Resources
About Us
Aerospace 3D Printing Market Size, Share, Forecast & Trends by Component (High Power Microwave Component, High Energy Laser Component, Plasma Weapons, Sonic Weapons) Technology (Lethal and Non-Lethal) Platform, and Material - Global Forecast to 2035
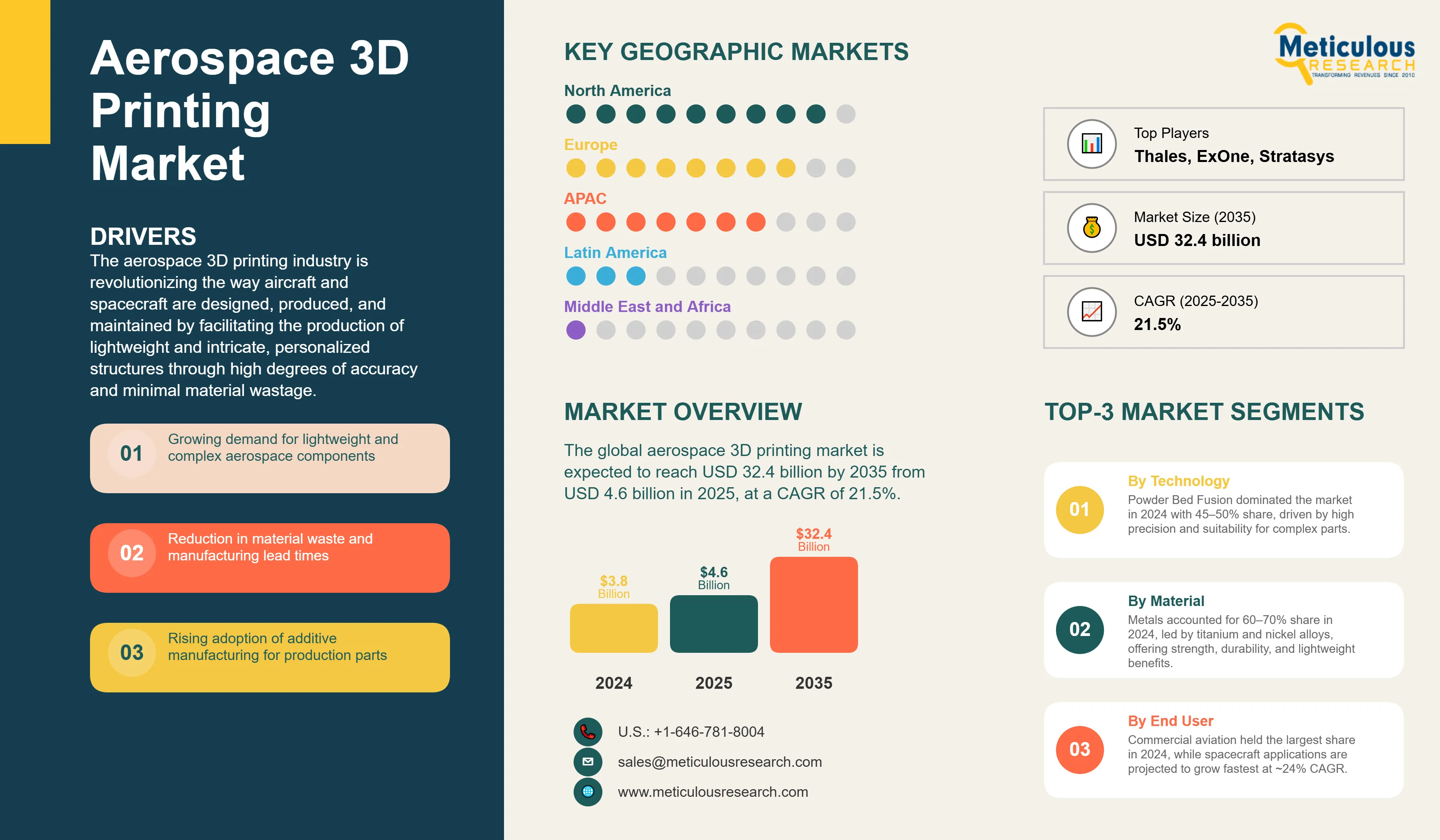
Report ID: MRAD - 1041561 Pages: 196 Aug-2025 Formats*: PDF Category: Aerospace and Defense Delivery: 24 to 72 Hours Download Free Sample ReportThe global aerospace 3D printing market was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2024. The market is expected to reach USD 32.4 billion by 2035 from USD 4.6 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 21.5%.
