Resources
About Us
Quantum Computing in Life Sciences Market by Application (Drug Discovery & Development, Genomics & Precision Medicine, Molecular Modeling & Simulation, Protein Folding), Deployment Mode (On-Premise, Cloud-Based, Hybrid), Technology, End User, and Geography - Global Forecast to 2035
Report ID: MRHC - 1041604 Pages: 240 Sep-2025 Formats*: PDF Category: Healthcare Delivery: 24 to 72 Hours Download Free Sample ReportWhat is the Quantum Computing in Life Sciences Market Size?
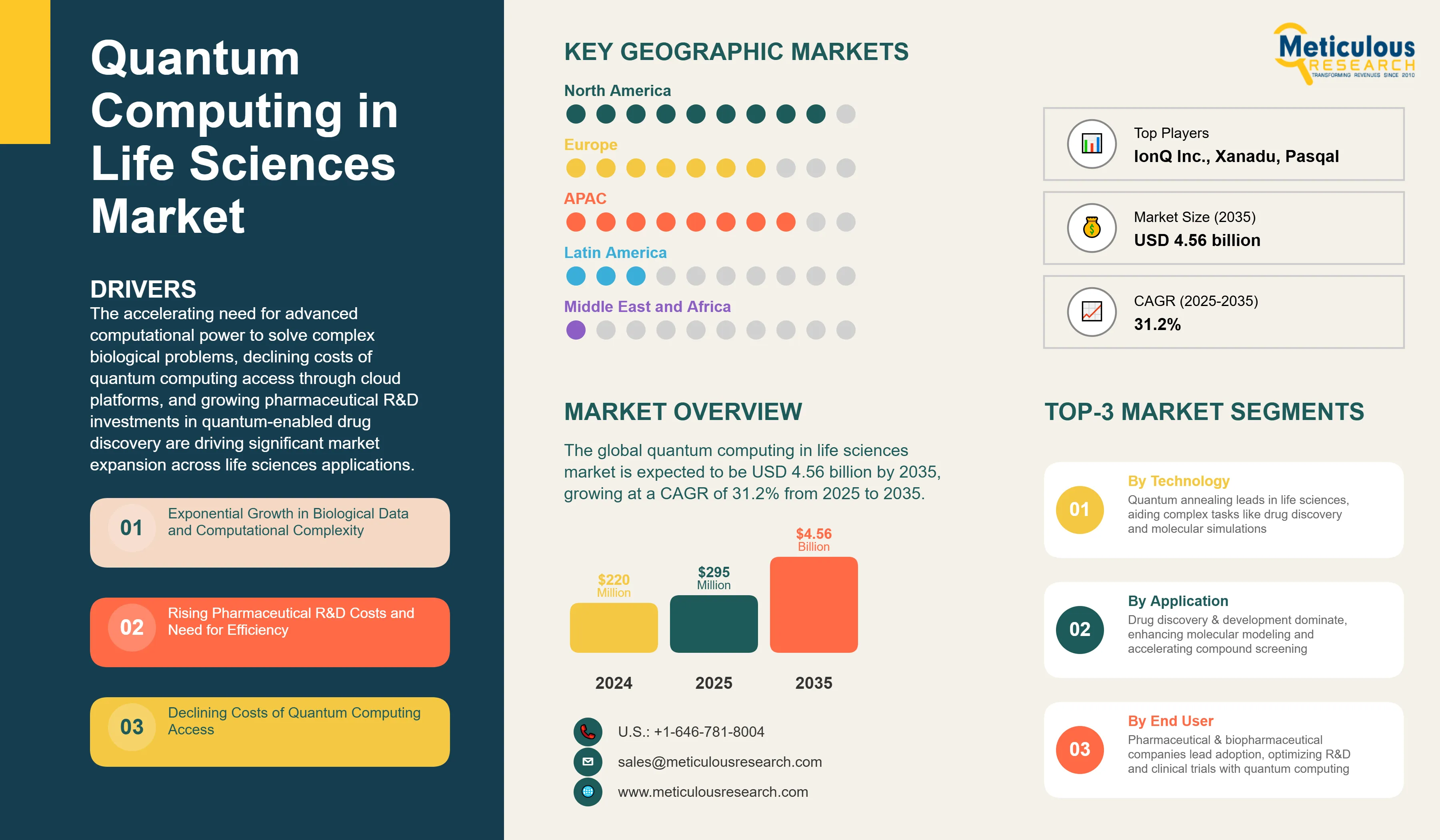
The global quantum computing in life sciences market was valued at USD 220 million in 2024. This market is expected to be USD 4.56 billion by 2035 from an estimated USD 295 million in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 31.2% from 2025 to 2035. The increasing need for advanced computational power to solve complex biological problems, declining costs of quantum computing access through cloud platforms, and growing pharmaceutical R&D investments in quantum-enabled drug discovery are driving significant market expansion across life sciences applications.
