competing for large-scale modernization contracts. The global next-generation military radar systems market is dominated by Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon Technologies (RTX), Thales Group, Leonardo S.p.A., and Saab AB, which have extensive portfolios of airborne, naval, and ground-based radar platforms. To provide adaptable systems for a variety of mission profiles, these companies are utilizing active electronically scanned array (AESA) technology, multi-band capabilities, and open-architecture frameworks.
Recent Developments in Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market
Raytheon Launches Next-Gen Radar With AI-Based Threat Classification
In January 2024, Raytheon Technologies launched the GhostEye MR radar system, hosting AI-based threat detection and virtual beamforming. The radar highlighted around 40% betterment in target identification during U.S. Army field trials. Developed for medium-range air defense, GhostEye MR assists redundant trailing of drones, cruise missiles, and rotary-wing aircraft. The platform is based on an open architecture, allowing modular enhancements and integration with the joint command system.
U.S. Army Approves Raytheon’s Next-Gen LTAMDS Radar for Low-Rate Production
In April 2025, the U.S. Army approved the Lower-Tier Air and Missile Defense Sensor (LTAMDS) developed by Raytheon for low-rate initial production in April 2025. This radar system will replace the legacy Patriot radar, offering 360-degree coverage and doubling detection and tracking capabilities.
Key Market Drivers
|
Category |
Key Factor |
Short-Term Impact (2025–2028) |
Long-Term Impact (2029–2035) |
Estimated CAGR Impact |
|||
|
Drivers |
1. AI integration enhances radar accuracy and multi-target tracking |
Accelerated procurement of AESA, multi-band radars, and AI upgrades |
Institutionalized integration into layered air/missile defense networks |
▲ +2.2% |
|||
|
|
2. Rising drone and hypersonic threats drive radar modernization |
Multi-role adoption across services; reduced need for multiple legacy systems |
Lifecycle cost savings and rapid adaptability via software upgrades |
▲ +1.5% |
|||
|
Restraints |
1. High development and procurement costs |
Limits adoption for smaller defense forces |
Slows modernization cycles |
▼ −1.7% |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
▼ −1.4% |
|||
|
Opportunities |
1. Counter-drone and hypersonic radar capabilities |
Rapid funding for niche radar programs |
Becomes standard requirement across new procurements |
▲ +1.9% |
|||
|
|
2. Space-based and multi-domain radar integration |
Pilot programs linking terrestrial, airborne, and orbital radars |
Full operational fusion for global persistent surveillance |
▲ +1.6% |
|||
|
Trends |
1. AI and machine learning integration in radar processing |
Improved threat discrimination and reduced workload |
Autonomous radar operations and predictive capabilities |
▲ +1.5% |
|||
|
Challenges |
1. Supply chain constraints for GaN and high-performance chips |
Component shortages delay program schedules |
Long-term dependency on secure, diversified semiconductor manufacturing |
▼ −0.9% |
Regional Analysis
North America is the Largest Next-generation Military Radar Systems Market, Driven by Advanced Programs and Export Leadership
North America dominates the global next-generation military radar systems market, with a large market share, anchored by the United States’ massive defense budget and extensive modernization programs. In 2024, North America was responsible for the maximum of global radar system upgrades, as reported by the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO). The U.S. Department of Defense is responsible for 18 active radar modernization programs. The AN/SPY-6 radar was deployed across naval platforms, and the Army's LTAMDS system entered final testing for integrated air and missile defense.
In addition to this, in 2024, the United States expanded radar integration across multiple platforms, including the Army's LTAMDS, Navy's AN/SPY-6, and Air Force's Three-Dimensional Expeditionary Long-Range Radar (3DELRR), according to the U.S. Department of Defense. During joint exercises, the LTAMDS system successfully tracked cruise missiles and unmanned aerial vehicles. These systems are intended to facilitate JADC2 and integrated deterrence strategies.
Canada enhanced its early warning capabilities by expanding its NORAD radar coverage in the Arctic with new long-range systems. The region is characterized by robust public-private partnerships, with companies such as Raytheon, Northrop Grumman, and L3Harris spearheading innovation. Interoperability among services and allies continues to be a strategic priority. Moreover, the region also leads in radar export capacity, supplying advanced systems to NATO allies and Indo-Pacific partners, strengthening interoperability in coalition operations.
Asia Pacific is the Fastest-Growing Market for Next-generation Military Radar Systems with Strategic Modernization Programs
The next-generation military radar systems market in the Asia-Pacific region is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR through 2035, driven by rising defense budgets and the urgent need to counter stealth aircraft, missile proliferation, and maritime security challenges.
