Resources
About Us
Space Robotics and Autonomous Systems Market by Solution (Products, Services), Application (Satellite Servicing, Planetary Exploration, Orbital Debris Removal, In-Space Manufacturing), End-User (Commercial, Government & Defense), and Orbit (LEO, GEO, Deep Space) – Global Forecast to 2036
Report ID: MRAD - 1041699 Pages: 275 Feb-2026 Formats*: PDF Category: Aerospace and Defense Delivery: 24 to 72 Hours Download Free Sample ReportWhat is the Space Robotics and Autonomous Systems Market Size?
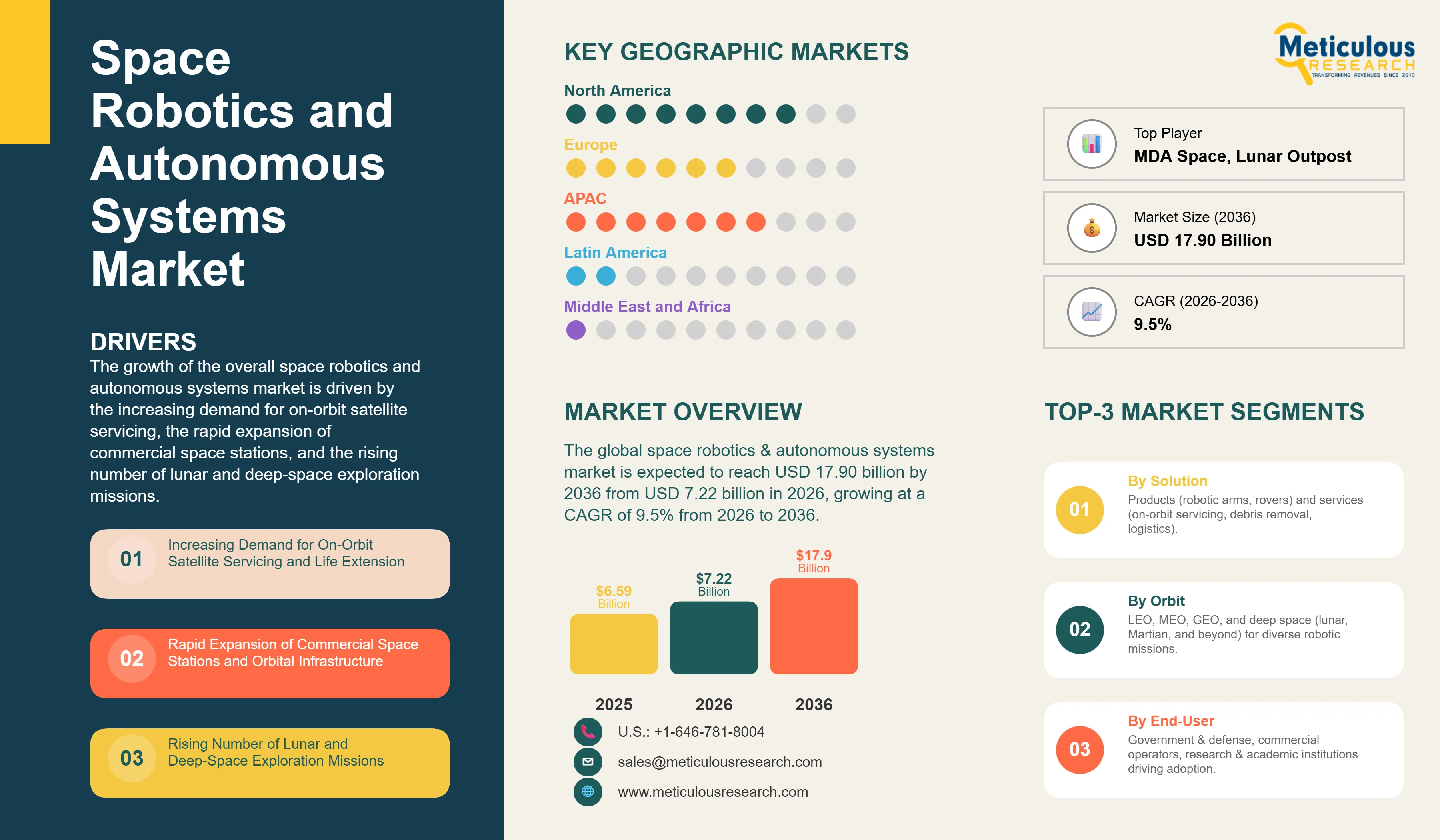
The global space robotics and autonomous systems market was valued at USD 6.59 billion in 2025. The market is expected to reach approximately USD 17.90 billion by 2036 from USD 7.22 billion in 2026, growing at a CAGR of 9.5% from 2026 to 2036. The growth of the overall space robotics and autonomous systems market is driven by the increasing demand for on-orbit satellite servicing, the rapid expansion of commercial space stations, and the rising number of lunar and deep-space exploration missions. As space agencies and private enterprises seek to extend the operational life of orbital assets and establish sustainable lunar bases, autonomous robotic systems have become essential for complex assembly, maintenance, and resource extraction tasks. The rapid expansion of the “NewSpace” sector, coupled with the increasing need for active debris removal to ensure orbital sustainability, continues to fuel significant growth of this market across all major geographic regions.
• In terms of revenue, the global space robotics and autonomous systems market is projected to reach USD 17.90 billion by 2036.
• The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.5% from 2026 to 2036.
• North America dominates the global space robotics and autonomous systems market with the largest market share in 2026, driven by NASA’s Artemis program, significant private investments from companies like SpaceX and Maxar, and a robust ecosystem of technology innovators.
• Asia Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period, supported by the rapid advancement of China’s Tiangong space station, India’s Gaganyaan and lunar missions, and Japan’s leadership in orbital debris removal technologies.
• By solution, the products segment (including robotic arms and rovers) holds the largest market share in 2026, particularly due to the high demand for manipulator systems on the International Space Station (ISS) and upcoming commercial platforms.
