Resources
About Us
DC Fast Charging Power Module Market by Power Output, Semiconductor Material (Silicon-Based, Silicon Carbide-Based, Gallium Nitride-Based), Charging Standard (CCS, CHAdeMO, GB/T, NACS, MCS), Cooling Technology, Application, End-User, and Geography—Global Forecast to 2035
Report ID: MRAUTO - 1041608 Pages: 205 Oct-2025 Formats*: PDF Category: Automotive and Transportation Delivery: 24 to 72 Hours Download Free Sample ReportWhat is the DC Fast Charging Power Module Market Size?
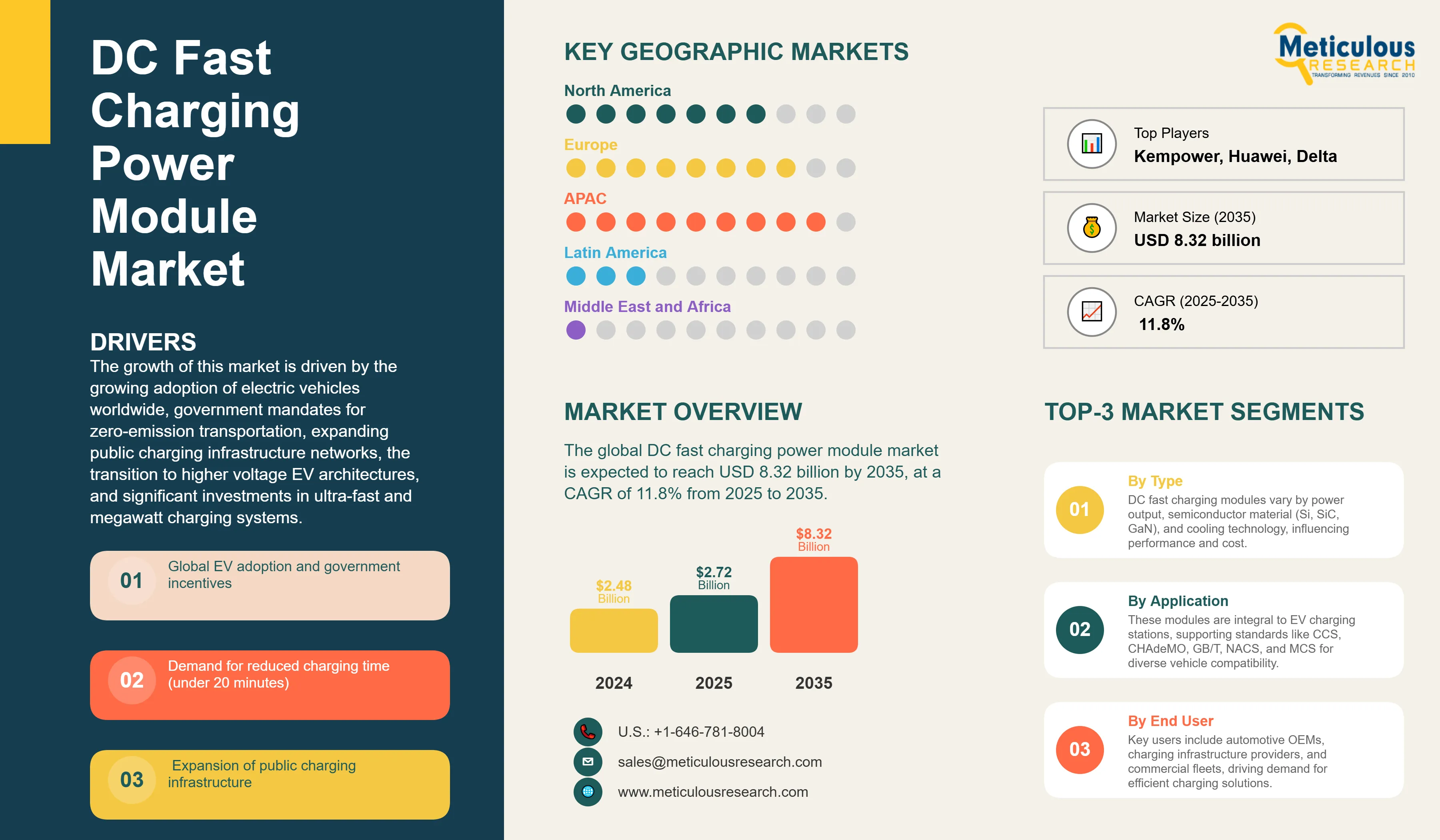
The global DC fast charging power module market was valued at USD 2.48 billion in 2024. This market is expected to reach USD 8.32 billion by 2035 from USD 2.72 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 11.8% from 2025 to 2035. The growth of this market is driven by the growing adoption of electric vehicles worldwide, government mandates for zero-emission transportation, expanding public charging infrastructure networks, the transition to higher voltage EV architectures (800V+), advancements in wide-bandgap semiconductor technologies (SiC and GaN), and significant investments in ultra-fast and megawatt charging systems for commercial vehicle electrification.