The aerospace 3D printing industry is revolutionizing the way aircraft and spacecraft are designed, produced, and maintained by facilitating the production of lightweight and intricate, personalized structures through high degrees of accuracy and minimal material wastage.
Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing, 3D printing enables engineers to create complex geometries and consolidate multiple parts into a single, larger, stronger, and more efficient component. In the aerospace sector, this technology is applied in both prototyping and the production of functional parts, including structural brackets, turbine blades, cabin interior elements, and satellite components. For instance, GE Aviation has produced 3D-printed fuel nozzles for jet engines that are exceptionally lightweight and wear-resistant, while NASA has successfully tested 3D-printed rocket engine components capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and pressure.
Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
Emerging market structure in the aerospace 3D printing is characterized by the competitive nature of established aerospace heavyweights, sophisticated manufacturing businesses, and 3D-printing-based specialists that compete to increase their levels of technology and market share. Airbus, Boeing, and Lockheed Martin are collaborating with or acquiring companies specializing in additive manufacturing, including Stratasys, EOS, and 3D Systems, to use cutting-edge 3D printing in their assembly lines.
Recent Developments
Agnikul Cosmos' single-piece Inconel rocket engine
In August 2025, Indian startup Agnikul announced the development of the world’s largest Inconel-based, single-piece, 3D-printed rocket engine. Featuring a weld-free structure, the design was awarded a U.S. patent and represents a significant milestone in additive manufacturing for space propulsion.
First 3D-printed cryogenic hydrogen tank for aviation
In April 2025, AIMEN in Spain revealed the first cryogenic steel tank used in the storage of liquid hydrogen in aero planes, which were 3D printed. Incorporated through the European OVERLEAF project, the carbon-fiber-reinforced thermoplastic tank is lightweight and can support the aims of sustainable aviation.
Key Market Drivers
Key Market Restraints
Base CAGR: 21.5%
|
Category |
Key Factor |
Short-Term Impact (2025–2028) |
Long-Term Impact (2029–2035) |
Estimated CAGR Impact |
|
Drivers |
1. Growing demand for lightweight and complex aerospace components |
Increased adoption of 3D-printed titanium and composite parts in commercial and defense aircraft |
Integration of additive manufacturing for major structural and interior components across fleets |
▲ +3.4% |
|
2. Supply Chain Resilience & On-Demand Manufacturing |
Localized printing of spare parts to reduce lead times in MRO operations |
Fully distributed additive manufacturing networks supporting global aerospace fleets |
▲ +3.0% |
|
|
3. Rapid Prototyping and Reduced Time-to-Market |
Faster design cycles for aerospace components and prototypes |
Permanent integration of AM into R&D and production pipelines |
▲ +2.7% |
|
|
Restraints |
1. High Certification and Qualification Costs |
Limits adoption to high-value and mission-critical parts initially |
Certification processes become standardized, reducing costs |
▼ −1.4% |
|
2. Limited Aerospace-Grade Materials & Build Sizes |
Restricts printing of large primary structures |
Development of new alloys and large-format printers expands application range |
▼ −1.2% |
|
|
Opportunities |
1. Expansion in Space Exploration Programs |
Increased demand for lightweight, high-performance parts for rockets and satellites |
Space-based manufacturing using 3D printing for in-orbit assembly |
▲ +3.1% |
|
2. Sustainability and Waste Reduction |
Reduced raw material waste compared to subtractive manufacturing |
Alignment with zero-emission and green aerospace manufacturing goals |
▲ +2.8% |
|
|
Trends |
1. Hybrid Manufacturing Integration |
Combined additive-subtractive production for precision aerospace parts |
Industry standard for critical component production |
▲ +2.4% |
|
Challenges |
1. Scaling Production for Large Aerospace Components |
Large structures remain difficult to produce efficiently |
Breakthroughs in printer scale and speed enable full structural printing |
▼ −0.9% |
North America’s Leadership in the Aerospace 3D Printing Market
North America accounts for the largest share of the global aerospace 3D printing market, driven by its mature aerospace sector, strong presence of leading manufacturers, and sustained government and defense investments. Key industry players such as GE Aviation, Boeing, Raytheon Technologies, and NASA are at the forefront of integrating additive manufacturing into production and R&D initiatives. The region’s leadership is reinforced by continuous innovation in advanced materials, complex design capabilities, and large-scale printing technologies. Furthermore, government and defense agencies are increasingly adopting 3D-printed aircraft components, including structural parts for fighter jets, underscoring North America’s early and active adoption of additive manufacturing across both commercial and military applications.
