Resources
About Us
Agricultural Robots Market by Type (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, Autonomous Tractors & Field Robots, Harvesting Robots, Milking Robots, Weeding & Spraying Robots, Sorting & Packing Robots), Application, Farm Type - Global Forecast to 2036
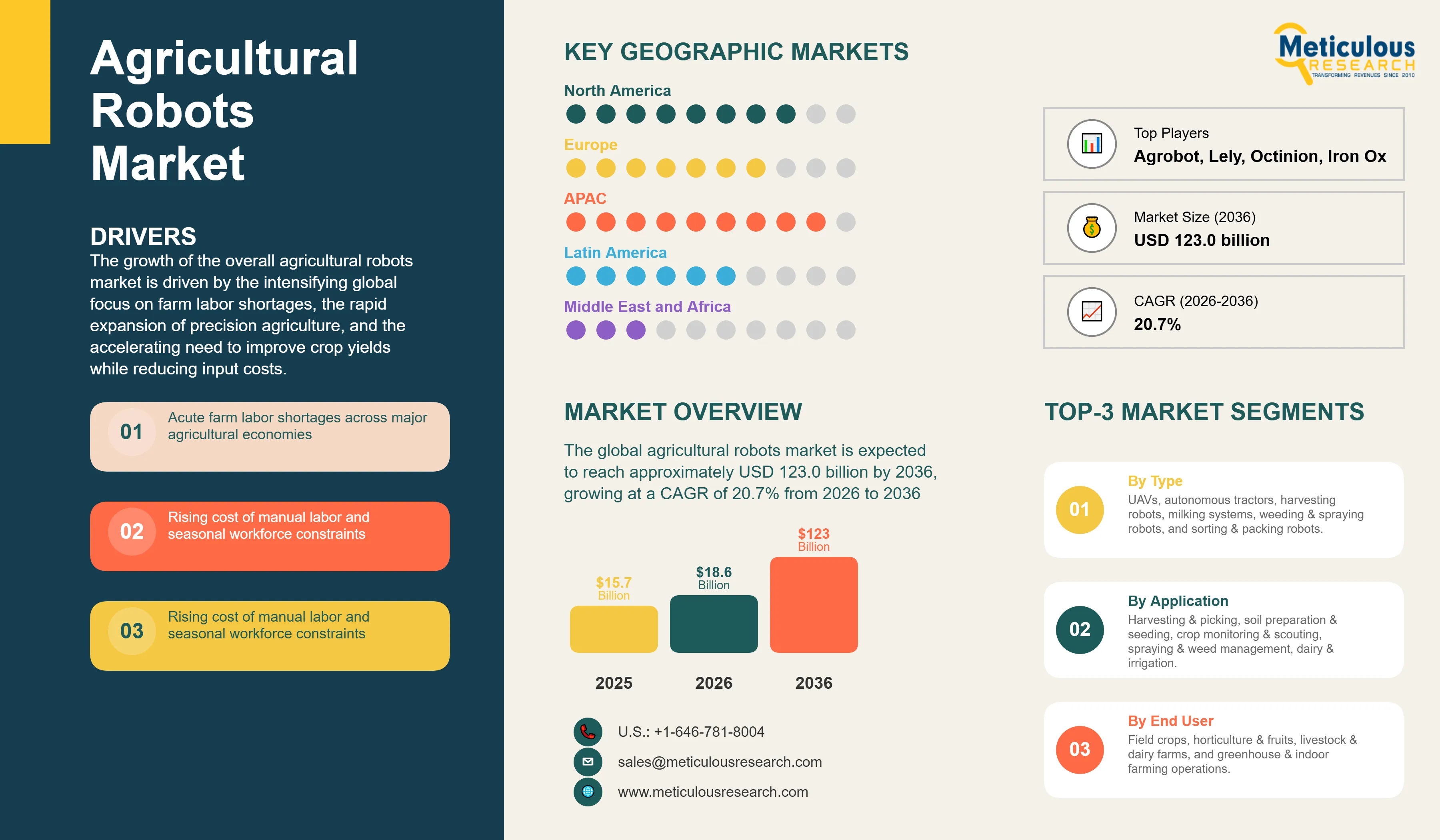
Report ID: MRAGR - 1041798 Pages: 268 Feb-2026 Formats*: PDF Category: Agriculture Delivery: 24 to 72 Hours Download Free Sample ReportThe global agricultural robots market was valued at USD 15.7 billion in 2025. The market is expected to reach approximately USD 123.0 billion by 2036 from USD 18.6 billion in 2026, growing at a CAGR of 20.7% from 2026 to 2036. The growth of the overall agricultural robots market is driven by the intensifying global focus on farm labor shortages, the rapid expansion of precision agriculture, and the accelerating need to improve crop yields while reducing input costs. As farm operators and agribusinesses seek to integrate greater automation and intelligence into their production cycles, agricultural robots have become essential for maintaining high-throughput field operations, food safety standards, and long-term farm profitability. The rapid adoption of autonomous field machinery, AI-enabled crop scouting platforms, and unmanned aerial vehicles continues to fuel significant growth of this market across all major geographic regions.
