Resources
About Us
AI in Defense & Aerospace Market Size, Share, & Forecast by Application (Autonomous Systems, Predictive Maintenance, Intelligence Analysis), Deployment Type, Technology, Platform, and End-User - Global Forecast (2026-2036)
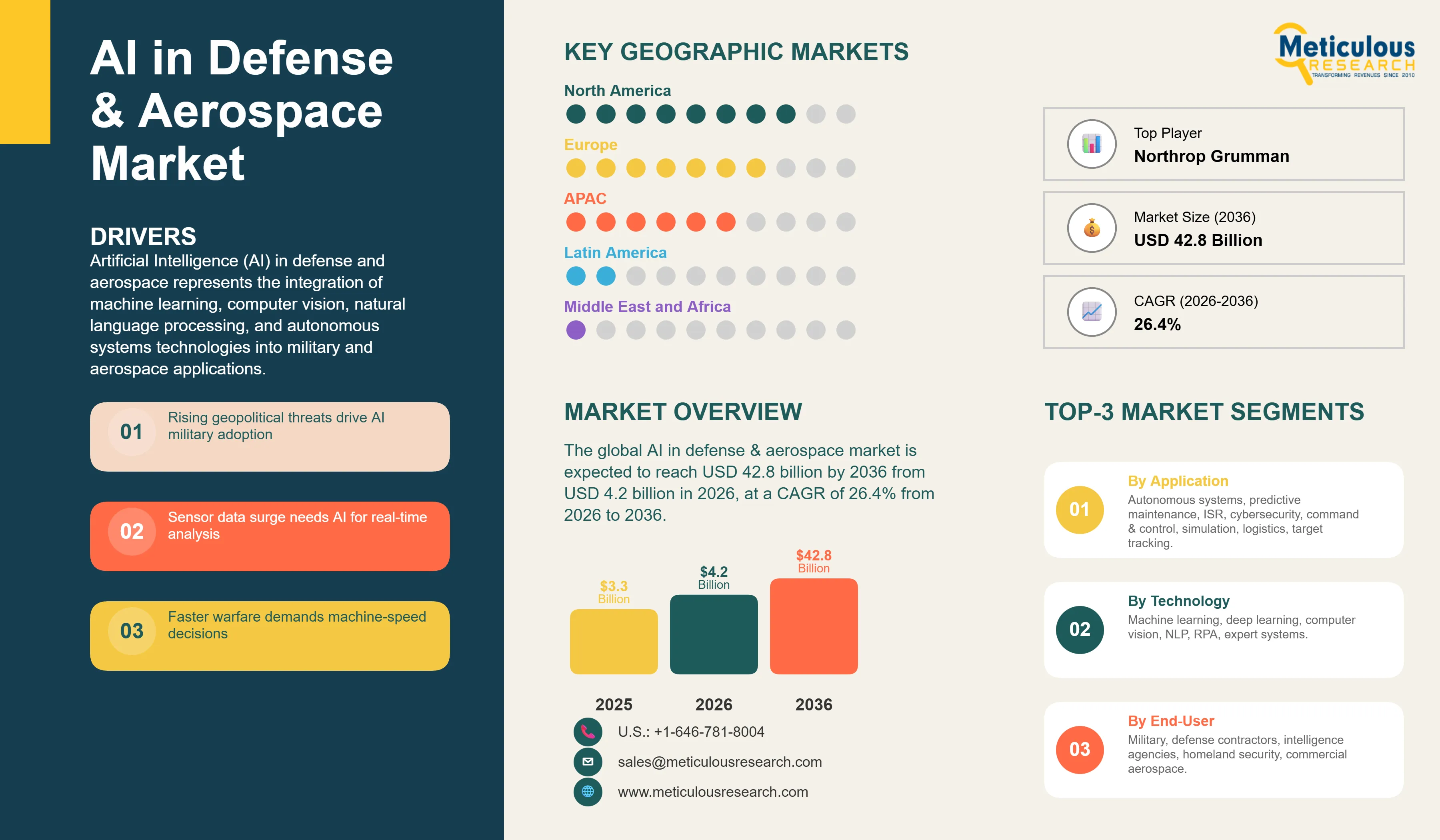
Report ID: MRAD - 1041696 Pages: 296 Jan-2026 Formats*: PDF Category: Aerospace and Defense Delivery: 24 to 72 Hours Download Free Sample ReportThe global AI in defense & aerospace market is expected to reach USD 42.8 billion by 2036 from USD 4.2 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 26.4% from 2026 to 2036.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in defense and aerospace represents the integration of machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing, and autonomous systems technologies into military and aerospace applications. These systems leverage advanced algorithms to process vast amounts of sensor data, enable autonomous decision-making, predict equipment failures, analyze intelligence information, optimize mission planning, and enhance situational awareness. Key applications include autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and ground vehicles capable of navigation and target recognition, predictive maintenance systems that analyze equipment telemetry to prevent failures and optimize logistics, AI-powered intelligence analysis platforms that process satellite imagery, signals intelligence, and open-source data, command and control systems that integrate multi-domain data for rapid decision support, cybersecurity solutions detecting and responding to threats in real-time, and simulation and training platforms providing adaptive learning environments. The technology employs various AI approaches including deep learning neural networks for image and pattern recognition, reinforcement learning for autonomous navigation and decision-making, natural language processing for intelligence analysis and communication systems, edge AI computing enabling real-time processing on deployed platforms, and federated learning allowing model training across distributed systems while maintaining security. These AI systems offer critical advantages including enhanced speed of decision-making in time-sensitive military operations, improved accuracy in target identification and threat assessment reducing civilian casualties, force multiplication allowing smaller units to achieve greater effectiveness, reduced human exposure to dangerous situations through autonomous systems, optimized resource allocation and logistics, and continuous learning and adaptation to evolving threats and environments.
