Resources
About Us
Rare Disease Diagnostics Market by Test Type (Genetic Testing, Biochemical Testing, Imaging Diagnostics), Disease Type (Neurological Disorders, Metabolic Disorders), Technology (Sequencing Technologies, PCR-based Technologies), Sample Type, and End User - Global Forecast to 2035
Report ID: MRHC - 1041637 Pages: 413 Dec-2025 Formats*: PDF Category: Healthcare Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours Download Free Sample ReportRare Disease Diagnostics Market Size & Forecast
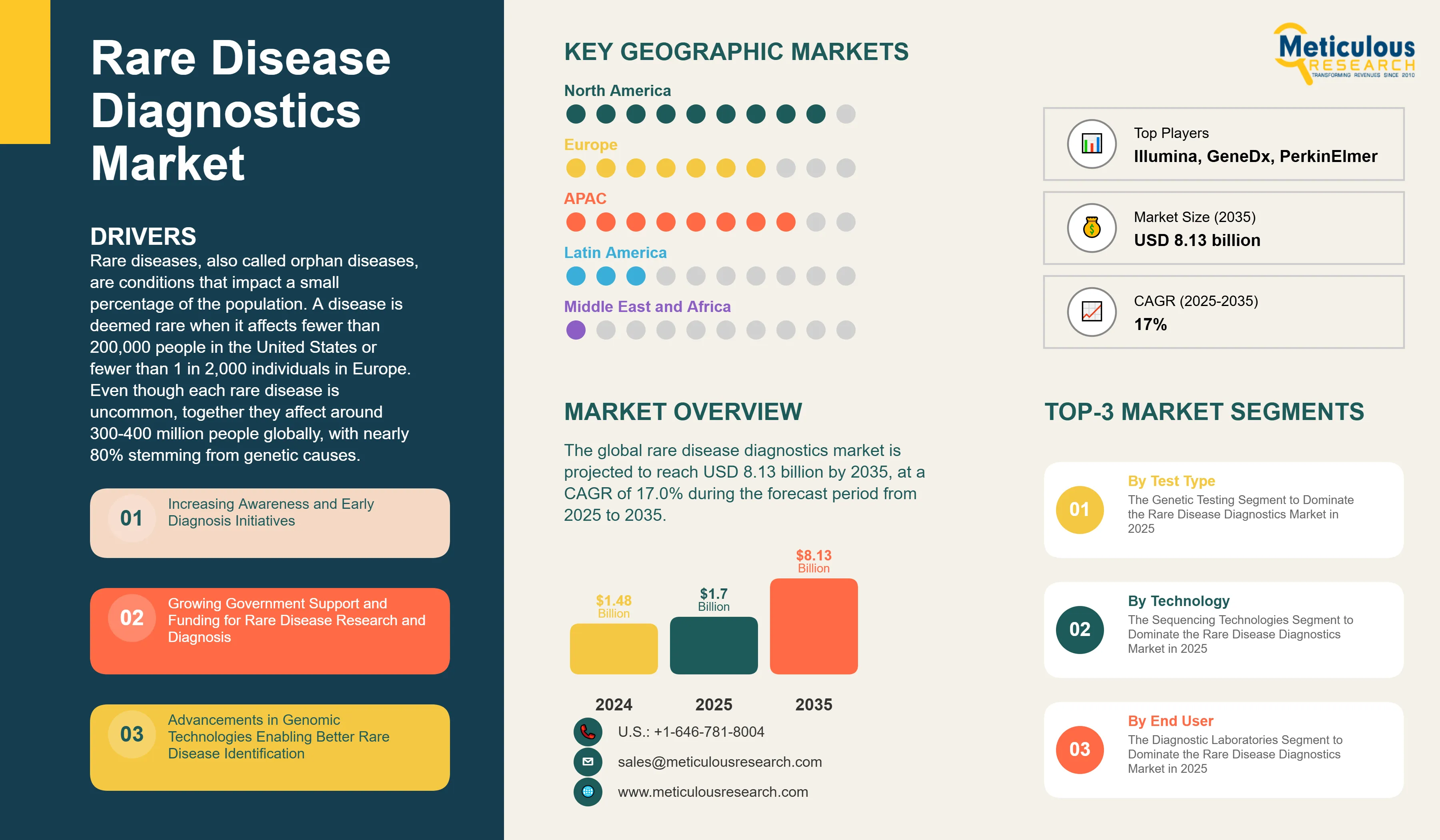
The global rare disease diagnostics market was valued at USD 1.48 billion in 2024. This market is projected to reach USD 8.13 billion by 2035 from an estimated USD 1.70 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 17.0% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2035.