Japan implemented new AESA radar systems as part of its F-X fighter program, while India's DRDO conducted border monitoring tests for long-range surveillance radars. Australia collaborated with the United States to upgrade its JORN over-the-horizon radar network, thereby improving its coverage of the Indo-Pacific region. Similarly, China integrated multi-band systems for naval and air surveillance in the South China Sea, thereby expanding its radar footprint. To mitigate their dependence on foreign systems, regional governments are emphasizing the development of indigenous radar capabilities, thereby driving the market growth.
Expanding Indigenous Capabilities for Counter-Stealth and Maritime Surveillance Propels Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Growth in China
China’s military radar systems market is growing rapidly due to significant local research and development and the strategic integration of radar networks into its anti-access/area-denial (A2/AD) defense strategy. In 2023, China deployed new long-range radar systems across South China Sea installations to improve maritime surveillance and airspace control, overseen by the China Electronics Technology Group Corporation (CETC). These radars use advanced AESA technology and connect directly to naval command centers, allowing for real-time threat monitoring and response.
Chinese defense contractors work closely with state research institutions to create radar systems with long-range detection, high-resolution imaging, and strong electronic counter-countermeasures. Notable innovations include AI-powered airborne radars that maintain over 99% tracking accuracy even under intense electronic jamming, marking significant progress in electronic warfare resilience.
The 14th Five-Year Plan and ongoing defense modernization efforts focus on increasing funding for radar research, particularly in hypersonic tracking and stealth target detection. Plans also include the development of quantum radar and silent radar technologies that improve detection while keeping the radar’s presence hidden.
These developments support China’s strategic goals of achieving regional military dominance and strategic independence, strengthening its leading position in the next-generation military radar systems market, with continuous investments expected throughout the forecast period.
France Invests in Advanced Technology Integration and Strategic Partnerships
France has a significant share of the European market for next-generation military radar systems. This is driven by strategic investments related to NATO commitments and broader European security efforts. The country’s defense industry focuses on developing multifunctional radar systems that integrate Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) technology. It benefits from strong aerospace capabilities, led by industry leaders such as Thales Group.
Modernization programs and larger defense budgets are fueling the growth of France’s radar sector. Recent investments include a major €50 million upgrade of the Nostradamus over-the-horizon radar, which improves the detection accuracy of ballistic and hypersonic threats over thousands of kilometers. This radar is a key part of France’s extended air defense strategy, using both monostatic and bistatic modes to provide continuous coverage from ground level to near-space altitudes.
In addition, France is developing space-based radar platforms and incorporating artificial intelligence into existing radars like the Ground Master 400 and GM200. This aims to improve the detection of complex and stealthy aerial targets in near-space. These efforts back France’s strategic goal of having autonomous, integrated defense capabilities that offer better early warning and situational awareness.
With a strong export market and innovative projects such as the Stratobus high-altitude airship and BalMan maneuverable balloon, France is in a good position to maintain and grow its leadership in next-generation military radar systems, both in Europe and worldwide. The focus on near-space operations and new sensor fusion techniques highlights France’s commitment to addressing emerging aerial and missile threats.
Segmental Analysis
Antenna Segment Dominates While Transmitter Leads in Growth
In 2025, antennas hold the highest market share in the next-generation military radar market, driven by the shift toward active electronically scanned arrays (AESA) that enable multi-beam tracking, rapid beam steering, and resilience against jamming. These antennas enable digital beamforming, multi-target tracking, and frequency agility, supporting both short- and long-range detection. Raytheon’s AN/SPY-6 uses scalable antenna modules for naval platforms, while Thales’ Ground Master series features compact, high-power antennas for mobile deployment. Antenna innovation is central to radar modernization, with firms investing in lightweight, low-maintenance designs for expeditionary forces. The segment's growth is also driven by increasing demand for military antennas capable of operating across multiple frequency bands while maintaining high directional accuracy and signal gain characteristics.
Long-Range Segment Dominates While Medium-Range Leads in Growth
By range, the long-range radars segment is expanding at the fastest CAGR, enabling early warning, ballistic missile detection, and wide-area surveillance with ranges often exceeding 500 km. The recent deployment of long-range radar systems across strategic installations, such as naval bases, missile defense sites, and border zones has increased. These systems provide early warning against ballistic and hypersonic threats and have detection ranges that exceed 400 km. India installed surveillance systems along its northern borders, while the United States deployed long-range radars in Guam and Alaska. Satellite and airborne sensors are being increasingly integrated with long-range platforms to provide comprehensive coverage that is critical for layered defense.