1. In 2026, North America is estimated to account for the largest share of the global AI in defense & aerospace market, driven by massive defense budgets, presence of leading AI defense contractors including Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and Palantir, extensive military AI research programs, and early adoption of autonomous systems across all military branches.
2. Asia-Pacific is projected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period, fueled by rapidly increasing defense budgets in China, India, and Japan, military modernization initiatives, development of domestic AI defense capabilities, territorial security concerns, and government investments in autonomous weapons systems.
3. Based on application, the autonomous systems segment is estimated to hold the largest share of the market in 2026, driven by widespread deployment of military drones, development of autonomous combat vehicles, swarm technology demonstrations, and strategic focus on unmanned capabilities reducing human casualties.
4. Based on deployment type, the cloud-based segment is expected to witness the highest growth during the forecast period, driven by secure military cloud infrastructure development, need for distributed AI training and updates, multi-domain integration requirements, and classified cloud computing initiatives.
5. Based on technology, the machine learning and deep learning segment dominates the market in 2026, representing the most mature and widely deployed AI technology for military applications including image recognition, predictive analytics, and autonomous navigation systems.
6. The intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period, driven by massive volumes of satellite and drone imagery requiring AI analysis, real-time threat detection needs, and fusion of multi-source intelligence data.
7. The military aviation segment accounts for the largest platform share, driven by autonomous fighter jet development programs, AI-enhanced pilot systems, unmanned combat aerial vehicles (UCAVs), and next-generation air combat training systems.
8. The U.S. AI in defense & aerospace market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 24% during the forecast period 2026 to 2036, driven by Department of Defense AI strategy, JAIC (Joint AI Center) initiatives, Silicon Valley defense partnerships, and extensive military AI procurement programs.
9. China is expected to lead the Asia-Pacific AI in defense & aerospace market, driven by aggressive military AI development targets, civil-military fusion strategy, domestic AI technology advancement, large-scale autonomous drone programs, and strategic focus on AI military superiority.
10. In 2026, the U.K. is projected to account for significant share of the European AI in defense & aerospace market, driven by Defence AI Centre establishment, Tempest sixth-generation fighter AI integration, NATO AI cooperation leadership, and BAE Systems AI development programs.
 Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
AI in Defense & Aerospace represents a transformative shift in military capabilities and aerospace operations, fundamentally changing how armed forces conduct operations, make decisions, and maintain technological superiority. Unlike traditional defense systems that rely on pre-programmed responses and human decision-making at every step, AI-enabled systems can process vast amounts of data in real-time, identify patterns humans might miss, make autonomous decisions within defined parameters, and continuously learn and adapt from experience. These systems offer significant strategic advantages, including decision speed measured in milliseconds rather than minutes enabling rapid response to threats, processing capability handling petabytes of sensor and intelligence data impossible for human analysts alone, 24/7 operational availability without fatigue or human limitations affecting performance, and cost-effectiveness allowing force multiplication with fewer personnel. As global military competition intensifies and emerging threats including hypersonic weapons, cyber warfare, and great power competition require faster decision-making and more sophisticated responses, defense establishments worldwide are investing heavily in AI to maintain strategic advantages. This creates substantial market opportunities for AI defense contractors, technology companies entering the defense sector, and nations seeking to develop indigenous AI military capabilities.
Several key trends are reshaping the AI in defense and aerospace market. These include the shift from pilot projects to operational deployment with AI systems moving beyond testing to active military use, development of multi-domain integration connecting AI across air, land, sea, space, and cyber domains for coordinated operations, emphasis on ethical AI and human oversight ensuring autonomous weapons comply with international law and maintain meaningful human control, edge AI deployment enabling processing on deployed platforms without constant connectivity, adversarial AI development both for offensive cyber capabilities and defending against AI-powered threats, and commercial-military technology transfer with defense forces leveraging Silicon Valley innovations while maintaining security requirements. The convergence of increasing global security threats creating demand for advanced capabilities, maturation of AI technologies proving military applicability and reliability, substantial government funding with the U.S. alone investing billions annually, and strategic competition between major powers driving AI military innovation has elevated AI from experimental technology to a core component of defense strategy. This transformation has attracted major technology companies into defense contracts, stimulated startup formation focused on military AI applications, and prompted billions in international defense AI investments.
The AI in defense and aerospace market is transitioning from research and development to operational deployment, with multiple technology applications competing to demonstrate military effectiveness and strategic value. Leading systems are showing increasingly sophisticated capabilities, including real-time autonomous target recognition and engagement within rules of engagement, predictive maintenance reducing aircraft downtime by 25-35% through AI analysis of sensor data, AI-powered intelligence fusion combining imagery, signals, and human intelligence for comprehensive threat assessments, cyber defense systems detecting and responding to attacks at machine speed, and multi-agent coordination enabling drone swarms operating with distributed intelligence. This competition is accelerating innovation as nations and companies race to achieve AI military superiority in what many analysts term a critical technology race.
Autonomous military systems represent the most visible and rapidly advancing application of defense AI. These include unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) like the MQ-9 Reaper and next-generation autonomous combat drones capable of independent navigation, target identification, and engagement decisions within defined parameters. The U.S. Air Force's Skyborg program and similar initiatives in China and Europe are developing AI pilots that can fly fighter jets alongside human pilots, execute complex maneuvers, and make tactical decisions. Ground systems including autonomous tanks and armored vehicles are under development with AI handling navigation, threat detection, and engagement recommendations while maintaining human authorization for lethal force. Naval applications include unmanned surface and underwater vehicles conducting surveillance, mine countermeasures, and offensive operations. These autonomous systems achieve response times under 100 milliseconds for threat detection and engagement, operate continuously without human fatigue limitations, and can undertake missions too dangerous for human personnel. The technology benefits from advances in computer vision enabling reliable target identification, edge computing allowing real-time processing without connectivity, and reinforcement learning improving decision-making through simulation training.
Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) applications leverage AI to process the overwhelming volumes of data modern sensors generate. Military satellites, reconnaissance aircraft, and ground sensors produce petabytes of imagery and signals intelligence that exceed human analyst capacity. AI-powered systems can automatically scan satellite imagery to detect military installations, vehicle movements, and infrastructure changes, analyze patterns in communications intercepts, correlate data from multiple intelligence sources, and identify anomalies indicating potential threats. The U.S. Project Maven, initiated in 2017, pioneered AI for analyzing drone video footage, achieving 70-80% accuracy in identifying vehicles and objects while reducing analyst workload by orders of magnitude. Similar systems are now processing synthetic aperture radar imagery, identifying ships at sea, monitoring troop movements, and tracking ballistic missile launches. These capabilities provide commanders with real-time situational awareness previously impossible, enable predictive intelligence forecasting enemy movements, and allow small intelligence teams to achieve coverage previously requiring large analyst pools. Commercial satellite companies including Planet Labs and Maxar are partnering with military intelligence to provide AI-analyzed imagery at unprecedented scale and frequency.
|
Parameter |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2026 |
USD 4.2 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2036 |
USD 42.8 Billion |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 26.4% from 2026 to 2036 |
|
Base Year for Estimation |
2025 |
|
Historical Data |
2020-2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2036 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Segments Covered |
Application, Deployment Type, Technology, Platform, End-User, Geography |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon Technologies, Boeing, BAE Systems, Palantir Technologies, Anduril Industries, Shield AI, General Dynamics, L3Harris Technologies, Thales Group, Leonardo S.p.A., CACI International, Booz Allen Hamilton, and others |
Escalating Global Security Threats and Military Modernization: Rising geopolitical tensions, particularly U.S.-China strategic competition, regional conflicts in Eastern Europe and Indo-Pacific, terrorism threats, and cyber warfare are driving massive military modernization programs worldwide. The U.S. Department of Defense has designated AI as a critical technology for maintaining military superiority, while China has announced goals to become the global AI leader by 2030 with explicit military applications. Russia, India, Israel, and European nations are similarly investing billions in AI defense capabilities. This competitive environment creates sustained demand for AI systems providing strategic advantages.
Data Volume Overwhelming Human Processing Capacity: Modern military sensors generate massive data volumes. A single Reaper drone produces 1,000 hours of video footage daily. Satellite constellations image entire continents every day. Signals intelligence systems monitor billions of communications. Human analysts cannot process this information volume, creating critical intelligence gaps. AI systems can analyze imagery at rates 100,000 times faster than humans, identify patterns across disparate data sources, and provide alerts on significant events in real-time. This capability transforms raw data into actionable intelligence, making AI essential for effective military operations.
Speed of Modern Warfare Requiring Automated Decisions: Hypersonic missiles traveling at Mach 5+ provide only minutes of warning time. Electronic warfare and cyber attacks operate at milliseconds. Adversary autonomous systems make decisions at machine speed. Human decision-making speeds are insufficient for these threats. AI systems can detect, analyze, and respond to threats orders of magnitude faster than human operators while providing decision support for complex scenarios. This speed advantage is critical for missile defense, electronic warfare, and air combat, driving adoption across all military domains.
Ethical Concerns and International Regulations: Autonomous weapons raise significant ethical questions about machines making life-or-death decisions. The United Nations has debated lethal autonomous weapons systems (LAWS) regulations since 2014. International humanitarian law requires maintaining meaningful human control over use of force. Public opposition to "killer robots" influences policy decisions. These concerns slow deployment, require extensive testing and oversight mechanisms, and may limit certain applications. Defense organizations must balance operational advantages with ethical considerations and international law compliance.
High Development Costs and Integration Complexity: Developing military-grade AI systems requires specialized expertise, extensive testing, security certification, and integration with legacy systems. Costs for AI programs can reach hundreds of millions or billions of dollars. The F-35 fighter program has spent over $500 million on AI pilot assistant development alone. Integration with existing command and control systems, communication networks, and weapons platforms involves significant technical challenges. Small and medium defense budgets may struggle to afford cutting-edge AI capabilities, potentially creating technological disparities between nations.