Market Highlights: DC Fast Charging Power Module Equipment
Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
The DC fast charging power module market encompasses the design, development, manufacturing, and deployment of high-power electronic systems that convert AC grid power to DC output for fast electric vehicle charging. These power modules are essential components of DC fast charging stations. They use modern semiconductor technologies and cooling systems to deliver power outputs ranging from 50 kW to over 500 kW. Unlike traditional AC charging systems, DC fast charging power modules enable much shorter charging times, often under 20 minutes for compatible vehicles. This happens because they bypass the vehicle's onboard charger and supply DC power directly to the battery.
The market is driven by the increasing global adoption of electric vehicles, government incentives for charging infrastructure, investments by car manufacturers in ultra-fast charging, updates to the electrical grid, and the use of renewable energy sources. These modules incorporate complex power conversion technologies, such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors, efficient liquid cooling systems, and modular designs that support scalable deployment across various settings, from public charging networks to fleet depots.
How is AI Transforming the DC Fast Charging Power Module Market?
Artificial intelligence is transforming the DC fast charging power module market. It enables better charging optimization, predictive maintenance, and greater system reliability. AI algorithms analyze real-time data from power modules to adjust charging curves based on battery health, temperature, and grid availability. This maximizes charging speed while maintaining the battery's health. Machine learning models can predict when components will wear out. This allows operators to schedule maintenance before problems occur, reducing downtime and lowering costs for charging point operators.
AI-driven thermal management systems adjust cooling parameters according to surrounding conditions and load profiles. This improves energy efficiency and extends component lifespan. Neural networks assist with smart grid integration. They can forecast demand patterns, optimize load distribution across different charging ports, and establish dynamic pricing during peak times. AI also enhances quality control in manufacturing by identifying small defects in semiconductor components and assemblies. This ensures higher reliability standards. Furthermore, AI strengthens cybersecurity by detecting unusual communication patterns and potential threats in connected charging infrastructure, safeguarding both the grid and user data.
What are the Key Trends in the DC Fast Charging Power Module Market?
Silicon Carbide and Gallium Nitride Adoption: A major change in the DC fast charging power module market is the shift from traditional silicon-based semiconductors to wide-bandgap materials like silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN). These new semiconductors provide better efficiency, with improvements of about 3-5%. They also have higher switching frequencies, better thermal conductivity, and smaller system sizes. SiC-based power modules allow for higher power densities while producing less heat, which cuts down on cooling needs and overall system costs. This change is speeding up as semiconductor makers boost production, lowering costs and making SiC technology more competitive with standard silicon solutions.
Modular and Scalable Power Architecture: Another important trend driving market growth is the creation of modular and scalable power module designs. These designs allow for flexible setups to meet different power needs. Manufacturers are making standardized building blocks that can be combined to reach power outputs from 50 kW to over 1 MW. This makes upgrades and maintenance easier. This method shortens development times, simplifies inventory management, improves system redundancy, and helps charging station operators increase capacity gradually based on demand. Modular architectures also accommodate different charging protocols, allowing a single station to charge vehicles with various standards at the same time.