Rare diseases, also called orphan diseases, are conditions that impact a small percentage of the population. A disease is deemed rare when it affects fewer than 200,000 people in the United States or fewer than 1 in 2,000 individuals in Europe. Even though each rare disease is uncommon, together they affect around 300-400 million people globally, with nearly 80% stemming from genetic causes. Diagnosing rare diseases involves various testing methods, such as genetic testing, biochemical testing, and imaging diagnostics. These methods help accurately identify and understand these conditions.
Key factors driving this market include rising awareness and efforts for early diagnosis of rare diseases, increased government support and funding for research and diagnosis, improvements in genomic technologies that help identify rare diseases better, a growing number of rare genetic disorders worldwide, and the rising use of next-generation sequencing in clinical settings. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential as it can significantly shorten the diagnostic journey, which often takes 5-7 years, and allow for timely treatment, genetic counseling, and family planning.
The dramatic drop in the cost of DNA sequencing technologies over the past two decades—from about $100 million per genome in 2001 to under $1,000 now—has made thorough genomic testing affordable for clinical use. The shift from single-gene testing to comprehensive genomic analysis has significantly changed how we diagnose rare diseases. This new approach allows for the simultaneous evaluation of thousands of genes and greatly improves diagnostic outcomes.
With the growth of newborn screening programs around the world, a heightened focus on precision medicine and personalized treatment, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in diagnostics, and better healthcare systems in emerging markets, the rare disease diagnostics market is expected to grow significantly. This growth is driven by the need for early detection, accurate molecular characterization, and treatment guidance in an increasingly complicated landscape of rare diseases.
Key Findings
Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
Increasing Awareness and Early Diagnosis Initiatives
Increasing awareness and early diagnosis efforts for rare diseases drive the rare disease diagnostics market. Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 to 400 million people globally. However, the combined burden of over 7,000 identified rare diseases creates significant healthcare challenges and diagnostic needs. Growing awareness among healthcare professionals and the public is reducing the lengthy diagnostic journey that rare disease patients have historically faced.
Rare Disease Day, which takes place annually on the last day of February, has expanded to over 100 countries since it started in 2008. This day raises awareness about rare diseases and highlights the importance of early diagnosis. Patient advocacy organizations are crucial for education; they provide resources for patients, families, and healthcare providers while pushing for better diagnostic access. These organizations have become influential in raising awareness and promoting policy changes to enhance rare disease diagnosis and treatment.
Education initiatives for healthcare professionals are improving the recognition of rare diseases and the proper use of testing. Medical schools and continuing education programs are increasingly including rare disease content. This helps clinicians identify clinical patterns that suggest rare diseases and understand the diagnostic options available. Pediatricians, geneticists, and other specialists are becoming more aware of the signs that warrant genetic evaluation.
Early diagnosis initiatives stress the importance of quick molecular diagnosis to enable timely treatments. For many rare diseases, diagnosing early—before irreversible complications set in—greatly improves outcomes. Newborn screening programs are examples of effective early diagnosis strategies. They identify affected infants before symptoms appear, allowing for pre-symptomatic treatment. Expanding newborn screening panels and better screening methods are helping to detect more conditions earlier.