Market Highlights: Quantum Computing in Life Sciences
Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
The quantum computing in life sciences market focuses on using quantum computing technologies to tackle complex biological and medical challenges that classical computers cannot handle. Quantum computers take advantage of quantum mechanics, like superposition and entanglement, to perform calculations much faster than traditional computers for specific problems. In life sciences, these systems are changing drug discovery by simulating molecular interactions, speeding up genomic sequencing analysis, improving predictions of protein folding, and supporting personalized medicine through complex data pattern recognition.
The market includes quantum hardware platforms, quantum algorithms designed for biological use, quantum-classical hybrid solutions, and quantum computing-as-a-service (QCaaS) options. Important applications include pharmaceutical research, biotechnology development, clinical diagnostics, agricultural genomics, and computational biology. This technology allows researchers to model complex biological systems at the quantum level, predict drug-target interactions with high precision, analyze large genomic datasets, and discover new therapeutic compounds. These advancements lead to shorter drug development times, lower research costs, and higher success rates in clinical trials. The market thrives on the rapid increase in biological data, the limitations of classical computing in addressing NP-hard problems in biology, growing partnerships between quantum computing firms and major pharmaceutical companies, and more investments from venture capital in quantum biotechnology startups.
How is AI Integration Transforming the Quantum Computing in Life Sciences Market?
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasing the impact of quantum computing in life sciences. Hybrid quantum-classical algorithms combine the strengths of both technologies. Quantum processors handle specific computation challenges, while classical AI systems manage data preprocessing, result interpretation, and optimization. Machine learning models that use quantum-generated data are improving drug candidate screening, predicting clinical trial outcomes, and identifying disease biomarkers. AI-powered quantum error correction techniques are increasing the reliability and accuracy of quantum computations, which is vital for medical applications. Natural language processing paired with quantum computing speeds up literature mining for drug repurposing opportunities. Quantum machine learning algorithms are being created specifically for genomic data analysis, allowing quicker identification of disease-causing mutations and therapeutic targets. This combination makes quantum computing more accessible to life sciences researchers who lack deep expertise in quantum physics. It also significantly improves the practical use of quantum solutions in real-world pharmaceutical and medical research workflows.
What are the Key Trends in the Quantum Computing in Life Sciences Market?
Quantum-as-a-Service (QaaS) adoption: A major trend shaping the quantum computing market in life sciences is the quick uptake of cloud-based Quantum-as-a-Service platforms. This model removes the need for organizations to spend money on costly quantum hardware and specialized maintenance skills. Pharmaceutical companies and research institutions can access quantum computing power through platforms from IBM, Amazon Braket, Microsoft Azure Quantum, and Google Cloud. This wider access to quantum computing speeds up experimentation. It allows smaller biotech firms to use quantum technologies and encourages collaborative research projects. The QaaS model also offers flexibility to adjust computational resources based on project needs and provides access to the latest quantum hardware upgrades without significant costs.