Market Scope
|
Report Coverage |
Details |
|
Market Size by 2035 |
USD 8.32 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 2.72 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 2.48 Billion |
|
Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2035 |
CAGR of 11.8% |
|
Dominating Region |
Asia-Pacific |
|
Fastest Growing Region |
Europe |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2035 |
|
Segments Covered |
Power Output, Semiconductor Material, Charging Standard, Cooling Technology, Application, End-User, and Region |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Global EV Adoption and Government Incentives
The key driver behind the DC fast charging power module market is the rapid increase in electric vehicle adoption around the world. This growth is supported by strong government policies and financial incentives. Countries are setting ambitious EV sales targets. For example, the EU mandates 100% zero-emission new car sales by 2035, and California has its Advanced Clean Cars II regulation. These initiatives are backed by significant investments in infrastructure. The U.S. National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) program allocates $5 billion for charging networks, while China plans to build millions of charging points. Tax credits, purchase subsidies, and easier access to urban areas for EVs help create strong demand from consumers. This, in turn, requires a rapid expansion of fast charging infrastructure and increases the need for efficient and reliable power modules.
Demand for Reduced Charging Time
Consumers expect charging times similar to traditional refueling, ideally under 20 minutes. This expectation is changing the design and features of power modules. Modern EVs with 800V systems can handle charging rates over 250 kW, allowing a charge from 10-80% in about 18 minutes. This demand urges manufacturers to create power modules with greater power density, better thermal management, and improved efficiency, reducing charging times. Charging networks now compete on how quickly they can charge vehicles, sparking a race to innovate in power electronics, cooling systems, and battery communication protocols.
Restraint
High Initial Capital Expenditure for Power Modules
Even with strong market growth, the DC fast charging power module sector faces major hurdles due to high upfront investment costs. High-power DC charging stations require significant capital outlay, with power modules accounting for 30-40% of the total system costs. Advanced materials like SiC are still much more expensive than standard silicon, although prices are falling as production scales up. The costs also include expenses for grid connection upgrades, electrical infrastructure improvements, cooling systems, and installation labor. These high initial costs create financial challenges, particularly for independent charging point operators, and can extend the timeline for profitability, often requiring 5-7 years for a return on investment without subsidies. This economic barrier slows down infrastructure growth in low-traffic areas and rural regions where usage rates might not justify the expense.
Opportunity
Megawatt Charging System (MCS) for Commercial Vehicles
The electrification of heavy-duty commercial vehicles presents an exceptional growth opportunity for the DC fast charging power module market. Long-haul trucks, buses, and construction equipment require extremely high power levels—up to 3.75 MW under the emerging MCS standard—to achieve practical charging times given their large battery capacities (500-1000 kWh). Current DC fast charging solutions are inadequate for these applications, creating a greenfield opportunity for manufacturers to develop next-generation power modules specifically designed for megawatt-level operation. The commercial vehicle segment offers attractive economics due to predictable usage patterns, depot-based charging that simplifies infrastructure planning, and strong total cost of ownership advantages over diesel alternatives when factoring in fuel and maintenance savings. Early movers establishing megawatt charging capabilities will capture significant market share as fleet electrification accelerates through the 2030s.
Power Output Insights
Why are 150-250 kW Power Modules Gaining Traction in Urban Charging Networks?
The 150-250 kW segment is expected to capture a significant market share by 2025. This power range is ideal for urban and suburban public charging applications. It offers much faster charging than 50-100 kW systems while keeping costs and grid connection requirements reasonable. These modules can charge most current passenger EVs from 20-80% in 15-25 minutes, meeting consumer needs for convenience. The segment sees strong demand for charging along highway corridors, at retail locations, and in mixed-use developments where moderate wait times match charging times. Its cost-effectiveness compared to ultra-high-power options makes it appealing for charging point operators looking for good returns on their investments. The above 500 kW (ultra-fast/megawatt charging) segment is projected to grow the fastest during the forecast period. This rapid growth results from 800V+ vehicle architectures that can handle extreme charging speeds, the development of MCS standards for commercial vehicles, and competition among charging networks to provide the fastest charging experience possible. These ultra-high-power modules are crucial for heavy-duty applications where large battery capacities would otherwise need impractically long charging sessions. They are increasingly used at flagship locations to set apart premium charging networks.