Clinical decision support tools that include rare disease differential diagnoses assist clinicians in considering rare diseases when assessing patients with unexplained symptoms. Computerized systems can alert doctors to possible rare diseases based on symptom patterns, lab findings, and clinical features. These tools help reduce missed diagnoses by encouraging consideration of conditions that clinicians might not think of otherwise. Telemedicine and virtual consultations also broaden access to rare disease expertise, allowing patients in underserved areas to consult with specialized geneticists and rare disease experts remotely.
Growing Government Support and Funding for Rare Disease Research and Diagnosis
Growing government support and funding for rare disease research and diagnosis drive market growth. Governments around the world are recognizing rare diseases as public health priorities. They are putting policies in place and allocating resources to improve diagnosis, treatment, and research. In the United States, the Orphan Drug Act of 1983 set up a system to encourage the development of therapies for rare diseases. It created the need for precise molecular diagnoses, which are often necessary to access targeted orphan drugs.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) provides significant funding for rare disease research, exceeding $5 billion each year across various institutes. These funds support gene discovery, natural history studies, and the development of diagnostic methods. The NIH Undiagnosed Diseases Network showcases government investment in rare disease diagnosis. This network employs advanced genomic and phenotyping techniques to solve complex diagnostic cases. It has diagnosed hundreds of previously undiagnosed patients and identified many new disease genes, which enhances knowledge about rare diseases and aids future diagnostic efforts.
European governments are prioritizing rare diseases through coordinated initiatives. The European Union Rare Disease Action Program offers a framework for activities among member states. Many countries in Europe have developed national rare disease plans that outline strategies for diagnosis, treatment, research, and care coordination. These plans often include provisions for diagnostic access, specialized reference centers, and patient registries.
Asian nations are also increasing their investments in rare diseases. China has started initiatives focused on the development of diagnostics and therapies for rare diseases. Japan offers subsidies for rare disease diagnostics and treatments for specific conditions. India is creating policies addressing access to diagnosis and treatment for rare diseases. Government funding supports patient registries and natural history studies, which collect systematic data on disease manifestations, progression, and outcomes.
Public health newborn screening programs represent significant government investments in the early diagnosis of rare diseases. State and national programs screen millions of infants each year for treatable conditions using modern diagnostic technologies. The substantial and increasing government funding for rare disease research, diagnostic infrastructure, patient registries, and screening programs strongly supports market growth.
Rare Disease Diagnostics Market Opportunity
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Rare Disease Diagnosis
Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications in rare disease diagnosis present significant technological opportunities. They improve diagnostic capabilities, boost efficiency, and increase access to expertise. AI algorithms can analyze complex clinical and genomic data, recognize subtle patterns, and support diagnostic decision-making in ways that complement human abilities.
Facial recognition systems using deep learning identify distinct facial features linked to genetic syndromes. These AI tools examine patient photographs and suggest possible diagnoses based on facial characteristics. This helps clinicians consider relevant rare diseases they might not have thought about. Diagnostic accuracy for well-known syndromes with clear facial features is similar to or even better than that of experienced clinical geneticists. Tools like Face2Gene have been trained on thousands of images covering hundreds of genetic syndromes. Clinicians around the world use them as diagnostic aids.
Variant interpretation greatly benefits from machine learning. Figuring out whether genetic variants found through sequencing are harmful, harmless, or uncertain is a major challenge. Machine learning algorithms bring together various sources of evidence, including population allele frequencies, predictions from computational tools, conservation scores, and phenotype data to classify variants. These tools enhance interpretation consistency across laboratories and help manage the significant issue of uncertain significance variants.
Clinical decision support systems that use AI help with rare disease diagnosis by analyzing clinical features and proposing differential diagnoses. These systems can evaluate patient symptoms, physical examination results, lab results, and imaging data to create lists of possible rare diseases for doctors to consider. By widening the differential diagnosis, these tools help reduce missed diagnoses and shorten diagnostic journeys.