• By application, the satellite servicing segment is expected to witness the fastest CAGR during the forecast period as operators shift from satellite replacement to life-extension and refueling strategies.
• By end-user, the government & defense segment holds the largest share of the overall market in 2026, though the commercial segment is rapidly gaining ground.
• By orbit, Low Earth Orbit (LEO) holds the largest share of the overall market in 2026 due to the proliferation of mega- constellations and orbital infrastructure.
 Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
Space robotics and autonomous systems represent a sophisticated domain of aerospace engineering that utilizes robotic manipulators, rovers, and autonomous spacecraft to perform tasks in the harsh environment of space. Unlike traditional pre-programmed satellites, modern autonomous systems leverage AI-driven navigation, computer vision, and machine learning to execute complex operations such as docking with non-cooperative targets, assembling large-scale structures in orbit, and navigating treacherous lunar terrain without real-time human intervention. The market is defined by high-reliability technologies that enable “in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing” (ISAM), optimizing mission architectures and reducing the total cost of ownership (TCO) for orbital and planetary assets.
The market includes a diverse range of systems, from high-precision robotic arms for space station maintenance to autonomous rovers designed for regolith sampling on the Moon and Mars. These systems are increasingly integrated with advanced haptic feedback for teleoperation and edge computing for real-time decision-making to ensure mission success in communication-constrained environments. The ability to operate in extreme thermal gradients and high-radiation zones while maintaining sub-millimeter precision has made space robotics the technology of choice for the next generation of orbital logistics and planetary colonization.
The global space sector is pushing hard to modernize orbital capabilities, aiming to enhance mission resilience and reduce the accumulation of space debris. This drive has increased the adoption of autonomous systems for active debris removal (ADR) and the repair of high-value satellites, with modular robotic platforms helping to stabilize operational costs. At the same time, the rapid growth in the lunar economy and the push for Mars exploration is increasing the need for high-performance, autonomous robotic explorers and resource extraction equipment.