Semiconductor Material Insights
How do Silicon Carbide Power Modules Enable Higher Efficiency?
The Silicon Carbide (SiC) Based Power Modules segment is expected to hold the largest market share by 2025, quickly overtaking traditional silicon technology. SiC semiconductors outperform silicon significantly in key areas: switching losses are cut by 50-70%, leading to higher efficiency (typically 96-98% versus 94-95% for silicon); thermal conductivity is three times better, lowering cooling needs; and higher operating temperatures (up to 200°C junction temperature) enhance reliability and power density.
For DC fast charging, SiC allows for more compact power modules that weigh less, have simpler cooling systems, and lose less energy, which lowers operating costs. The maturing technology and expanding capacity of semiconductor manufacturers are driving costs down by about 10-15% each year, speeding up adoption across all power levels. The Gallium Nitride (GaN) Based Power Modules segment is expected to see the fastest CAGR through 2035, though it starts from a smaller base. GaN provides even higher switching frequencies than SiC, allowing for very compact designs and excellent efficiency, especially at lower power levels. Current uses focus mainly on auxiliary power supplies and lower-power charging modules, but ongoing research in high-voltage GaN devices might disrupt the market as technology improves and manufacturing scales boost competitiveness.
Charging Standard Insights
How Does CCS Dominance Shape Module Design Requirements?
The CCS (Combined Charging System) segment holds the largest market share in 2025, reflecting its status as the global standard in North America and Europe. The widespread use of CCS by nearly all non-Tesla manufacturers gives big advantages in scale to power module makers focusing on this standard. CCS supports both AC and DC charging through a single vehicle inlet, currently offering DC fast charging capabilities up to 350 kW, with plans to extend to 500 kW+. Power modules designed for CCS must meet extensive safety and communication protocols outlined in ISO 15118, supporting features like Plug & Charge authentication and bidirectional power flow for Vehicle-to-Grid applications.
The technical sophistication of the standard, along with broad industry support, ensures its ongoing dominance, although module makers are increasingly creating multi-protocol solutions to maximize market reach. The Megawatt Charging System (MCS) segment is expected to grow the fastest during the forecast period. This new standard, specifically for heavy-duty commercial vehicles, will support charging up to 3.75 MW using a newly designed connector and communication protocol. MCS introduces completely new requirements for power module design, such as extreme current handling (up to 3000A), advanced liquid-cooled cables and connectors, and effective thermal management. The first deployments are anticipated in 2025-2026, with faster adoption as major truck manufacturers launch compatible vehicles.
Cooling Technology Insights
Why is Liquid Cooling Becoming Essential for High-Power Applications?
The Liquid Cooling segment is projected to dominate the market with a share by 2025, driven by the thermal management needs of power modules over 150 kW. At high power levels, air cooling can't keep semiconductor devices at optimal temperatures, especially SiC components that benefit from cooler junction temperatures. Liquid cooling systems—including cold plate cooling, direct liquid cooling, and immersion cooling offer superior thermal conductivity (25-30 times better than air), allowing for more compact designs with higher power density. Cold plate cooling, where liquid channels are embedded in heat sinks that contact power semiconductors, is the most common method and provides excellent performance with manageable complexity.
Direct liquid cooling and immersion cooling technologies are emerging for ultra-high-power applications above 350 kW, where even cold plates struggle to remove heat effectively. The growth of the liquid cooling segment is further boosted by increasing efficiency requirements for power modules, as each percentage point of efficiency directly lessens the size and energy use of cooling systems. Advanced liquid cooling systems with integrated temperature sensors and AI-driven controls adjust coolant flow rates and temperatures, extending component life while keeping coolant pump energy use to a minimum.
Application Insights
How Do Public Charging Stations Drive Power Module Demand?