Click here to: Get Free Sample Pages of this Report
Agricultural robots are purpose-built automated systems that perform repetitive, labor-intensive, or precision-sensitive farming tasks with minimal human intervention. These systems span a wide spectrum of technologies, from GPS-guided autonomous tractors and AI-powered harvesting arms to multi-rotor drones equipped with multispectral sensors and computer vision. The market is shaped by the convergence of robotics, machine learning, and agronomic intelligence, enabling farmers to monitor field health, manage inputs, and automate production tasks with a level of accuracy that was previously unattainable through manual methods.
The market includes a diverse range of solutions, from compact weeding robots designed for vegetable rows to large-scale autonomous platforms capable of operating across thousands of acres without operator input. These systems are increasingly integrated with advanced components such as LiDAR sensors, real-time kinematic positioning, and cloud-based farm management software that enable continuous field monitoring, data-driven decision-making, and remote fleet management. The ability to deliver consistent operational performance while reducing labor dependency and input waste has made agricultural robots the preferred investment for forward-looking farm enterprises, corporate agribusinesses, and government-backed farming modernization programs.
The global food production sector is under mounting pressure to increase output while simultaneously reducing its environmental footprint and dependence on seasonal labor. This challenge has created strong structural demand for automated solutions, with advanced agricultural robots enabling farmers to achieve higher productivity per acre, optimize the use of agrochemicals and water, and ensure consistent harvest quality across growing seasons. At the same time, the rapid emergence of vertical farming, controlled environment agriculture, and high-value specialty crop production is creating entirely new addressable markets for compact, high-precision robotic platforms built specifically for indoor and greenhouse environments.
Rapid Adoption of AI-Driven Autonomous Field Machinery
Farm equipment manufacturers are moving decisively toward fully autonomous field operations, integrating deep learning, computer vision, and real-time path planning into their core product lines. John Deere's autonomous 8R tractor platform and its See & Spray technology have demonstrated the commercial viability of machine-guided weed detection and targeted herbicide application at scale, reducing chemical usage significantly compared with conventional broadcast spraying. Similarly, CNH Industrial and AGCO Corporation have both accelerated their autonomy roadmaps, embedding connectivity and AI-based guidance directly into their next-generation tractor and planting platforms. These developments reflect a broader industry shift where autonomous capability is becoming a standard product feature rather than an optional add-on, making precision automation accessible to a wider base of commercial farm operators across grain, oilseed, and row crop sectors.
Expansion of Specialized Harvesting and Selective Picking Robots
The harvesting segment is witnessing a wave of innovation as robotics developers target the persistent labor shortfall in fruit, vegetable, and specialty crop production. Purpose-built harvesting robots for strawberries, apples, tomatoes, and lettuce are moving from pilot deployments into early commercial availability, with companies like Agrobot, Harvest CROO Robotics, and Octinion advancing platform maturity through iterative field testing and machine learning refinements. These systems combine high-resolution imaging, soft robotic grippers, and multi-arm picking architectures to achieve picking speeds and selectivity rates that are increasingly competitive with manual labor costs. Parallel advances in post-harvest sorting and packing robots are further extending automation throughout the fresh produce value chain, enabling continuous throughput and reducing product damage in packinghouse environments.
|
Parameter |
Details |
|
Market Size by 2036 |
USD 123.0 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2026 |
USD 18.6 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 15.7 Billion |
|
Market Growth Rate (2026–2036) |
CAGR of 20.7% |
|
Dominating Region |
Asia-Pacific |
|
Fastest Growing Region |
North America |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026 to 2036 |
|
Segments Covered |
Type, Application, Farm Type, and Region |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Drivers: Acute Farm Labor Shortage and the Rising Cost of Manual Operations
A key driver of the agricultural robots market is the deepening structural shortage of agricultural labor across developed and developing economies alike. Declining rural populations, aging farm workforces, tightening immigration policies, and the physical demands of seasonal harvesting work have collectively created a situation where available labor supply is unable to meet peak-season farm demand in many countries. This gap is most pronounced in high-value specialty crop production, where manual picking remains the dominant practice yet is increasingly unviable from a cost and availability standpoint. Agricultural robots address this challenge directly by providing consistent, scalable workforce capacity that is not subject to seasonal fluctuations, worker availability, or wage inflation. As the economics of robotic automation continue to improve through scale and technological refinement, the return on investment case for farm operators has strengthened considerably, accelerating adoption across farm types and geographies.