Rapid Rise in Aerospace 3D Printing in the Asia-Pacific Region
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is experiencing rapid growth in the aerospace 3D printing industry, fueled by rising air travel demand, increasing defense budgets, and government-led digital manufacturing initiatives. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in additive manufacturing to strengthen aerospace capabilities and reduce dependency on imported components.
China has made significant progress through state-backed aerospace projects, with COMAC and AVIC integrating 3D-printed structural and engine components into next-generation aircraft. India, through ISRO and startups like Agnikul Cosmos, is adopting additive manufacturing for rocket engines and propulsion systems, while Japan and South Korea are focusing on advanced materials and partnerships with global OEMs to accelerate adoption.
China’s Expanding Footprint in Aerospace 3D Printing
China is rapidly emerging as a key player in the aerospace 3D printing market, driven by substantial government investment, rising demand in commercial aviation, and a strong push for technological self-sufficiency. The strategic objective is to reduce reliance on foreign suppliers while enhancing production efficiency through additive manufacturing. This approach enables the domestic production of lightweight, high-strength aircraft and spacecraft components.
A significant milestone was achieved in 2024, when the Commercial Aircraft Corporation of China (COMAC) incorporated titanium 3D-printed parts into its C919 jetliner. This innovation not only reduced the aircraft’s overall weight but also improved fuel efficiency, marking a breakthrough in China’s efforts to integrate advanced manufacturing into its aerospace sector.
Strategic Advancements in Aerospace 3D Printing in the UAE
The United Arab Emirates is positioning itself as a global hub for advanced manufacturing and aerospace innovation, with 3D printing playing a central role in its strategy. Driven by strong government initiatives and partnerships with leading aerospace companies, the country is increasingly applying additive manufacturing in aircraft maintenance, repair, and production.
In 2023, Emirates Engineering deployed 3D printing technology to produce certified aircraft cabin components, such as video monitor shrouds. These parts can be manufactured and replaced more quickly, reducing maintenance turnaround times while maintaining stringent aviation safety standards. This development highlights how the UAE is not only adopting but also certifying 3D-printed parts for critical aerospace applications, reinforcing its ambition to lead in the aviation technology landscape.
Powder Bed Fusion Technology Leads Market with 45-50% Revenue Share
In the aerospace 3D printing market, PBF technology is the largest segment at 45-50% of the total revenue. This category remains the dominant technology with the highest share as it is uniquely positioned to make complex geometries with high mechanical performance that adhere to the rigorous aerospace certification process. Within the PBF category, Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM) processes are the leading technologies that are specifically adopted to manufacture various critical flight components, including turbine blades, fuel nozzles, and structural brackets. In addition to high mechanical performance, the value of PBF in aerospace is to process high-end and high-performance materials such as titanium alloys and nickel-based superalloys with limited porosity and an exceptional surface finish.
The major aerospace manufacturers have invested heavily in PBF systems. GE Aviation has over 300 machines around the globe for making fuel nozzles for the LEAP engine. By consolidating the 20 individual components into one 3D printed, aerospace-grade component, one can see the optimization of the part by PBF technology. The future of PBF is bright as the segment will benefit from sequential improvements in production capacity potential with new multi-laser systems that can reduce production times by 40-50%, thereby allowing for greater consideration of serial production methodologies.