What are the Key Trends in the Space Robotics and Autonomous Systems Market?
Proliferation of Autonomous Satellite Servicing and Life Extension
Satellite operators are rapidly shifting toward life-extension services, moving well beyond the traditional “launch and replace” model toward smarter orbital logistics. Northrop Grumman’s Mission Extension Vehicles (MEV) have already demonstrated successful docking and life extension for geostationary satellites, while Maxar’s upcoming OSAM-1 mission aims to deliver refueling and assembly capabilities in LEO. The real game-changer comes with “smart” servicing vehicles featuring multi-arm robotic systems and AI-driven proximity operations that can repair and upgrade satellites in-situ. These advancements make high-efficiency orbital maintenance practical and cost-effective for everyone from telecommunication giants to defense agencies chasing sustained orbital dominance.
Innovation in Lunar Infrastructure and Autonomous Resource Extraction
Innovation in planetary robotics is rapidly driving the market as the global community scales up lunar exploration. Equipment suppliers are now designing autonomous rovers and excavators specifically for the lunar south pole, with tight control over power management and dust mitigation to meet the challenges of the lunar night. This often involves advanced mobility systems and autonomous navigation stacks capable of traversing unmapped terrain without GPS. At the same time, growing focus on “In-Situ Resource Utilization” (ISRU) is pushing manufacturers to develop robotic solutions tailored to water-ice extraction and regolith processing. These systems help establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon, extending the reach of exploration instead of relying solely on Earth-based supplies. By combining high-autonomy navigation with robust mechanical designs, these new systems support both scientific discovery and the burgeoning lunar economy.
|
Parameter |
Details |
|
Market Size by 2036 |
USD 17.90 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2026 |
USD 7.22 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 6.59 Billion |
|
Market Growth Rate (2026-2036) |
CAGR of 9.5% |
|
Dominating Region |
North America |
|
Fastest Growing Region |
Asia Pacific |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026 to 2036 |
|
Segments Covered |
Solution, Application, End-User, Orbit, and Region |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Drivers: Demand for Orbital Sustainability and Life Extension
A key driver of the space robotics market is the rapid movement of the global space industry toward orbital stewardship and the mitigation of space debris. Global requirements for ensuring the long-term sustainability of LEO have created significant incentives for the adoption of active debris removal (ADR) and satellite servicing technologies. The ability to de-orbit defunct satellites and repair aging assets drives operators toward scalable robotic solutions. It is estimated that as the number of active satellites triples through 2036, the need for autonomous traffic management and robotic intervention increases significantly; therefore, space robotic systems, with their ability to extend asset life by up to 5-10 years, are considered a crucial enabler of modern space strategies.
Opportunity: Expansion of the Lunar Economy and Commercial Space Stations
The rapid growth of the lunar economy provides great opportunities for the space robotics market. Indeed, the global surge in lunar exploration initiatives, such as the Artemis Accords, has created a compelling demand for autonomous systems that can build and maintain lunar habitats. These applications require high reliability, long operational life, and the ability to handle extreme environmental conditions, all attributes that are met with advanced planetary rovers and robotic excavators. The lunar logistics market is set to expand significantly through 2036, with robotics poised for an expanding share as agencies seek to monetize resource extraction services. Furthermore, the transition from the ISS to commercial orbital platforms like Axiom Station and Orbital Reef is stimulating demand for modular robotic arms that provide maintenance flexibility and payload handling.
Solution Insights
Why Do Robotic Products Dominate the Market?
The products segment, comprising robotic arms, rovers, and landers, accounts for around 65-70% of the overall space robotics market in 2026. This is mainly attributed to the primary use of these hardware systems in mission-critical operations across space stations and planetary missions. Robotic arms, such as the Canadarm3 and European Robotic Arm (ERA), offer the most efficient way to manage external maintenance and payload transfers. The government and commercial space station sectors alone consume the vast majority of these systems, with major projects in North America and Europe demonstrating the technology’s capability to handle high-value infrastructure management.