Adversarial AI and Vulnerability Concerns: AI systems face unique vulnerabilities including adversarial attacks that fool classifiers with subtle input modifications, data poisoning corrupting training data, and spoofing creating false sensor inputs. Military AI must operate in contested environments with adversaries actively attempting to defeat these systems. Ensuring robustness and security of AI systems against sophisticated attacks requires extensive red-team testing, adversarial training, and defense mechanisms. These security requirements increase complexity and development time while creating uncertainty about system reliability in combat.
Commercial AI Technology Transfer to Defense: The commercial AI sector has achieved breakthrough capabilities in natural language processing, computer vision, and autonomous systems. Defense organizations are increasingly partnering with technology companies to leverage these advances. The U.S. Department of Defense's Defense Innovation Unit works with Silicon Valley startups. Commercial satellite imagery companies provide AI-analyzed intelligence. Cloud computing giants offer secure AI infrastructure. This technology transfer accelerates military AI development, reduces costs through dual-use technologies, and opens markets for commercial companies entering defense sector.
International AI Defense Cooperation: Allied nations are increasingly cooperating on AI defense development to share costs, establish interoperability, and counter adversary AI capabilities. NATO is developing AI standards and sharing frameworks. The AUKUS partnership between Australia, UK, and U.S. includes AI cooperation. European defense initiatives like FCAS (Future Combat Air System) incorporate collaborative AI development. These partnerships create markets for AI systems deployable across multiple nations, reduce individual development costs, and establish common standards benefiting contractors serving allied militaries.
Edge AI and Autonomous Operations in Contested Environments: Future military operations will increasingly occur in environments where communication with command centers is degraded or denied. Edge AI enables autonomous systems to operate independently with processing on-board the platform rather than requiring constant connectivity. This capability is critical for operations in GPS-denied environments, electronic warfare scenarios, and deep strike missions. Development of low-power, high-performance edge AI chips and algorithms enables new classes of autonomous systems previously impossible, creating opportunities for specialized AI hardware and software providers.
The AI in defense & aerospace market is expected to grow from USD 4.2 billion in 2026 to USD 42.8 billion by 2036.
The AI in defense & aerospace market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 26.4% from 2026 to 2036.
Major players include Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon Technologies, Boeing, BAE Systems, Palantir Technologies, Anduril Industries, Shield AI, General Dynamics, L3Harris Technologies, Thales Group, Leonardo, CACI International, and Booz Allen Hamilton, among others.
Main factors include escalating global security threats and military modernization programs, massive data volumes requiring AI processing, speed requirements of modern warfare, autonomous systems development for force multiplication, predictive maintenance cost savings, and government investments in military AI capabilities.
North America is estimated to account for the largest share in 2026 due to massive defense budgets and leading AI defense contractors, while Asia-Pacific is expected to register the highest growth rate during 2026-2036 driven by China and India's military modernization.
1. Introduction
1.1. Market Definition
1.2. Market Segmentation
1.3. Research Methodology
2. Executive Summary
2.1. Key Findings
2.2. Market Size and Growth
2.3. Competitive Landscape
3. Market Dynamics
3.1. Drivers
3.2. Restraints
3.3. Opportunities
3.4. Challenges
4. Technology Landscape