The Public Charging Stations segment makes up the largest market share in 2025, acting as the primary deployment scenario for DC fast charging infrastructure. Public charging networks fulfill the critical need for on-the-go and destination charging for EV owners lacking home charging, strategically placed along highways, in urban centers, at retail spots, and near transportation hubs. This segment needs power modules that guarantee high reliability (99.5%+ uptime), compatibility with multiple protocols to serve various vehicle types, user-friendly interfaces connected to mobile apps, and payment system integration. Charging point operators here prioritize total cost of ownership, including energy efficiency to cut operational expenses, remote diagnostics to lower maintenance costs, and modular designs that enable upgrades without needing to replace entire systems.
The Fleet and Depot Charging segment is expected to grow the fastest during the forecast period. Electrifying commercial fleets like delivery vehicles, transit buses, taxis, and ride-sharing services creates concentrated charging needs at central depots where vehicles charge overnight or during shift changes. This application presents power module manufacturers with attractive economics thanks to higher equipment utilization rates, easier site planning with predictable load profiles, and chances for smart charging integration that optimizes grid demand. Fleet operators value charging speed to keep vehicles on the road, making DC fast charging critical despite its higher initial costs.
End-User Insights
Why are Charging Point Operators the Largest End-User Segment?
The Charging Point Operators (CPOs) segment holds the largest market share in 2025. CPOs are specialized firms focused on deploying, operating, and maintaining charging infrastructure, including ChargePoint, EVgo, Electrify America, Ionity, and many regional players. They make purchasing decisions based on thorough financial modeling that consider equipment and installation costs, energy prices, maintenance needs, and utilization forecasts. CPOs look for power modules with proven reliability, standardized interfaces for easier maintenance, robust warranty packages, and software that allows for dynamic load management, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance. Their purchasing power and technical know-how make them savvy customers who push module manufacturers toward ongoing cost reductions and performance enhancements.
The Electric Utility Companies segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR as utilities increasingly see EV charging as a strategic business opportunity and a tool for managing the grid. Utilities have unique strengths, including existing grid infrastructure, established customer relationships, expertise in regulations, and access to low-cost capital. Their move into charging infrastructure—through owned networks or partnerships with CPOs—represents a significant growth factor in the market. Utilities particularly seek power modules with Vehicle-to-Grid capabilities to support grid stability, those that integrate smoothly with distributed energy resources and energy storage systems, and solutions that enable dynamic load management to enhance grid use.
Regional Insights
How is the Asia-Pacific DC Fast Charging Power Module Market Growing Dominantly Across the Globe?
Asia-Pacific is expected to hold the largest share of the global DC fast charging power module market in 2025, driven by China as it’s the leading EV market with over 60% of global electric vehicle sales. The strong electrification policies of China, including production mandates from the New Energy Vehicle program, generous purchase subsidies, and urban license plate restrictions that favor EVs, create immense demand for charging infrastructure. The country has rolled out hundreds of thousands of DC fast charging points, with state-owned enterprises, technology companies like Huawei and BYD, and specialized charging operators building comprehensive networks. The GB/T charging standard holds strong domestic market share, though CCS is increasingly adopted for export-focused EVs.
Japan and South Korea also significantly contribute to the region's strength, with established automotive industries (Toyota, Nissan, Honda, Hyundai, Kia) actively building EV platforms and supporting charging infrastructure growth. The CHAdeMO standard of Japan remains important, especially for commercial vehicles and earlier EV models, while newer models are gradually adopting CCS.
The region enjoys robust domestic power module manufacturing, with companies like Delta Electronics, Huawei Digital Power, BYD, and TGOOD supplying both regional and global markets. Government efforts in coordinating charging standards, grid planning, and infrastructure subsidies create a favorable atmosphere for market growth.
Which Factors Support the Europe DC Fast Charging Power Module Market Growth?
Europe is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR from 2025 to 2035, driven by its bold climate policies and shifts in the automotive industry. The European Green Deal and the "Fit for 55" package aim for a 55% reduction in emissions by 2030, with electrifying transport playing a key part in reaching these goals.
The Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR) requires member states to place DC fast charging points every 60 km along major highways, ensuring demand for infrastructure. Countries like Germany, France, the Netherlands, and Norway have introduced additional incentives and requirements that boost deployment beyond EU standards.