Quantum-enabled personalized medicine: Another significant trend is using quantum computing to improve personalized and precision medicine. Researchers are developing quantum algorithms to analyze individual patient genomic data along with environmental and lifestyle factors. This analysis helps predict disease risk, optimize treatment plans, and reduce harmful drug reactions. The technology can handle large combinations of data, which helps match patients with the best therapeutic options based on their unique molecular profiles. This trend is especially important in oncology. Quantum computing aids in identifying specific cancer mutations and predicting responses to targeted therapies and immunotherapies, moving medicine closer to truly personalized treatment approaches.
|
Report Coverage |
Details |
|
Market Size by 2035 |
USD 4.56 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 295 Million |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 220 Million |
|
Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2035 |
CAGR of 31.2% |
|
Dominating Region |
North America |
|
Fastest Growing Region |
Asia Pacific |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2035 |
|
Segments Covered |
Application, Deployment Mode, Technology, End User, and Region |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Exponential Growth in Biological Data and Computational Complexity
A major factor driving the growth of the quantum computing market in life sciences is the rapid increase in biological data generation and the complexity of analyzing this data. The cost of genome sequencing has fallen significantly. This has led to huge genomic databases with billions of data points. Proteomics, metabolomics, and multi-omics methods produce petabytes of complex, interconnected data that overwhelm traditional computing power. Standard computers have a hard time with the combinatorial explosion problem in drug discovery. Analyzing molecular interactions requires looking at a vast number of possible configurations. Quantum computers can explore many solution pathways at the same time through superposition. This offers potential speedups from years to days for certain calculations. This advantage is becoming crucial as pharmaceutical companies try to model more complex biological systems, predict drug efficacy and safety earlier in development, and identify new therapeutic targets in rare diseases where data is limited but highly detailed.
Restraint
Technical Limitations and Quantum Hardware Challenges
Despite its promising potential, the quantum computing market in life sciences faces serious technical challenges. Current quantum computers have limited qubit counts, high error rates, and short coherence times. These issues restrict the complexity and duration of calculations. Quantum decoherence, which happens when quantum states collapse due to environmental interference, remains a major hurdle. This challenge requires costly cryogenic cooling systems and electromagnetic shielding. Most existing quantum algorithms for life sciences are still in proof-of-concept stages. They have not yet shown clear advantages over classical methods for practical, large-scale problems. There is also a shortage of professionals who are skilled in both quantum computing and life sciences, creating a talent bottleneck. Furthermore, quantum computers are good at solving specific types of problems but are not always better than classical computers. This means that careful assessment is needed to determine which biological problems can truly benefit from quantum methods. The high costs of quantum hardware, maintenance, and specialized infrastructure limit access, especially for smaller research organizations and developing countries.
Opportunity
Strategic Partnerships Between Quantum Computing and Pharmaceutical Companies
The growing trend of partnerships between quantum computing firms and pharmaceutical companies offers significant growth potential. Major pharmaceutical players like Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Biogen, and Johnson & Johnson are joining forces with quantum computing firms such as IBM, Google, and D-Wave to investigate how quantum technology can be used in drug discovery and development. These collaborations mix pharmaceutical knowledge with advanced quantum tools, speeding up the development and testing of algorithms.
These partnerships give quantum companies practical applications and funding, while pharmaceutical firms gain early access to groundbreaking technology that can offer them a competitive edge. The collaborative approach is also expanding to include contract research organizations, academic institutions, and government research agencies, establishing environments that encourage innovation. Additionally, these alliances are promoting the creation of industry-specific quantum software tools, approved measures for quantum performance in life sciences, and standardized methods that will help foster broader acceptance in the market.
Application Insights
Why is Drug Discovery & Development the Dominant Application for Quantum Computing?