4.1. AI Technology Evolution in Defense
4.2. Key Technology Developments
4.3. Patent Analysis
5. Regulatory Framework
5.1. International Laws and Treaties
5.2. National AI Defense Strategies
5.3. Ethical Guidelines
6. Value Chain Analysis
6.1. Component Suppliers
6.2. Technology Developers
6.3. System Integrators
6.4. End Users
7. Global AI in Defense & Aerospace Market, by Application
7.1. Introduction
7.2. Autonomous Systems
7.2.1. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
7.2.2. Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs)
7.2.3. Unmanned Maritime Systems
7.2.4. Drone Swarm Technology
7.3. Predictive Maintenance
7.3.1. Aircraft Fleet Management
7.3.2. Vehicle and Equipment Maintenance
7.3.3. Naval Systems Maintenance
7.4. Intelligence, Surveillance & Reconnaissance (ISR)
7.4.1. Image and Video Analysis
7.4.2. Signals Intelligence (SIGINT)
7.4.3. Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT)
7.4.4. Multi-Intelligence Fusion
7.5. Cybersecurity and Threat Detection
7.6. Command and Control Systems
7.7. Simulation and Training
7.8. Logistics and Supply Chain Optimization
7.9. Target Recognition and Tracking
8. Global AI in Defense & Aerospace Market, by Deployment Type
8.1. Introduction
8.2. On-Premise
8.2.1. Classified Network Deployments
8.2.2. Tactical Edge Computing
8.3. Cloud-Based
8.3.1. Secure Military Cloud
8.3.2. Commercial Cloud Integration
8.4. Hybrid
9. Global AI in Defense & Aerospace Market, by Technology
9.1. Introduction
9.2. Machine Learning and Deep Learning
9.2.1. Supervised Learning
9.2.2. Unsupervised Learning
9.2.3. Reinforcement Learning
9.3. Computer Vision
9.4. Natural Language Processing
9.5. Robotic Process Automation
9.6. Expert Systems
10. Global AI in Defense & Aerospace Market, by Platform
10.1. Introduction
10.2. Airborne
10.2.1. Fighter Aircraft
10.2.2. Military Helicopters
10.2.3. Transport Aircraft
10.2.4. UAVs and Drones
10.3. Land-Based
10.3.1. Armored Vehicles
10.3.2. Artillery Systems
10.3.3. Ground Support Systems
10.4. Naval
10.4.1. Warships and Submarines
10.4.2. Unmanned Surface Vessels
10.4.3. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles
10.5. Space-Based
10.6. Ground Stations and Command Centers
11. Global AI in Defense & Aerospace Market, by End-User
11.1. Introduction
11.2. Military
11.2.1. Army
11.2.2. Navy
11.2.3. Air Force
11.2.4. Space Force
11.3. Defense Contractors and OEMs
11.4. Intelligence Agencies
11.5. Homeland Security
11.6. Commercial Aerospace
12. AI in Defense & Aerospace Market, by Geography
12.1. Introduction
12.2. North America
12.2.1. U.S.
12.2.2. Canada
12.3. Europe
12.3.1. U.K.
12.3.2. Germany
12.3.3. France
12.3.4. Italy
12.3.5. Spain
12.3.6. Rest of Europe
12.4. Asia-Pacific
12.4.1. China
12.4.2. India
12.4.3. Japan
12.4.4. South Korea
12.4.5. Australia
12.4.6. Rest of Asia-Pacific
12.5. Middle East & Africa
12.5.1. Israel
12.5.2. Saudi Arabia
12.5.3. UAE
12.5.4. South Africa
12.5.5. Rest of Middle East & Africa
12.6. Latin America
12.6.1. Brazil
12.6.2. Mexico
12.6.3. Rest of Latin America
13. Competitive Landscape
13.1. Introduction
13.2. Market Share Analysis
13.3. Competitive Benchmarking
13.4. Key Strategic Developments
14. Company Profiles
(Business Overview, Financial Overview, Product Portfolio, Strategic Developments, SWOT Analysis)
14.1. Lockheed Martin Corporation
14.2. Northrop Grumman Corporation
14.3. Raytheon Technologies Corporation
14.4. The Boeing Company
14.5. BAE Systems plc
14.6. Palantir Technologies Inc.
14.7. Anduril Industries Inc.
14.8. Shield AI
14.9. General Dynamics Corporation
14.10. L3Harris Technologies Inc.
14.11. Thales Group
14.12. Leonardo S.p.A.
14.13. CACI International Inc.
14.14. Booz Allen Hamilton Inc.
14.15. Saab AB
14.16. Elbit Systems Ltd.
14.17. Leidos Holdings Inc.
14.18. SparkCognition Inc.
14.19. C3.ai Inc.
14.20. IBM Corporation
14.21. Others
15. Appendix
15.1. Questionnaire
15.2. Available Customization
























Published Date: Sep-2025
Please enter your corporate email id here to view sample report.
Subscribe to get the latest industry updates