The automotive industry in Europe, comprising Volkswagen Group, Stellantis, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Renault, and Volvo, is fully transitioning to electric vehicles, with most manufacturers pledging to sell only electric models during 2030-2035. This industry transformation drives investment in charging infrastructure not just from CPOs like Ionity, Allego, and Fastned, but also from OEMs creating their own networks and oil companies (Shell, BP, TotalEnergies) upgrading service stations.
The focus on integrating renewable energy with charging infrastructure, strict grid connection standards, and a preference for locally produced equipment creates unique demands that favor advanced power modules with better efficiency and V2G capabilities. European manufacturers like ABB, Siemens, and Schneider Electric gain from their closeness to end markets and established ties with utilities and automakers.
Value Chain Analysis
This stage focuses on advancing power electronics technology through semiconductor material research, power module design optimization, thermal management innovation, and development of next-generation topologies for improved efficiency, power density, and reliability at higher voltage and current levels.
Key Players: Infineon Technologies, STMicroelectronics, Wolfspeed, ON Semiconductor, ROHM Semiconductor
This stage involves producing critical components including power semiconductor devices (IGBTs, MOSFETs, SiC and GaN modules), capacitors, inductors, transformers, cooling systems, and control electronics requiring precision manufacturing and stringent quality control.
Key Players: Infineon Technologies, STMicroelectronics, ON Semiconductor, Wolfspeed, Mitsubishi Electric, Fuji Electric, ROHM Semiconductor
This stage encompasses assembling individual power components into complete modules, including power stage integration, thermal interface application, testing and validation, and system integration with controllers, communication interfaces, and safety systems.
Key Players:
Charging Station Manufacturing and Deployment
This stage involves integrating power modules into complete charging stations with user interfaces, payment systems, communication modules, and safety features, followed by installation, grid connection, and commissioning at deployment sites.
Key Players: ABB E-mobility, Schneider Electric, Siemens, ChargePoint, EVgo, Electrify America
Recent Developments
March 2025 — BYD revealed its groundbreaking Super e-Platform, capable of delivering ultra-fast charging speeds up to 1,000 kW, enabling a full charge in just 5 to 8 minutes.
April 2025 — ABB E-mobility launched three new advanced charging products, the MCS1200 Megawatt Charging System capable of supplying up to 1,200 kW (1.2 MW) of continuous power for heavy-duty vehicles.
August 2024 — India's largest EV charger manufacturer Exicom Tele-systems Limited announced the acquisition of Tritium, a distinguished global leader in DC Fast Chargers headquartered in Australia.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Power Output
By Semiconductor Material
By Charging Standard
By Cooling Technology
By Application
By End-User
By Region
The DC fast charging power module market is expected to increase from USD 2.72 billion in 2025 to USD 11.8 billion by 2035.
The DC fast charging power module market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.8% from 2025 to 2035.
The major players in the DC fast charging power module market include Delta Electronics, Inc., Huawei Digital Power Technologies Co., Ltd., BYD Company Limited, ABB Ltd. (ABB E-mobility), Infineon Technologies AG, Siemens AG (eMobility Division), Kempower Oyj, TGOOD Global Ltd., Schneider Electric SE, Phihong Technology Co., Ltd., Vicor Corporation, STMicroelectronics N.V., ON Semiconductor Corporation, Wolfspeed, Inc., TDK Corporation (TDK-Lambda), ROHM Semiconductor, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., Shindengen Electric Manufacturing Co., Ltd., BRUSA Elektronik AG, Vertiv Holdings Co., Power Integrations, Inc., Other Key Players.
The main factors driving the DC fast charging power module market include the growing global adoption of electric vehicles, government incentives for charging infrastructure, investments by automotive manufacturers in ultra-fast charging, updates to the electrical grid, and the use of renewable energy sources.
Asia-Pacific region will lead the global DC fast charging power module market during the forecast period 2025 to 2035.
























Published Date: Jan-2025
Please enter your corporate email id here to view sample report.
Subscribe to get the latest industry updates