Metal Materials Capture 60-70% Market Share Driven by Structural Applications
The aerospace 3D printing market is dominated by metal materials, accounting for 60-70% of total revenue, emphasizing the industry's need for high strength to weight ratio components that exhibit durability under the most rigorous performance demands. Titanium alloys (Ti-6Al-4V) holds the largest share of the metal segment due to their superb performance in aircraft structural components and associated engine parts, which require excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. Nickel-based superalloys such as Inconel 718 and Inconel 625 comprise the second most common alloy category. Nickel superalloys are mainly used in hot-section engine components and exhibit strength at temperatures in excess of 1,000°C under operational conditions.
Aluminum alloys, especially AlSi10Mg and Scalmalloy, are gaining traction due to improved powder quality and declining costs, with aluminum growing at a CAGR of 22%. Possible uses for AlSi10Mg and Scalmalloy can range from structural, non-critical parts to satellite components.
Airbus is leading in advancements in metal 3D printing especially for the aircraft industry, they have qualified over 1,000 3D printed, metal parts for the A350 XWB aircraft, which includes titanium brackets that have resulted in a 30% weight saving from the original design. An increase in eligible metals is apparent in recent developments involving copper alloys for rocket engine combustion chamber applications and refractory metals for hypersonic applications. Another trend propelling metal 3D printing growth is the availability of powder recycling facilities in 2023 which contribute to a reduction of around 35-40% in materials cost, and improving the production case of metal additive manufacturing applications.
Aircraft Platform Commands 50-60% Market Share Led by Commercial Aviation Demand
The aircraft platform category is the largest categorical segment contributing about 50-60% of the aerospace 3D printing space, with commercial aviation markets rapidly accepting additive manufacturing technologies to produce both production parts and MRO applications. Commercial aircraft manufacturers use additive manufacturing (AM) to produce a wide range of certified flying parts for each aircraft, ranging from cabin interior components to mission-critical engine parts. For example, Boeing’s 787 Dreamliner currently incorporates around 20 to 30 certified 3D-printed parts, primarily titanium structural components produced by specialized suppliers. The newer Boeing 777X model is projected to include over 310 additive manufactured parts per aircraft, demonstrating a clear transition from prototyping to serial production using AM technologies.
Military aviation accounts for approximately 35% of the aircraft segment’s additive manufacturing volume, with fighter jets like the F-35 featuring hundreds of 3D-printed parts that contribute to weight reduction and consolidation of complex assemblies, thereby improving overall performance.
The U.S. Air Force’s Rapid Sustainment Office has successfully recreated over 150 obsolete aircraft parts using 3D printing, reducing the lead time for replacement parts from more than nine months to as little as 15 days or less. This highlights the growing role of additive manufacturing in on-demand, rapid aerospace part production and supply chain resilience
General aviation and Business Jets are now using 3D printing to customize their interior components and request low-volume spare parts. The spacecraft segment, although smaller with an estimated 15-20% share, has the highest growth rate at a whopping 24% CAGR mostly with companies like SpaceX and Relativity Space using 3D printing for engine components. The inclusion of these diverse platforms shows how AM is addressing each sector's unique requirements ranging from commercial production to specialized/one-off aerospace applications from airlines to space flight.
|
Report Attribute |
Details |
|
Market size (2025) |
USD 4.6 billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2035 |
USD 32.4 billion |
|
CAGR (2025-2035) |
21.5% |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2025 – 2035 |
|
Report coverage |
Market size and forecast, competitive landscape and benchmarking, country/regional level analysis, key trends, growth drivers and restraints |
|
Segments covered |
Component (High Power Microwave Component, High Energy Laser Component, Plasma Weapons, Sonic Weapons, and Particle Beam Weapons), Technology (Lethal and Non-Lethal), Platform, Material, Geography |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
|
Key companies profiled |
Thales, Spirit AeroSystems, Lockheed Martin, Booz Allen Hamilton, Melrose Industries, ExOne, Stratasys, Danaher, EOS GmbH, Formlabs, and Other Key Players. |
|
Customization |
Comprehensive report customization with purchase. Addition or modification to country, regional & segment scope available |
|
Pricing Details |
Access customized purchase options to meet your specific research requirements. Explore flexible pricing models |
Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By Technology
Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By Material Type
Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By Application
Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By Platform
Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By End-User
The aerospace 3D printing market size is estimated to be USD 4.6 billion in 2025 and grow at a CAGR of 21.5% to reach USD 32.4 billion by 2035.