The drug discovery and development segment holds the largest share, accounting for 40 to 45% of the overall quantum computing in life sciences market in 2025. This dominance comes from the pharmaceutical industry's urgent need to cut the time and cost of getting new drugs to market, which currently averages 10 to 15 years and over USD 2 billion per drug. Quantum computing tackles major bottlenecks in the drug development process. These include molecular simulation, virtual screening of compound libraries, predicting drug-target binding affinities, optimizing lead compounds, and assessing ADMET (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity) properties. The technology allows for accurate modeling of molecular interactions at the quantum level. This modeling is essential for understanding how drug molecules bind to protein targets. Pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in quantum computing to improve hit-to-lead conversion rates, reduce reliance on costly animal testing, and find drug candidates with a higher chance of success in clinical trials.
The genomics and precision medicine segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate during the forecast period. This rapid growth is driven by the surge of genomic data from next-generation sequencing technologies and the healthcare industry's move toward personalized treatments. Quantum computing can analyze vast genomic datasets, identify complex genetic patterns linked to diseases, predict how individual patients will respond to therapies, and optimize treatment plans for specific genetic profiles. This makes it a transformative technology for precision medicine initiatives around the world.
Deployment Mode Insights
How Does Cloud-Based Deployment Drive Market Accessibility?
The cloud-based segment accounts for the largest share, 55-60%, of the overall quantum computing market in life sciences by 2025. Cloud-based quantum computing platforms have made this technology more accessible. Organizations no longer need to invest in costly quantum hardware, specialized facilities, or expert maintenance teams. Major cloud providers offer quantum computing services that anyone can access via standard internet connections. Pay-per-use pricing models make experimentation affordable for startups, academic researchers, and smaller biotech companies. Cloud platforms give access to various types of quantum hardware from different manufacturers. This allows researchers to compare performance across different qubit technologies for their specific life sciences applications. The cloud model also supports collaboration. Geographically distributed research teams can access shared quantum computing resources and datasets. Integration with classical cloud computing services allows for smooth hybrid quantum-classical workflows, which are crucial for practical life sciences applications.
The hybrid deployment segment is likely to grow at the fastest rate through 2035. Hybrid deployment models combine on-premise classical computing infrastructure with cloud-based quantum resources. This gives organizations more control over sensitive proprietary data and intellectual property while still accessing quantum capabilities. This method is especially appealing to pharmaceutical companies that manage confidential drug development data and patient information, which are subject to strict regulations. Hybrid architectures also optimize workloads. Routine classical computations take place on local infrastructure, while only quantum-specific tasks are sent to cloud quantum processors. This approach reduces costs and latency.
Technology Insights
How Do Gate-Based Quantum Computers Support Life Sciences Research?
The gate-based quantum computing segment accounts for the largest share of 50-55% of the overall quantum computing market in life sciences in 2025. Gate-based quantum computers, also known as universal quantum computers, use quantum gates to manipulate qubits. They can theoretically solve any computable problem, making them versatile for various life sciences applications. Major quantum computing companies like IBM, Google, Rigetti, and IonQ focus on this technology and have developed increasingly powerful gate-based systems.
Gate-based quantum computers excel at running quantum algorithms like the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) and the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA). These algorithms show promise in areas such as molecular simulation, protein folding prediction, and optimizing drug discovery. The technology also supports quantum error correction techniques. These techniques are crucial for achieving fault-tolerant quantum computing, which is necessary for important life sciences applications. As gate-based systems scale up with higher qubit counts and lower error rates, they are expected to deliver significant advantages for a growing range of pharmaceutical and biotechnology uses.
The quantum annealing segment is seeing notable adoption in life sciences for optimization problems. Quantum annealers, mainly developed by D-Wave Systems, excel at solving combinatorial optimization problems commonly found in drug discovery. This includes tasks like molecular conformation searches, optimizing protein folding pathways, and analyzing drug-target interactions. While quantum annealers are less versatile than gate-based systems, they are currently more mature and stable. This stability makes them appealing for organizations looking for immediate practical applications. The technology works particularly well for problems mapped to finding the lowest energy state of a system, which fits many molecular and biological scenarios..
End User Insights
Why Do Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies Lead Market Adoption?