|
Report Attribute |
Details |
|
Market size (2025) |
USD 19.4 billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2035 |
USD 32.7 billion |
|
CAGR (2025-2035) |
5.3% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2025 – 2035 |
|
Report coverage |
Market size and forecast, competitive landscape and benchmarking, country/regional level analysis, key trends, growth drivers and restraints |
|
Segments covered |
By Component (Transmitter, Antenna, Receiver, Duplexer, and Others), By Frequency (HF-Band, C-Band, S-Band, X-Band, L-Band, UHF/VHF, Ku/K/Ka-Band, and Multi Band Systems), By Range (Long, Medium, Short, and Very Short), By Platform (Airborne Radar, Land Radar, Naval Radar, and Space Radar), By Application (Weapon Guidance, Airspace Monitoring & Traffic Management, Airborne Mapping, Ground Surveillance & Intruder Detection, Navigation, and Others), Geography |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
|
Key companies profiled |
BAE Systems plc., Hanwha Systems Co. Ltd., Hensoldt AG, Honeywell International Inc., Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd., L3Harris Technologies, Inc., Leonardo S.p.A, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, Saab AB |
|
Customization |
Comprehensive report customization with purchase. Addition or modification to country, regional & segment scope available |
|
Pricing Details |
Access customized purchase options to meet your specific research requirements. Explore flexible pricing models |
Market Segmentation
The Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market is estimated to be USD 19.4 billion in 2025 and grow at a CAGR of 5.3% to reach USD 32.7 billion by 2035.
In 2024, the Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market was estimated at USD 18.6 billion, with projections to reach USD 19.4 billion in 2025.
Lockheed Martin Corporation, Raytheon Technologies (RTX), Northrop Grumman Corporation, Thales Group, and Leonardo S.p.A. are the major companies operating in the Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market.
The Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth in the Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market, driven by rising defense budgets, indigenous radar development, and heightened regional security tensions.
The Antenna segment under holds the largest share in the Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market, driven by the widespread adoption of AESA technology.
1. Market Definition & Scope
1.1. Market Definition
1.2. Market Ecosystem
1.3. Currency
1.4. Key Stakeholders
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Process of Data Collection and Validation
2.2.1. Secondary Research
2.2.2. Primary Research/Interviews with Key Opinion Leaders from the Industry
2.3. Market Sizing and Forecast
2.3.1. Market Size Estimation Approach
2.3.1.1. Bottom-up Approach
2.3.1.2. Top-down Approach
2.3.2. Growth Forecast Approach
2.3.3. Assumptions for the Study
3. Executive Summary
3.1. Overview
3.2. Segmental Analysis
3.2.1. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market, by Component
3.2.2. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market, by Frequency
3.2.3. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market, by Range
3.2.4. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market, by Platform
3.2.5. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market, by Application
3.2.6. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market, by Region
3.3. Competitive Landscape
3.4. Strategic Recommendations
4. Market Insights
4.1. Overview
4.2. Factors Affecting Market Growth
4.2.1. Drivers
4.2.1.1. AI integration enhances radar accuracy and multi-target tracking
4.2.1.2. Rising drone and hypersonic threats drive radar modernization
4.2.1.3. Multi-domain operations require interoperable and scalable radar systems
4.2.2. Restraints
4.2.2.1. High development and procurement costs
4.2.2.2. Environmental interference reduces radar performance in certain terrains
4.2.3. Opportunities
4.2.3.1. Counter-drone and counter-hypersonic radar capabilities
4.2.3.2. Space-based and multi-domain radar integration
4.2.4. Trends
4.2.4.1. AI and machine learning integration in radar processing
4.2.4.2. Growth of quantum radar research for counter-stealth detection
4.2.5. Challenges
4.2.5.1. Supply chain constraints for GaN and high-performance chips
4.2.5.2. Increasing vulnerability to advanced electronic warfare tactics
4.3. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
4.3.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.3.2. Bargaining Power of Buyers
4.3.3. Threat of Substitutes
4.3.4. Threat of New Entrants
4.3.5. Degree of Competition
4.4. Technology Impact on the Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market
4.4.1. Multi-Band and Multi-Mission Capability
4.4.1.1. Integration of radars operating across multiple frequency bands (S, X, L, and Ku) for layered defense and improved target discrimination.
4.4.1.2. Deployment of multi-mission radars capable of air surveillance, missile tracking, counter-drone operations, and artillery spotting within a single platform.
4.4.2. AI-Enhanced Signal Processing and Automation
4.4.2.1. Use of AI/ML algorithms for automated target recognition, clutter suppression, and trajectory prediction in high-threat environments.