However, the services segment (including on-orbit servicing and debris removal) is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period, driven by the growing number of commercial satellite constellations and the rising regulatory pressure for orbital cleanup. The ability to provide “Robotics-as-a-Service” (RaaS) makes these solutions highly attractive for modern satellite operators.
Application Insights
How Does Satellite Servicing Lead the Market?
Based on application, the satellite servicing segment holds the largest share of the overall market in 2026, accounting for around 40-45% of the overall market. From refueling and battery replacement to structural repair, the use of robotic systems is central to modernizing orbital infrastructure. Current large-scale projects are increasingly specifying autonomous docking and manipulator systems for their ability to handle non-cooperative targets with high efficiency and lower risk compared to human-led missions.
The planetary exploration and in-space manufacturing segments continue to find critical applications in missions where the construction of large antennas and the extraction of lunar resources are essential. However, the shift toward autonomous orbital logistics is pushing the requirement for standardized robotic interfaces that allow businesses to scale their servicing capacity while minimizing their operational footprint.
End-User Insights
Why Does the Government & Defense Segment Maintain a Significant Share?
Based on end-user, the government & defense segment holds the largest share of the overall market in 2026, accounting for around 65-70% of the overall market. This dominance is primarily driven by substantial investments from national space agencies (e.g., NASA, ESA, CNSA) in large-scale exploration missions, such as lunar infrastructure development and deep-space probes. Additionally, military and defense organizations increasingly leverage space robotics for surveillance, reconnaissance, and in-orbit asset protection. These high-value, long-term programs necessitate robust, space-qualified robotic systems, ensuring a sustained demand from this segment.
However, the commercial segment is expected to witness the fastest CAGR during the forecast period, fueled by the rapid growth of private space ventures, satellite operators, and emerging lunar logistics companies. The increasing adoption of commercial satellite servicing and the development of private space stations are key drivers for this accelerated growth.
Orbit Insights
Why Does Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Dominate the Market?
Based on orbit, the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) segment holds the largest share of the overall market in 2026, accounting for around 55-60% of the overall market. This is primarily due to the proliferation of mega-constellations for broadband internet (e.g., Starlink, OneWeb) and the increasing deployment of Earth observation satellites. The high density of assets in LEO drives significant demand for robotic solutions related to active debris removal, in-orbit servicing, and satellite inspection to ensure the long-term sustainability and safety of this critical orbital region.
However, the deep space segment (including lunar, Martian, and beyond) is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period, driven by ambitious international and commercial missions targeting the Moon and Mars. The need for autonomous rovers, landers, and robotic construction systems for planetary exploration and potential resource utilization is a major catalyst for this growth.
Regional Insights
How is North America Maintaining Dominance in the Global Space Robotics Market?
North America holds the largest share of the global space robotics and autonomous systems market in 2026. The largest share of this region is primarily attributed to the massive investments in the Artemis program and the presence of the world’s leading commercial space companies, particularly in the United States. The U.S. alone accounts for a significant portion of global space robotics consumption, with its position as a leading hub for lunar exploration and military space modernization driving sustained growth. The presence of leading manufacturers like Northrop Grumman, MDA Space, Maxar Technologies, and Redwire, along with a well-developed NewSpace ecosystem, provides a robust market for both standard and high-capacity robotic solutions.
Which Factors Support Asia Pacific and Europe Market Growth?
Asia Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by the need for sovereign space capabilities and the expansion of the lunar and orbital infrastructure sectors. Countries like China and India are at the forefront, with significant focus on integrating autonomous robotics into their space station and lunar landing environments. In Europe, the leadership in robotic arm innovation and the push for orbital sustainability are driving the adoption of high-efficiency servicing systems. Germany, France, and the UK are leading the way, with a strong focus on active debris removal and the integration of robotics into the ESA’s exploration roadmap through players like Airbus and Leonardo.