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies segment holds the largest share of around 50-55% in 2025. This segment's dominance shows the pharmaceutical industry's need for new computing methods to tackle rising drug development costs, declining research and development productivity, and stricter regulatory requirements. Major pharmaceutical companies have set up dedicated quantum computing research divisions and partnerships to explore applications throughout the drug development process. These companies have the financial means to invest in new quantum technologies and the technical know-how to integrate quantum solutions into their existing computational chemistry and bioinformatics workflows. Biotechnology firms, especially those focusing on new therapeutic methods like gene therapy, cell therapy, and synthetic biology, are using quantum computing to model complex biological systems and design accurate molecular interventions. This segment benefits from a growing recognition among pharmaceutical leaders that quantum computing could offer significant competitive edges in finding breakthrough therapies and speeding up the time it takes to bring essential medications to market.
The research institutions and academia segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate through 2035. Academic and government research institutions play key roles in developing fundamental quantum algorithms, validating quantum methods for biological issues, and training the next generation of professionals in quantum life sciences. Universities are creating interdisciplinary quantum computing centers that bring together physicists, computer scientists, biologists, and medical researchers. Government funding agencies around the world are prioritizing quantum computing research grants with a clear focus on life sciences applications. Academic institutions have more freedom to pursue exploratory research without facing immediate commercial pressures, allowing them to investigate new quantum applications that may not provide clear benefits in the short term. The rapid growth of this segment is driven by increasing government investments in quantum research infrastructure, collaborations between universities and industry, and a growing number of quantum-trained graduates joining the workforce.
U.S. Quantum Computing in Life Sciences Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2035
The U.S. quantum computing in life sciences market is projected to be worth around USD 1.96 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 30.5% from 2025 to 2035.
How is the North America Quantum Computing in Life Sciences Market Leading Global Innovation?
North America holds the largest market share of nearly 45-50% in 2025. The region's leadership position is anchored by the presence of pioneering quantum computing companies including IBM, Google, Rigetti Computing, IonQ, and D-Wave Systems, all headquartered in the United States. The concentration of leading pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies in North America, including Pfizer, Merck, Johnson & Johnson, and Amgen, creates strong demand and provides validation for quantum computing applications in drug discovery. Substantial government support through initiatives like the U.S. National Quantum Initiative Act, which authorized USD 1.2 billion in quantum research funding, and similar programs in Canada, accelerates research and commercialization. The region benefits from a mature venture capital ecosystem that has invested billions in quantum computing startups and a robust academic infrastructure with leading quantum research centers at MIT, Harvard, Caltech, Stanford, and the University of Waterloo. The presence of major cloud computing platforms offering quantum services (AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud) and established partnerships between quantum computing firms and pharmaceutical companies further strengthen North America's dominant position.
Which Factors Support the Asia Pacific Quantum Computing in Life Sciences Market Growth?
Asia Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth rate from 2025 to 2035. This accelerated growth is driven by aggressive government investments in quantum technologies, particularly in China, Japan, South Korea, and India. China has committed over USD 10 billion to quantum research and has established the world's largest quantum research facility, with significant focus on quantum computing applications in biotechnology and medicine. Japan's Quantum Leap Flagship Program and South Korea's Quantum Technology Development Plan include substantial funding for quantum computing in life sciences. The region's rapidly growing pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, led by companies like Takeda, Astellas, Daiichi Sankyo, and emerging Chinese biotech firms, are increasingly adopting advanced computational technologies. Asia Pacific's large population and high disease burden create urgent demand for accelerated drug discovery and personalized medicine solutions. The region is also investing heavily in quantum computing education and workforce development, producing a growing pool of quantum-trained scientists and engineers. Strategic collaborations between Asian pharmaceutical companies and global quantum computing firms, combined with government policies encouraging technology adoption in healthcare, are creating a favorable environment for quantum computing integration in life sciences research and development.
Which Factors Support the Europe Quantum Computing in Life Sciences Market Growth?