4.4.2.2. Implementation of adaptive beamforming and dynamic resource allocation to optimize radar performance in real time.
4.4.3. Advanced Materials and Power Technologies
4.4.3.1. Adoption of gallium nitride (GaN) transmit/receive modules to increase range, reduce power consumption, and enhance thermal performance.
4.4.3.2. Development of lightweight composite materials for antennas to improve mobility and reduce radar cross-section
5. Impact of Sustainability on Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market
5.1. Energy-Efficient Radar Designs Reducing Operational Carbon Footprint
5.2. Adoption of Recyclable and Lightweight Composite Materials in Antenna Structures
5.3. Lifecycle Management and Upgradeability to Extend System Service Life
5.4. Reduced Hazardous Material Use in Electronics and Power Modules
5.5. ESG-Driven Procurement Policies in Defense Contracts
5.6. Optimization of Manufacturing Processes to Minimize Waste and Emissions
5.7. Integration of Renewable Energy Sources for Remote Radar Installations
6. Competitive Landscape
6.1. Overview
6.2. Key Growth Strategies
6.3. Competitive Benchmarking
6.4. Competitive Dashboard
6.4.1. Industry Leaders
6.4.2. Market Differentiators
6.4.3. Vanguards
6.4.4. Contemporary Stalwarts
6.5. Market Share/Ranking Analysis, by Key Players, 2024
7. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market Assessment—By Component
7.1. Overview
7.2. Transmitter
7.3. Antenna
7.4. Receiver
7.5. Duplexer
7.6. Others
8. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market Assessment—By Frequency
8.1. Overview
8.2. HF-Band
8.3. C-Band
8.4. S-Band
8.5. X-Band
8.6. L-Band
8.7. UHF/VHF
8.8. Ku/K/Ka-Band
8.9. Multi-Band Systems
9. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market Assessment—By Range
9.1. Overview
9.2. Long
9.3. Medium
9.4. Short
9.5. Very Short
10. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market Assessment—By Platform
10.1. Overview
10.2. Airborne Radar
10.3. Land Radar
10.4. Naval Radar
10.5. Space Radar
11. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market Assessment—By Application
11.1. Overview
11.2. Weapon Guidance
11.3. Airspace Monitoring & Traffic Management
11.4. Airborne Mapping
11.5. Ground Surveillance & Intruder Detection
11.6. Navigation
11.7. Others
12. Next-Generation Military Radar Systems Market Assessment—By Geography
12.1. Overview
12.2. North America
12.2.1. U.S.
12.2.2. Canada
12.3. Europe
12.3.1. Germany
12.3.2. U.K.
12.3.3. France
12.3.4. Netherlands
12.3.5. Switzerland
12.3.6. Rest of Europe
12.4. Asia-Pacific
12.4.1. China
12.4.2. Japan
12.4.3. South Korea
12.4.4. Taiwan
12.4.5. India
12.4.6. Singapore
12.4.7. Australia
12.4.8. Rest of Asia-Pacific
12.5. Latin America
12.5.1. Brazil
12.5.2. Mexico
12.5.3. Argentina
12.5.4. Rest of Latin America
12.6. Middle East & Africa
12.6.1. UAE
12.6.2. Saudi Arabia
12.6.3. Israel
12.6.4. South Africa
12.6.5. Rest of Middle East & Africa
13. Company Profiles (Business Overview, Financial Overview, Product Portfolio, Strategic Developments, and SWOT Analysis)
13.1. Lockheed Martin Corporation
13.2. RTX Corporation (Raytheon Technologies)
13.3. Northrop Grumman Corporation
13.4. BAE Systems plc
13.5. Thales Group
13.6. Leonardo S.p.A.
13.7. L3Harris Technologies Inc.
13.8. Saab AB
13.9. General Dynamics Corporation
13.10. Honeywell International Inc.
13.11. Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd. (IAI)
13.12. Airbus Defence and Space
13.13. Hensoldt AG
13.14. Indra Sistemas S.A.
13.15. FLIR Systems (Teledyne FLIR)
13.16. Hanwha Systems Co. Ltd.
13.17. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
13.18. Aselsan A.S.
13.19. Elbit Systems Ltd.
13.20. Terma A/S
13.21. Reutech Radar Systems
13.22. CETC (China Electronics Technology Corporation)
13.23. Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL)
13.24. DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation)
13.25. Other Key Players
14. Appendix
14.1. Available Customization
14.2. Related Reports
























Published Date: Oct-2024
Published Date: Aug-2025
Please enter your corporate email id here to view sample report.
Subscribe to get the latest industry updates