The companies such as Northrop Grumman Corporation, MDA Space, Maxar Technologies, and Redwire Space lead the global space robotics and autonomous systems market with a comprehensive range of manipulator and servicing solutions, particularly for large-scale orbital and planetary applications. Meanwhile, players including Astroscale Holdings Inc., Oceaneering International, Inc., Honeybee Robotics (Blue Origin), and GITAI focus on specialized debris removal, subsea-heritage robotics, and high-precision autonomous systems targeting the commercial and lunar sectors. Emerging manufacturers and integrated players such as Lunar Outpost, Astrobotic Technology, D-Orbit, and ClearSpace are strengthening the market through innovations in lunar mobility and autonomous orbital logistics.
The global space robotics and autonomous systems market is projected to reach a valuation of USD 17.90 billion by 2036, expanding from USD 7.22 billion in 2026. This significant growth trajectory is underpinned by a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.5% over the forecast period, reflecting the technology’s transition from experimental missions to mainstream orbital and lunar logistics.
The Products segment (Robotic Arms, Rovers, Landers) is anticipated to maintain its dominance, accounting for the largest market share in 2026. This is primarily due to its critical role in space station infrastructure and planetary exploration missions, where high-reliability hardware is the prerequisite for all orbital and surface operations.
The Satellite Servicing application commands the largest share of the market. The dominance is driven by the critical shift toward orbital sustainability and life extension, where robotic systems are used to refuel, repair, and relocate high-value satellites, thereby maximizing the return on investment for fleet operators.
Asia Pacific is forecast to exhibit the fastest CAGR during the 2026–2036 period. This accelerated growth is fueled by massive national space programs in China and India, coupled with the rapid expansion of the commercial space sector in Japan and Australia that are increasingly adopting autonomous robotics for both exploration and orbital cleanup.
The market is being fundamentally reshaped by two major trends: the Proliferation of Autonomous Satellite Servicing, which integrates AI with robotic manipulators for in-situ repair, and the Innovation in Lunar Infrastructure, driven by the need for autonomous rovers and resource extraction systems to support sustainable planetary bases.
Key market players include Northrop Grumman (MEV/MRV servicing vehicles), MDA Space (Canadarm3/SKYMAKER), Maxar Technologies (Robotic arms/OSAM-1), and Astroscale (Debris removal systems), all of whom are focused on expanding their product portfolios to address the growing demand for autonomous space operations.
1. Introduction
1.1. Market Definition
1.2. Market Ecosystem
1.3. Currency and Limitations
1.3.1. Currency
1.3.2. Limitations
1.4. Key Stakeholders
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Collection & Validation
2.2.1. Secondary Research
2.2.2. Primary Research
2.3. Market Assessment
2.3.1. Market Size Estimation
2.3.2. Bottom-Up Approach
2.3.3. Top-Down Approach
2.3.4. Growth Forecast
2.4. Assumptions for the Study
3. Executive Summary
4. Market Insights
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Drivers
4.2.1. Increasing Demand for On-Orbit Satellite Servicing and Life Extension
4.2.2. Rapid Expansion of Commercial Space Stations and Orbital Infrastructure
4.2.3. Rising Number of Lunar and Deep-Space Exploration Missions
4.3. Restraints
4.3.1. High Development Costs and Technical Complexity of Space-Qualified Robotics