In 2024, the Aerospace 3D Printing Market size was estimated at USD 3.8 billion, with projections to reach USD 4.6 billion in 2025.
Stratasys, 3D Systems, GE Additive, EOS, Nikon SLM, Renishaw are the major companies operating in the Aerospace 3D Printing Market.
The North America region is projected to grow at the highest CAGR over the forecast period (2025-2035).
In the aerospace 3D printing market, PBF technology is the largest segment at 45-50% of the total revenue.
1. Market Definition & Scope
1.1. Market Definition
1.2. Market Ecosystem
1.3. Currency
1.4. Key Stakeholders
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Process of Data Collection and Validation
2.2.1. Secondary Research
2.2.2. Primary Research/Interviews with Key Opinion Leaders from the Industry
2.3. Market Sizing and Forecast
2.3.1. Market Size Estimation Approach
2.3.1.1. Bottom-up Approach
2.3.1.2. Top-down Approach
2.3.2. Growth Forecast Approach
2.3.3. Assumptions for the Study
3. Executive Summary
3.1. Overview
3.2. Segmental Analysis
3.2.1. Aerospace 3D Printing Market, by Technology
3.2.2. Aerospace 3D Printing Market, by Material Type
3.2.3. Aerospace 3D Printing Market, by Application
3.2.4. Aerospace 3D Printing Market, by Platform
3.2.5. Aerospace 3D Printing Market, by End-User
3.2.6. Aerospace 3D Printing Market, by Region
3.3. Competitive Landscape
3.4. Strategic Recommendations
4. Market Insights
4.1. Overview
4.2. Factors Affecting Market Growth
4.2.1. Drivers
4.2.1.1. Growing demand for lightweight and complex aerospace components
4.2.1.2. Reduction in material waste and manufacturing lead times
4.2.1.3. Rising adoption of additive manufacturing for production parts
4.2.1.4. Increasing investments by aerospace OEMs in 3D printing capabilities
4.2.1.5. Supply chain resilience and on-demand manufacturing requirements
4.2.2. Restraints
4.2.2.1. High initial investment costs for industrial 3D printing systems
4.2.2.2. Limited material certification and qualification processes
4.2.2.3. Regulatory and safety certification challenges for flight-critical parts
4.2.3. Opportunities
4.2.3.1. Development of new high-performance aerospace materials
4.2.3.2. Integration of AI and machine learning for quality control
4.2.3.3. Expansion into space manufacturing and in-orbit production
4.2.4. Trends
4.2.4.1. Hybrid manufacturing combining additive and subtractive processes
4.2.4.2. Large-scale 3D printing for structural aerospace components
4.2.4.3. Digital inventory and distributed manufacturing networks
4.2.5. Challenges
4.2.5.1. Ensuring repeatability and consistency in production parts
4.2.5.2. Post-processing requirements and surface finish standards
4.2.5.3. Intellectual property protection in digital manufacturing
4.3. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
4.3.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.3.2. Bargaining Power of Buyers
4.3.3. Threat of Substitutes
4.3.4. Threat of New Entrants
4.3.5. Degree of Competition
4.4. Technology Impact on Aerospace 3D Printing Market
4.4.1. Advanced Process Monitoring and Control
4.4.1.1. In-situ monitoring systems for defect detection
4.4.1.2. Closed-loop control for process optimization
4.4.1.3. Digital twin integration for predictive maintenance
4.4.2. Material Innovation and Development
4.4.2.1. High-temperature superalloys for turbine applications
4.4.2.2. Ceramic matrix composites for thermal protection
4.4.2.3. Multi-material and functionally graded structures
4.4.3. Software and Automation Advances
4.4.3.1. Generative design and topology optimization
4.4.3.2. Automated support generation and removal
4.4.3.3. Cloud-based simulation and workflow management