Natural language processing applied to electronic health records and medical literature supports rare disease identification. NLP algorithms can pull relevant clinical information from unstructured text, spot patterns that indicate rare diseases, and link patient characteristics to disease descriptions in databases. Phenotype matching algorithms use AI to compare clinical features of patients with databases that describe known genetic diseases, allowing for effective matching between patient characteristics and disease-related profiles.
Rare Disease Diagnostics Market Analysis: Top Market Opportunities
By Test Type: The Genetic Testing Segment to Dominate the Rare Disease Diagnostics Market in 2025
Based on test type, the rare disease diagnostics market is segmented into genetic testing, biochemical testing, imaging diagnostics, and other diagnostic tests. In 2025, the genetic testing segment is expected to account for the largest share of ~81.0% of the rare disease diagnostics market. The large share of this segment is attributed to the genetic etiology of approximately 80% of rare diseases, dramatic cost reductions in DNA sequencing technologies over the past two decades, expanding clinical adoption of comprehensive genomic testing approaches, and growing insurance coverage for genetic diagnostic procedures.
The evolution from single-gene sequential testing to comprehensive genomic analysis has fundamentally transformed rare disease diagnostic paradigms, enabling simultaneous evaluation of thousands of genes and improving diagnostic yields substantially. Within the genetic testing segment, next-generation sequencing is expected to dominate, driven by its ability to simultaneously analyze multiple genes or entire genomes, providing comprehensive diagnostic information.
Moreover, the genetic testing segment is also expected to register the highest CAGR of 18.3% during the forecast period of 2025–2035, driven by continuous technological improvements in sequencing platforms delivering enhanced accuracy and throughput, increasing physician comfort with ordering comprehensive genetic tests, expanding evidence base demonstrating clinical utility and cost-effectiveness, and rising insurer acceptance based on demonstrated diagnostic value.
By Disease Type: The Neurological Disorders Segment to Dominate the Rare Disease Diagnostics Market in 2025
Based on disease type, the rare disease diagnostics market is segmented into neurological disorders, metabolic disorders, hematological disorders, immunological disorders, endocrine disorders, cardiovascular disorders, and other rare diseases. In 2025, the neurological disorders segment is expected to account for the largest share of ~32% of the rare disease diagnostics market. The segment's large share is attributed to neurological rare diseases frequently having a strong genetic basis, disorders such as epilepsy syndromes, neuromuscular disorders, leukodystrophies, and mitochondrial disorders having highly heterogeneous presentations making advanced diagnostics essential, and high diagnostic odyssey rates leading clinicians to rely more heavily on specialized genomic and metabolic testing.
Moreover, this segment is also expected to register the highest CAGR of 20% during the forecast period, driven by accelerating adoption of next-generation sequencing, exome sequencing, and targeted gene panels for neurological conditions.
By Technology: The Sequencing Technologies Segment to Dominate the Rare Disease Diagnostics Market in 2025
Based on technology, the rare disease diagnostics market is segmented into sequencing technologies, PCR-based technologies, microarray technologies, mass spectrometry, immunoassays, and other technologies. In 2025, the sequencing technologies segment is expected to account for the largest share of ~58% of the rare disease diagnostics market. The large share is attributed to the capability for comprehensive genetic analysis enabling simultaneous evaluation of thousands of genes, dramatic cost reductions making sequencing economically feasible for clinical applications (costs declining from approximately $3 billion per genome in 2003 to under $1,000 currently), detection of virtually all variant types, and expanding clinical evidence demonstrating diagnostic utility and cost-effectiveness.
The transformation from research tool to routine clinical diagnostic has fundamentally altered rare disease diagnostic paradigms. Moreover, the sequencing technologies segment is also expected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period, driven by continuous technological improvements, accumulating clinical evidence, expanding insurance coverage, and integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning enhancing variant interpretation.