Opportunity: Precision Agriculture and Data-Driven Farm Management
The rapid integration of precision agriculture technologies into mainstream farming operations presents substantial growth opportunities for the agricultural robots market. Modern robotic systems generate continuous streams of high-resolution agronomic data, including soil moisture readings, crop canopy measurements, pest and disease detection signals, and yield mapping outputs that feed directly into farm management platforms. This data layer is becoming a competitive asset for farm enterprises seeking to optimize input use, reduce waste, and maximize revenue per acre. The growing availability of satellite imagery, edge computing, and cloud-based analytics tools is further enabling robot-generated data to be actionable in near real-time, creating new value propositions for equipment manufacturers and agronomic service providers. As farm operators become more data-literate and outcome-oriented, the demand for robotic systems that function as intelligent data-collection platforms alongside physical task performers is expected to grow substantially through 2036.
Why Do Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) Lead the Market?
The unmanned aerial vehicles segment accounts for the largest share of the overall agricultural robots market in 2026. This leadership position is primarily driven by the versatility, low operating cost, and rapid deployment capability of agricultural drones across a wide range of applications, including multispectral crop scouting, variable-rate spraying, seeding, and damage assessment. UAVs offer farm operators the ability to cover large field areas quickly and generate high-resolution imagery for agronomic analysis without the need for substantial infrastructure investment. The growth of regulatory frameworks supporting commercial agricultural drone operations in major markets, combined with falling hardware costs and improved battery endurance, has significantly broadened the accessible farmer base for this technology. DJI's Agras series and Trimble's aerial mapping platforms remain widely deployed across grain and specialty crop operations globally.
However, the harvesting robots segment is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period. The commercial maturation of selective picking systems for high-value crops such as strawberries, tomatoes, apples, and peppers is beginning to unlock a market that was previously considered technologically out of reach. As vision systems, gripper technologies, and machine learning models achieve greater reliability in unstructured field environments, harvesting robots are expected to attract significant investment from both equipment manufacturers and fresh produce businesses seeking to secure labor-independent picking capacity.
How Does the Crop Monitoring and Scouting Segment Dominate?
Based on application, the crop monitoring and scouting segment holds the largest share of the overall market in 2026. The widespread and repeatable nature of crop scouting as a farm management task, combined with the maturity and affordability of sensor-equipped drone platforms, has made automated field monitoring the most commercially accessible entry point into agricultural robotics for the majority of farm operators. Current large-scale deployments in grain, soybean, and cotton production demonstrate the measurable agronomic benefit of frequent, high-resolution field monitoring, particularly for early detection of nutrient stress, disease outbreaks, and pest pressure.
The spraying and weed management segment is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period. The convergence of computer vision-based plant identification, GPS-guided navigation, and precision application nozzle technology has made targeted robotic spraying a commercially compelling alternative to conventional broadcast applications. The demonstrable reduction in herbicide and fungicide volumes, combined with the avoidance of compaction from heavy sprayer equipment, is creating strong agronomic and economic justification for adoption across row crop and specialty crop producers.
Why Does the Field Crops Segment Lead the Market?
The field crops segment commands the largest share of the global agricultural robots market in 2026. This dominance stems from the large operational scale of row crop farming, the commercial maturity of autonomous guidance and precision application technologies for open-field environments, and the strong financial incentive to reduce per-acre labor and input costs across large cropping areas. Large-scale operations in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are deploying autonomous tractor platforms, seeding robots, and crop monitoring UAVs at increasing rates, with companies like Deere & Company and Kubota Corporation enabling scalable automation across millions of farming acres.
The greenhouse and indoor farming segment is poised for rapid growth through 2036, fueled by expanding investment in controlled environment agriculture and the growing commercial viability of year-round specialty crop production. Operators of vertical farms and glass greenhouse complexes are investing in autonomous logistics platforms, transplanting robots, and AI-enabled crop management systems to maximize throughput in high-capital, high-output growing environments.