5. Impact of Sustainability on Aerospace 3D Printing Market
5.1. Reduction in material waste through near-net-shape manufacturing
5.2. Energy efficiency improvements in additive manufacturing processes
5.3. Lightweight component design for fuel efficiency
5.4. Recycling and reuse of metal powders and materials
5.5. Local production reducing transportation emissions
5.6. Life cycle assessment of 3D printed aerospace parts
5.7. Sustainable material development and bio-based alternatives
6. Competitive Landscape
6.1. Overview
6.2. Key Growth Strategies
6.3. Competitive Benchmarking
6.4. Competitive Dashboard
6.4.1. Industry Leaders
6.4.2. Market Differentiators
6.4.3. Vanguards
6.4.4. Contemporary Stalwarts
6.5. Market Share/Ranking Analysis, by Key Players, 2024
7. Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By Technology
7.1. Overview
7.2. Powder Bed Fusion
7.2.1. Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
7.2.2. Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
7.2.3. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
7.3. Directed Energy Deposition (DED)
7.4. Material Extrusion
7.5. Vat Photopolymerization
7.6. Binder Jetting
7.7. Material Jetting
7.8. Others
8. Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By Material Type
8.1. Overview
8.2. Metal
8.2.1. Titanium Alloys
8.2.2. Aluminum Alloys
8.2.3. Nickel-based Superalloys
8.2.4. Stainless Steel
8.2.5. Others
8.3. Polymer
8.3.1. Thermoplastics
8.3.2. Thermosets
8.4. Ceramic
8.5. Composite Materials
9. Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By Application
9.1. Overview
9.2. Engine Components
9.3. Structural Components
9.4. Interior Components
9.5. Tooling and Fixtures
9.6. Prototyping
9.7. Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO)
9.8. Others
10. Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By Platform
10.1. Overview
10.2. Aircraft
10.2.1. Commercial Aviation
10.2.2. Military Aviation
10.2.3. General Aviation
10.3. Spacecraft
10.4. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
10.5. Helicopters
11. Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By End-User
11.1. Overview
11.2. OEMs
11.3. Part Suppliers and Contract Manufacturers
11.4. MRO Service Providers
11.5. Government and Defense
11.6. Space Agencies
12. Aerospace 3D Printing Market Assessment—By Geography
12.1. Overview
12.2. North America
12.2.1. U.S.
12.2.2. Canada
12.3. Europe
12.3.1. Germany
12.3.2. U.K.
12.3.3. France
12.3.4. Italy
12.3.5. Russia
12.3.6. Rest of Europe
12.4. Asia-Pacific
12.4.1. China
12.4.2. Japan
12.4.3. India
12.4.4. South Korea
12.4.5. Singapore
12.4.6. Australia
12.4.7. Rest of Asia-Pacific
12.5. Latin America
12.5.1. Brazil
12.5.2. Mexico
12.5.3. Argentina
12.5.4. Rest of Latin America
12.6. Middle East & Africa
12.6.1. UAE
12.6.2. Saudi Arabia
12.6.3. Israel
12.6.4. South Africa
12.6.5. Rest of Middle East & Africa
13. Company Profiles (Business Overview, Financial Overview, Product Portfolio, Strategic Developments, and SWOT Analysis)
13.1. Stratasys Ltd.
13.2. 3D Systems Corporation
13.3. EOS GmbH
13.4. GE Additive (General Electric Company)
13.5. Nikon SLM Solutions AG
13.6. Renishaw plc
13.7. Trumpf Group
13.8. Velo3D, Inc.
13.9. Desktop Metal, Inc.
13.10. Markforged, Inc.
13.11. HP Inc. (HP 3D Printing)
13.12. ExOne Company (Desktop Metal)
13.13. Materialise NV
13.14. Arcam AB (GE Additive)
13.15. Optomec, Inc.
13.16. Sciaky, Inc.
13.17. BeAM (AddUp)
13.18. Norsk Titanium AS
13.19. Other Key Players
14. Appendix
14.1. Available Customization
14.2. Related Reports
























Published Date: Jan-2026
Published Date: Sep-2025
Please enter your corporate email id here to view sample report.
Subscribe to get the latest industry updates