By Sample Type: The Blood Samples Segment to Dominate the Rare Disease Diagnostics Market in 2025
Based on sample type, the rare disease diagnostics market is segmented into blood samples, urine samples, saliva samples, tissue samples, amniotic fluid, and other sample types. In 2025, the blood samples segment is expected to account for the largest share of the rare disease diagnostics market. The large share is attributed to blood samples' versatility supporting the broadest range of diagnostic testing approaches including genetic testing from DNA extracted from leukocytes, biochemical testing from plasma or serum, hematological testing from whole blood, and immunological testing from various blood components.
Well-established infrastructure for blood collection exists in healthcare facilities from tertiary medical centers to primary care clinics. Blood contains or reflects information about virtually all organ systems, making it suitable for diagnosing diverse systemic diseases. Moreover, this segment is also expected to register the highest CAGR of during the forecast period, driven by expanding applications of blood-based genetic testing, growing adoption of dried blood spot sampling, and technological advances enabling extraction of more information from smaller blood volumes.
By End User: The Diagnostic Laboratories Segment to Dominate the Rare Disease Diagnostics Market in 2025
Based on end user, the rare disease diagnostics market is segmented into diagnostic laboratories, hospital laboratories, academic & research institutes, pharmaceutical & biotechnology companies, and other end users. In 2025, the diagnostic laboratories segment is expected to account for the largest share of ~52% of the rare disease diagnostics market. The large share is attributed to diagnostic laboratories' role as specialized reference facilities concentrating rare disease testing expertise that individual hospitals cannot economically maintain, achievement of economies of scale through sample aggregation from multiple healthcare systems, substantial investments in advanced technologies including latest-generation sequencing platforms, and employment of specialized personnel including medical geneticists, genetic counselors, and metabolic specialists.
Moreover, this segment is also expected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period, driven by increasing test referrals from hospitals and clinics, expanding test menus, and growing adoption of comprehensive genomic testing.
Geographical Analysis
North America Dominates the Rare Disease Diagnostics Market in 2025
Based on geography, the global rare disease diagnostics market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. In 2025, North America is expected to account for the largest share of ~46% of the global rare disease diagnostics market.
The large market share of North America is attributed to the region's most developed rare disease testing infrastructure including leading genetic testing companies and advanced academic medical centers, comprehensive newborn screening programs testing approximately 3.8 million infants annually in the United States alone, expanding insurance coverage for genetic testing removing financial barriers to access, substantial government research funding through the National Institutes of Health exceeding $5 billion annually for rare disease research, and favorable regulatory environment for orphan drug development creating diagnostic demand.
The region benefits from well-established reimbursement frameworks compared to other regions, high healthcare expenditure enabling adoption of advanced diagnostic technologies, and concentration of pharmaceutical companies developing rare disease therapeutics requiring companion diagnostics.
However, Asia-Pacific is expected to register the highest CAGR of 22.7% during the forecast period. The rapid growth is driven by rapid healthcare infrastructure development in major economies particularly China and India, rising middle-class populations with increasing healthcare purchasing power, government investments in genomics and precision medicine programs, expanding insurance coverage improving diagnostic access, increasing awareness of genetic diseases and available testing, and large population bases creating substantial absolute numbers of rare disease patients despite lower per-capita prevalence.
Key Companies
Major companies in the global rare disease diagnostics market have implemented various strategies to expand their product offerings and augment their market shares. The key strategies followed by most companies include partnerships, agreements & collaborations, product launches & enhancements, and expansions. Partnerships and collaborations accounted for a major share of strategic developments from key players between 2023 and 2025.
Some of the prominent players operating in the global rare disease diagnostics market include Illumina, Inc. (U.S.), Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (U.S.), F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Switzerland), QIAGEN N.V. (Netherlands), PerkinElmer, Inc. (U.S.), Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (U.S.), Agilent Technologies, Inc. (U.S.), CENTOGENE N.V. (Germany), GeneDx, LLC (U.S.), Invitae Corporation (U.S.), Blueprint Genetics (Finland/U.S.), Eurofins Scientific (Luxembourg), Fulgent Genetics, Inc. (U.S.), OPKO Health, Inc. (U.S.), and Strand Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd. (India).