How is Asia-Pacific Maintaining Dominance in the Global Agricultural Robots Market?
Asia-Pacific holds the largest share of the global agricultural robots market in 2026. The primary driver of this regional leadership is the combination of large agricultural land areas, significant government investment in farm mechanization programs, and the acute urgency of addressing farm labor shortfalls in economies where rural-to-urban migration has accelerated sharply. China alone accounts for a substantial portion of global agricultural drone deployments, with DJI and FJ Dynamics Technology Co., Ltd. serving as the primary domestic manufacturers of widely adopted agricultural UAV and autonomous field equipment platforms. Japan's aging agricultural workforce has similarly driven strong institutional and government support for robotic automation in rice cultivation, fruit harvesting, and dairy operations. India's rapidly growing precision agriculture ecosystem is creating new demand for affordable entry-level robotic scouting and spraying tools suited to smallholder farming conditions.
Which Factors Support North America and Europe Market Growth?
North America and Europe together account for a substantial share of the global agricultural robots market and represent the regions with the most advanced commercial deployments of high-autonomy farming platforms. In North America, the growth of this market is driven primarily by the scale of grain and row crop production, the financial resources of large commercial farm operators, and the active innovation ecosystem centered on agricultural technology companies and university research programs. Deere & Company, AGCO Corporation, and CNH Industrial lead the deployment of autonomous machinery across U.S. and Canadian farming operations, while a growing base of agricultural technology start-ups continue to commercialize specialized robotic platforms for fruit, vegetable, and specialty crop sectors.
In Europe, regulatory support for sustainable farming through the European Green Deal and Farm to Fork Strategy is accelerating the adoption of precision robotic tools that reduce chemical inputs and improve resource efficiency. Countries such as the Netherlands, Germany, France, and Spain are at the forefront, with Dutch greenhouse operators and French and Spanish fruit producers actively deploying harvesting, weeding, and logistics robots developed by regional innovators including Naïo Technologies and Octinion, alongside global platform providers.
Companies such as Deere & Company, CNH Industrial N.V., AGCO Corporation, and Kubota Corporation lead the global agricultural robots market with comprehensive portfolios of autonomous field machinery, precision planting platforms, and connected farm management solutions, particularly targeting large-scale grain, row crop, and mixed farming operations. Meanwhile, players including Lely, DeLaval (Tetra Laval Group), Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd., and Trimble Inc. focus on specialized applications spanning dairy automation, compact field robotics, and GPS-based precision guidance systems targeting the livestock and horticulture sectors. Emerging manufacturers and focused technology players such as Naïo Technologies, Agrobot, Harvest CROO Robotics, FJ Dynamics Technology Co., Ltd., Iron Ox, and Octinion are strengthening the market through innovations in selective harvesting, autonomous weeding, and controlled environment agriculture robotics.
The global agricultural robots market is expected to grow from USD 18.6 billion in 2026 to USD 123.0 billion by 2036.
The global agricultural robots market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 20.7% from 2026 to 2036.
The unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) segment is expected to dominate the market in 2026 due to its broad applicability across crop monitoring, spraying, and scouting operations. However, the harvesting robots segment is projected to be the fastest-growing segment, driven by the commercial maturation of selective picking systems for high-value specialty crops and the intensifying pressure to replace manual harvest labor.
AI and machine learning are transforming the agricultural robots landscape by enabling machines to make real-time agronomic decisions in complex, unstructured field environments. These technologies power computer vision-based weed and disease detection, autonomous path planning, selective crop picking, and predictive yield modeling, allowing robotic platforms to perform with a level of situational intelligence that was previously exclusive to experienced farm workers. The integration of AI capabilities directly into onboard hardware is reducing reliance on connectivity and enabling effective robotic operation even in remote, low-bandwidth farming environments.
Asia-Pacific holds the largest share of the global agricultural robots market in 2026. This regional leadership is primarily attributed to the scale of agricultural land under management, significant government-backed mechanization investments, and the prominent position of domestic manufacturers serving large drone and autonomous equipment deployments in China, Japan, and India.
The leading companies include Deere & Company, CNH Industrial N.V., AGCO Corporation, Kubota Corporation, Lely, DeLaval (Tetra Laval Group), Trimble Inc., Naïo Technologies, FJ Dynamics Technology Co., Ltd., and Agrobot.
























Published Date: Feb-2026
Published Date: Feb-2024
Published Date: Jun-2023
Please enter your corporate email id here to view sample report.
Subscribe to get the latest industry updates