4.3.2. Stringent Regulatory and Legal Frameworks for Orbital Operations
4.4. Opportunities
4.4.1. Growth of the Lunar Economy and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU)
4.4.2. Emerging Market for Active Debris Removal (ADR) and Orbital Cleanup
4.5. Challenges
4.5.1. Harsh Environmental Conditions and Radiation Hardening Requirements
4.5.2. Communication Latency and Autonomy Limitations in Deep Space
4.6. Trends
4.6.1. Integration of AI and Machine Learning for Autonomous Navigation and Docking
4.6.2. Development of Modular and Standardized Robotic Interfaces (ISAM)
4.7. Pricing Analysis
4.8. Value Chain Analysis
4.9. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
5. Global Space Robotics and Autonomous Systems Market, by Solution
5.1. Introduction
5.2. Products
5.2.1. Robotic Arms and Manipulators
5.2.2. Rovers and Landers
5.2.3. Autonomous Spacecraft and Probes
5.2.4. Robotic End-Effectors and Tools
5.3. Services
5.3.1. On-Orbit Servicing (Refueling, Repair, Upgrades)
5.3.2. Active Debris Removal (ADR)
5.3.3. Orbital Logistics and Transportation
5.3.4. Space Exploration Support Services
6. Global Space Robotics and Autonomous Systems Market, by Application
6.1. Introduction
6.2. Satellite Servicing and Life Extension
6.3. Planetary Exploration (Lunar, Martian, Asteroid)
6.4. Orbital Debris Removal and Mitigation
6.5. In-Space Assembly and Manufacturing (ISAM)
6.6. Space Station Operations and Maintenance
6.7. Space Transportation and Logistics
7. Global Space Robotics and Autonomous Systems Market, by End-User
7.1. Introduction
7.2. Government & Defense
7.2.1. National Space Agencies (NASA, ESA, CNSA, ISRO, JAXA)
7.2.2. Military and Defense Organizations
7.3. Commercial
7.3.1. Satellite Operators and Fleet Managers
7.3.2. Commercial Space Station Developers
7.3.3. Lunar Logistics and Mining Companies
7.4. Research & Academic Institutions
8. Global Space Robotics and Autonomous Systems Market, by Orbit
8.1. Introduction
8.2. Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
8.3. Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
8.4. Geostationary Orbit (GEO)
8.5. Deep Space (Lunar, Martian, and Beyond)
9. Global Space Robotics and Autonomous Systems Market, by Region
9.1. Introduction
9.2. North America
9.2.1. U.S.
9.2.2. Canada
9.3. Europe
9.3.1. Germany
9.3.2. France
9.3.3. U.K.
9.3.4. Italy
9.3.5. Russia
9.3.6. Rest of Europe
9.4. Asia-Pacific
9.4.1. China
9.4.2. Japan
9.4.3. India
9.4.4. South Korea
9.4.5. Australia
9.4.6. Rest of Asia-Pacific
9.5. Latin America
9.5.1. Brazil
9.5.2. Mexico
9.5.3. Argentina
9.5.4. Rest of Latin America
9.6. Middle East & Africa
9.6.1. UAE
9.6.2. Saudi Arabia
9.6.3. Israel
9.6.4. South Africa
9.6.5. Egypt
9.6.6. Nigeria
9.6.7. Rest of Middle East & Africa
10. Competitive Landscape
10.1. Introduction
10.2. Key Growth Strategies
10.3. Market Share Analysis (2025)
10.4. Competitive Benchmarking
11. Company Profiles
(Business Overview, Financial Overview, Product Portfolio, Strategic Developments)
11.1. Northrop Grumman Corporation (SpaceLogistics)
11.2. MDA Space
11.3. Maxar Technologies
11.4. Redwire Space
11.5. Astroscale Holdings Inc.
11.6. Oceaneering International, Inc.
11.7. Honeybee Robotics (Blue Origin)
11.8. GITAI
11.9. Airbus SE
11.10. Leonardo S.p.A. (Thales Alenia Space)
11.11. Lockheed Martin Corporation
11.12. Boeing Company
11.13. Astrobotic Technology
11.14. Lunar Outpost
11.15. D-Orbit S.p.A.
11.16. ClearSpace SA
11.17. Motiv Space Systems
11.18. Effective Space Solutions (Starship)
11.19. Orbit Fab
11.20. Starfish Space
12. Appendix
12.1. Questionnaire
12.2. Available Customization
























Please enter your corporate email id here to view sample report.
Subscribe to get the latest industry updates