Rare Disease Diagnostics Market Industry Overview: Latest Developments from Key Industry Players
|
Particulars |
Details |
|
Number of Pages |
413 |
|
Format |
|
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2035 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
CAGR (Value) |
17.0% |
|
Market Size (Value) in 2025 |
USD 1.70 billion |
|
Market Size (Value) in 2035 |
USD 8.13 billion |
|
Segments Covered |
By Test Type
|
|
Countries Covered |
North America (U.S., Canada), Europe (Germany, France, U.K., Italy, Spain, and Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, Australia, South Korea, and Rest of Asia-Pacific), Latin America (Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, and Rest of Latin America), and the Middle East & Africa (Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, and Rest of Middle East & Africa) |
|
Key Companies |
Illumina, Inc. (U.S.), Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (U.S.), F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Switzerland), QIAGEN N.V. (Netherlands), PerkinElmer, Inc. (U.S.), Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (U.S.), Agilent Technologies, Inc. (U.S.), CENTOGENE N.V. (Germany), GeneDx, LLC (U.S.), Invitae Corporation (U.S.), Blueprint Genetics (Finland/U.S.), Eurofins Scientific (Luxembourg), Fulgent Genetics, Inc. (U.S.), OPKO Health, Inc. (U.S.), and Strand Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd. (India) |
The global rare disease diagnostics market size is projected to reach USD 1.70 billion in 2025.
The market is projected to grow from USD 1.70 billion in 2025 to USD 8.13 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of 17.0%.
The rare disease diagnostics market analysis indicates substantial growth, with projections indicating the market will reach USD 8.13 million by 2035, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.0% from 2025 to 2035.
The key companies operating in this market include Illumina, Inc. (U.S.), Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (U.S.), F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Switzerland), QIAGEN N.V. (Netherlands), PerkinElmer, Inc. (U.S.), Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (U.S.), Agilent Technologies, Inc. (U.S.), CENTOGENE N.V. (Germany), GeneDx, LLC (U.S.), Invitae Corporation (U.S.), Blueprint Genetics (Finland/U.S.), Eurofins Scientific (Luxembourg), Fulgent Genetics, Inc. (U.S.), OPKO Health, Inc. (U.S.), and Strand Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd. (India).
Integration of genomic sequencing into newborn screening, artificial intelligence and machine learning in rare disease diagnosis, and expanding focus on precision medicine and personalized treatment approaches are prominent trends in the rare disease diagnostics market.
By test type, the genetic testing segment is forecasted to hold the largest market share during 2025-2035; by disease type, the neurological disorders segment is expected to dominate the market during 2025-2035; by technology, the sequencing technologies segment is expected to hold the largest share during 2025-2035; by sample type, the blood samples segment is expected to dominate during 2025-2035; by end user, the diagnostic laboratories segment is expected to hold the largest share during 2025-2035; and by geography, North America is expected to hold the largest share of the market during 2025-2035.
By region, North America is expected to hold the largest share of the rare disease diagnostics market in 2025. The large share is attributed to the region's most developed rare disease testing infrastructure, comprehensive newborn screening programs, expanding insurance coverage for genetic testing, and substantial government research funding. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to register the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by rapid healthcare infrastructure development and government investments in genomics programs.
Key drivers include increasing awareness and early diagnosis initiatives for rare diseases, growing government support and funding for rare disease research and diagnosis, advancements in genomic technologies enabling better rare disease identification, rising prevalence of rare genetic disorders globally, and increasing adoption of next-generation sequencing in clinical settings. These factors are collectively driving the adoption of rare disease diagnostic technologies across clinical and research applications.
























Published Date: Jan-2025
Published Date: Jan-2025
Please enter your corporate email id here to view sample report.
Subscribe to get the latest industry updates