Europe represents a significant market with strong growth potential, driven by the European Quantum Flagship program, which has committed €1 billion over 10 years to quantum technology development. The region's pharmaceutical powerhouses including Roche, Novartis, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, and Bayer are actively exploring quantum computing applications and forming partnerships with quantum computing companies. Germany's quantum computing initiatives, including significant funding for quantum research centers and the procurement of quantum computers for research institutions, support life sciences applications. The United Kingdom's National Quantum Technologies Programme and France's National Quantum Strategy include specific provisions for quantum computing in drug discovery and healthcare. European regulatory emphasis on data privacy and security aligns well with the development of secure quantum communication networks for healthcare data. The region's strong tradition of academic research and collaboration between universities and pharmaceutical companies facilitates quantum computing algorithm development and validation for biological applications.
Value Chain Analysis
Research and Development
This stage focuses on developing quantum algorithms specifically designed for life sciences applications, improving quantum hardware performance, creating quantum-classical hybrid architectures, and validating quantum approaches against classical methods for biological problems.
Key Players: IBM Research, Google Quantum AI, Microsoft Quantum, Intel Quantum, academic institutions (MIT, Stanford, Oxford, ETH Zurich)
Quantum Hardware Development
This stage involves designing and manufacturing quantum processors, developing qubit technologies (superconducting, trapped ion, photonic, topological), building cryogenic and control systems, and scaling quantum computers to higher qubit counts with lower error rates.
Key Players: IBM, Google, Rigetti Computing, IonQ, PsiQuantum, D-Wave Systems, Honeywell Quantum Solutions (now Quantinuum), Atom Computing
Quantum Software and Algorithm Development
This stage encompasses creating quantum programming languages and development frameworks, building quantum software libraries for life sciences applications, developing quantum machine learning algorithms, and creating simulation tools for quantum-classical hybrid workflows.
Key Players: Zapata Computing, Xanadu, Cambridge Quantum Computing (now Quantinuum), QC Ware, Classiq, Q-CTRL
Cloud Platform and Service Providers
This stage involves providing cloud-based access to quantum computing hardware, offering quantum computing as a service (QCaaS), integrating quantum capabilities with classical cloud infrastructure, and providing technical support and consulting services.
Key Players: Amazon Web Services (AWS Braket), Microsoft Azure Quantum, Google Cloud, IBM Quantum Network, Alibaba Cloud
Application Development and Integration
This stage focuses on developing industry-specific quantum applications for drug discovery and life sciences, integrating quantum computing into pharmaceutical R&D workflows, conducting pilot projects and proof-of-concept studies, and providing training and support to life sciences researchers.
Key Players:
Recent Developments
Segments Covered in the Report
By Application
By Deployment Mode
By Technology
By End User
By Region
The quantum computing in life sciences market size is expected to increase from USD 295 million in 2025 to USD 4.56 billion by 2035.
The quantum computing in life sciences market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 31.2% from 2025 to 2035.
The major players in the quantum computing in life sciences market include IBM Corporation, Google (Alphabet Inc.), Microsoft Corporation, Amazon Web Services (AWS), D-Wave Systems Inc., IonQ Inc., Rigetti Computing, Quantinuum, Xanadu, Zapata Computing, QC Ware, Atos (Eviden), Fujitsu Limited, Toshiba Corporation, Alibaba Group, Baidu, PsiQuantum, Pasqal, Q-CTRL, and ProteinQure Inc., among others.
The main factors driving the quantum computing in life sciences market include the exponential growth of biological data requiring advanced computational capabilities, increasing pharmaceutical R&D costs driving demand for efficiency improvements, declining costs of quantum computing access through cloud platforms, growing strategic partnerships between quantum computing firms and pharmaceutical companies, and government investments in quantum technology development with emphasis on healthcare applications.
North America will lead the global quantum computing in life sciences market during the forecast period 2025 to 2035.
























Published Date: Jan-2024
Published Date: Sep-2013
Published Date: Jan-2025
Published Date: Jan-2025
Published Date: Aug-2024
Please enter your corporate email id here to view sample report.
Subscribe to get the latest industry updates